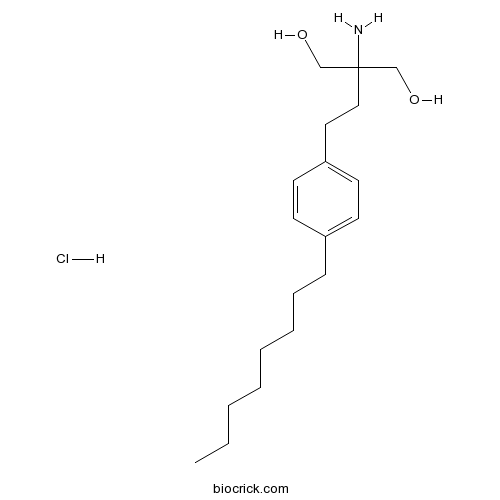
Fingolimod hydrochlorideS1P receptors agonist CAS# 162359-56-0 |
- BAF312 (Siponimod)
Catalog No.:BCC5114
CAS No.:1230487-00-9
- PF-543
Catalog No.:BCC1854
CAS No.:1415562-82-1
- SKI II
Catalog No.:BCC5029
CAS No.:312636-16-1
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 162359-56-0 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 107969 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C19H34ClNO2 | M.Wt | 343.93 |
| Type of Compound | Miscellaneous | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Synonyms | FTY720 | ||
| Solubility | DMSO : ≥ 100 mg/mL (290.76 mM) H2O : 50 mg/mL (145.38 mM; Need ultrasonic) *"≥" means soluble, but saturation unknown. | ||
| Chemical Name | 2-amino-2-[2-(4-octylphenyl)ethyl]propane-1,3-diol;hydrochloride | ||
| SMILES | CCCCCCCCC1=CC=C(C=C1)CCC(CO)(CO)N.Cl | ||
| Standard InChIKey | SWZTYAVBMYWFGS-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C19H33NO2.ClH/c1-2-3-4-5-6-7-8-17-9-11-18(12-10-17)13-14-19(20,15-21)16-22;/h9-12,21-22H,2-8,13-16,20H2,1H3;1H | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Fingolimod hydrochloride is an oral sphingosine-1-phosphate analogue that was approved by the FDA in 2010 for the treatment of relapsing forms of multiple sclerosis (MS). Fingolimod hydrochloride , a pak1 activator, can inhibit astemizole-induced hypertrophy and cytotoxicity in H9c2 cells, suggests that antihistamine-induced cardiac adverse effects are associated with pak1 expression and function.The gels containing 0.50% fingolimod hydrochloride (FNGL) and FNGL 0.50% plus 6% colloidal oatmeal have potential for the treatment of atopic dermatitis (AD). |
| Targets | COX | PGE | Histamine Receptor | PAK | p21 | S1P |
| In vivo | Overview and safety of fingolimod hydrochloride use in patients with multiple sclerosis.[Pubmed: 24935480]Expert Opin Drug Saf. 2014 Jul;13(7):989-98.Fingolimod (Gilenya®, FTY720) is an oral sphingosine-1-phosphate analogue that was approved by the FDA in 2010 for the treatment of relapsing forms of multiple sclerosis (MS). Fingolimod hydrochloride suppresses inflammatory reaction of blood vessels after balloon injury of the carotid artery[Reference: WebLink]Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2014 ,18 (11):1712-7.
|
| Kinase Assay | P21 (Cdc42/Rac)-activated kinase 1 (pak1) is associated with cardiotoxicity induced by antihistamines.[Pubmed: 27681411 ]Arch Pharm Res. 2016 Dec;39(12):1644-1652.Astemizole, a non-sedating histamine H1 receptor blocker, is widely known to cause cardiac arrhythmia, which prolongs the QT interval. However, the precise molecular mechanism involved in antihistamine-induced cardiovascular adverse effects other than hERG channel inhibition is still unclear. |
| Animal Research | Fingolimod hydrochloride gel shows promising therapeutic effects in a mouse model of atopic dermatitis.[Pubmed: 27465785 ]J Pharm Pharmacol. 2016 Oct;68(10):1268-77.To assess the efficacy of topically applied 2% hydroxypropyl cellulose gels containing 0.5% Fingolimod hydrochloride (FNGL) with or without 6% colloidal oatmeal in an in vivo model of atopic dermatitis (AD). |

Fingolimod hydrochloride Dilution Calculator

Fingolimod hydrochloride Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.9076 mL | 14.5378 mL | 29.0757 mL | 58.1514 mL | 72.6892 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.5815 mL | 2.9076 mL | 5.8151 mL | 11.6303 mL | 14.5378 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.2908 mL | 1.4538 mL | 2.9076 mL | 5.8151 mL | 7.2689 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0582 mL | 0.2908 mL | 0.5815 mL | 1.163 mL | 1.4538 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0291 mL | 0.1454 mL | 0.2908 mL | 0.5815 mL | 0.7269 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
Fingolimod is a mechanistically novel, orally bioavailable therapy for multiple sclerosis (MS) [1].
Fingolimod is a FDA approved drug for Multiple sclerosis treatment. It is a folk medicine emerged from Fungi. Fingolimod was firstly found to be a therapeutic agent in organ transplantation. Then Fingolimod was found to have similar structure with natural sphingosine and interact with S1P1, S1P4, S1P5 and S1P3 receptors as high affinity agonist with EC50 values of 0.3-3.1 nM. It plays the role in MS treatment through receptor-mediated actions both on the immune system and in the CNS. Fingolimod can prevent normal lymphocyte egress and reduce the infiltration of autoaggressive lymphocytes into the CNS [1, 2].
References:
[1] Chun J, Brinkmann V. A mechanistically novel, first oral therapy for multiple sclerosis: the development of fingolimod (FTY720, Gilenya). Discovery medicine, 2011, 12(64): 213.
[2] Chun J, Hartung H P. Mechanism of action of oral fingolimod (FTY720) in multiple sclerosis. Clinical neuropharmacology, 2010, 33(2): 91.
- 2-Amino-2-[2-(4-octylphenyl)ethyl]-1,3-propandiol
Catalog No.:BCN1542
CAS No.:162359-55-9
- Acetamide, N-[1,1-bis[(acetyloxy)methyl]-3-(4-octylphenyl)propyl]-
Catalog No.:BCN2254
CAS No.:162358-09-0
- Diethyl 2-acetamido-2-(4-octylphenethyl)malonate
Catalog No.:BCN1543
CAS No.:162358-08-9
- 1-(2-iodoethyl)-4-octylbenzene
Catalog No.:BCN2253
CAS No.:162358-07-8
- Benzeneethanol, 4-octyl
Catalog No.:BCN2255
CAS No.:162358-05-6
- Benzeneethanol, 4-octyl-, 1-acetate
Catalog No.:BCN2252
CAS No.:162358-04-5
- 1-Octanone,1-[4-[2-(acetyloxy)ethyl]phenyl]
Catalog No.:BCN2251
CAS No.:162358-03-4
- Hydramicromelin D
Catalog No.:BCN7548
CAS No.:1623437-86-4
- Baccatin IX
Catalog No.:BCN7213
CAS No.:1623410-12-7
- Baccatin VIII
Catalog No.:BCN7212
CAS No.:1623410-10-5
- Oplopanaxoside C
Catalog No.:BCC8226
CAS No.:162341-29-9
- Baccatin X
Catalog No.:BCN7214
CAS No.:1623069-76-0
- 3-Amino-3-(hydroxymethyl)-1-(4-octylphenyl)-1,4-butanediol
Catalog No.:BCN1541
CAS No.:162361-49-1
- Vibralactone K
Catalog No.:BCN6746
CAS No.:1623786-66-2
- Vibralactone L
Catalog No.:BCN6914
CAS No.:1623786-67-3
- 3-O-Methyl-Estrone
Catalog No.:BCC8640
CAS No.:1624-62-0
- Roflumilast
Catalog No.:BCN2182
CAS No.:162401-32-3
- 3-Cyclopropylmethoxy-4-difluoromethoxybenzoic acid
Catalog No.:BCC8628
CAS No.:162401-62-9
- GR 103691
Catalog No.:BCC6941
CAS No.:162408-66-4
- Stilbostemin B
Catalog No.:BCN4697
CAS No.:162411-67-8
- VR23
Catalog No.:BCC6523
CAS No.:1624602-30-7
- Subelliptenone G
Catalog No.:BCN1720
CAS No.:162473-22-5
- Salirasib
Catalog No.:BCC1918
CAS No.:162520-00-5
- CDP 840 hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC7814
CAS No.:162542-90-7
P21 (Cdc42/Rac)-activated kinase 1 (pak1) is associated with cardiotoxicity induced by antihistamines.[Pubmed:27681411]
Arch Pharm Res. 2016 Dec;39(12):1644-1652.
Astemizole, a non-sedating histamine H1 receptor blocker, is widely known to cause cardiac arrhythmia, which prolongs the QT interval. However, the precise molecular mechanism involved in antihistamine-induced cardiovascular adverse effects other than hERG channel inhibition is still unclear. In this study, we used DNA microarray analysis to detect the mechanisms involved in life-threatening adverse effects caused by astemizole. Rat primary cardiomyocytes were treated with various concentrations of astemizole for 24 h and the corresponding cell lysates were analyzed using a DNA microarray. Astemizole altered the expression profiles of genes involved in calcium transport/signaling. Using qRT-PCR analysis, we demonstrated that, among those genes, p21 (Cdc42/Rac)-activated kinase 1 (pak1) mRNA was downregulated by treatment with terfenadine and astemizole. Astemizole also reduced pak1 protein levels in rat cardiomyocytes. In addition, astemizole decreased pak1 mRNA and protein levels in H9c2 cells and induced an increase in cell surface area (hypertrophy) and cytotoxicity. Fingolimod hydrochloride (FTY720), a pak1 activator, inhibited astemizole-induced hypertrophy and cytotoxicity in H9c2 cells. These results suggest that antihistamine-induced cardiac adverse effects are associated with pak1 expression and function.
Fingolimod hydrochloride gel shows promising therapeutic effects in a mouse model of atopic dermatitis.[Pubmed:27465785]
J Pharm Pharmacol. 2016 Oct;68(10):1268-77.
OBJECTIVES: To assess the efficacy of topically applied 2% hydroxypropyl cellulose gels containing 0.5% Fingolimod hydrochloride (FNGL) with or without 6% colloidal oatmeal in an in vivo model of atopic dermatitis (AD). METHODS: AD-like lesions were induced in SKH1/Hr hairless mice and were treated with FNGL gels, non-medicated base gels and Elidel((R)) cream for 6 weeks. The severity/improvement of the lesions was assessed regularly using the Eczema Area and Severity Index (EASI), pH of the skin, transepidermal water loss, g/m(2) /h (TEWL), humidity and temperature. At the end of the experiments, the plasma levels of cytokines, FNGL and white blood cells were determined. KEY FINDINGS: The EASI score was almost unchanged for the vehicle-only groups compared to before the treatments, whereas the medicated groups showed a significant decrease in the overall EASI score (P < 0.01), although there was non-significant differences among them (P > 0.081). Both the FNGL groups also showed a significant (P < 0.05) reduction in blood WBC. CONCLUSION: This study shows that the gels containing 0.50% FNGL and FNGL 0.50% plus 6% colloidal oatmeal have potential for the treatment of AD. The presence of colloidal oatmeal may provide additional benefits.
Overview and safety of fingolimod hydrochloride use in patients with multiple sclerosis.[Pubmed:24935480]
Expert Opin Drug Saf. 2014 Jul;13(7):989-98.
INTRODUCTION: Fingolimod (Gilenya(R), FTY720) is an oral sphingosine-1-phosphate analogue that was approved by the FDA in 2010 for the treatment of relapsing forms of multiple sclerosis (MS). Fingolimod's mechanism of action is primarily related to lymphocyte sequestration in primary and secondary lymphoid tissues. Phase III trials demonstrated a reduction in annualized relapse rate and MRI progression in fingolimod-treated subjects compared with both placebo and IFN-beta-treated subjects. Frequent adverse effects include fatigue, gastrointestinal disturbance, headache and upper respiratory tract infection. More serious, but rare, adverse events associated with fingolimod include atrioventricular block, symptomatic bradycardia, herpetic viral infections and macular edema. AREAS COVERED: We discuss the mechanism of action, pharmacokinetics, clinical efficacy and safety profile of fingolimod in patients with relapsing MS. EXPERT OPINION: Fingolimod is an effective treatment for relapsing MS and its oral route of administration may be preferred by some. Fingolimod is generally well tolerated but requires diligence in patient selection and monitoring. Additional information is needed regarding risk of infection, malignancy and rebound disease with long-term use of fingolimod.


