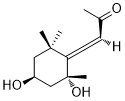
Grasshopper ketoneCAS# 41703-38-2 |
Quality Control & MSDS
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 41703-38-2 | SDF | File under preparation. |
| PubChem ID | N/A | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C13H20O3 | M.Wt | 224.3 |
| Type of Compound | Sesquiterpenoids | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | Soluble in Chloroform,Dichloromethane,Ethyl Acetate,DMSO,Acetone,etc. | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||

Grasshopper ketone Dilution Calculator

Grasshopper ketone Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 4.4583 mL | 22.2916 mL | 44.5831 mL | 89.1663 mL | 111.4579 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.8917 mL | 4.4583 mL | 8.9166 mL | 17.8333 mL | 22.2916 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.4458 mL | 2.2292 mL | 4.4583 mL | 8.9166 mL | 11.1458 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0892 mL | 0.4458 mL | 0.8917 mL | 1.7833 mL | 2.2292 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0446 mL | 0.2229 mL | 0.4458 mL | 0.8917 mL | 1.1146 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- Cannabisin E
Catalog No.:BCN0727
CAS No.:
- Bisdemethoxyboehmenan
Catalog No.:BCN0726
CAS No.:146918-26-5
- 6-Hydroxyisosativan
Catalog No.:BCN0725
CAS No.:2172624-69-8
- Erythrinin F
Catalog No.:BCN0724
CAS No.:1616592-60-9
- Derrisisoflavone I
Catalog No.:BCN0723
CAS No.:2172624-66-5
- Derrisisoflavone K
Catalog No.:BCN0722
CAS No.:2172624-68-7
- Derrisisoflavone H
Catalog No.:BCN0721
CAS No.:2172624-65-4
- Epimedonin L
Catalog No.:BCN0720
CAS No.:2215102-38-6
- Derrisisoflavone J
Catalog No.:BCN0719
CAS No.:2172624-67-6
- Pinobanksin 3-(2-methyl)butyrate
Catalog No.:BCN0718
CAS No.:1221923-43-8
- 3'',4''-Di-O-p-coumaroylquercitrin
Catalog No.:BCN0717
CAS No.:437615-43-5
- Quercetin dimer
Catalog No.:BCN0716
CAS No.:167276-19-9
- Byzantionoside B
Catalog No.:BCN0729
CAS No.:189109-45-3
- Securisteroside
Catalog No.:BCN0730
CAS No.:54964-57-7
- Wallicoside
Catalog No.:BCN0731
CAS No.:88797-59-5
- Hydroxytyrosol 1-O-glucoside
Catalog No.:BCN0732
CAS No.:76873-99-9
- Isosilychristin
Catalog No.:BCN0733
CAS No.:77182-66-2
- Bocconoline
Catalog No.:BCN0734
CAS No.:32906-88-0
- 3-O-Methylellagic acid 3'-O-alpha-rhamnopyranoside
Catalog No.:BCN0735
CAS No.:352280-34-3
- Yinxiancaoside C
Catalog No.:BCN0736
CAS No.:1159908-74-3
- Methylpicraquassioside B
Catalog No.:BCN0737
CAS No.:1443757-89-8
- Methyl 2-hydroxy-3,4-dimethoxybenzoate
Catalog No.:BCN0738
CAS No.:6395-23-9
- 3'-O-Methylviolanone
Catalog No.:BCN0739
CAS No.:56973-42-3
- Lariciresinol 4-O-glucoside
Catalog No.:BCN0740
CAS No.:143663-00-7
[Chemical constituents of Physalis minima].[Pubmed:34472261]
Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2021 Aug;46(15):3865-3872.
Fifteen compounds(1-15) were isolated from the 95% EtOH extract of the whole herb of Physalis minima by various chromatography techniques including silica gel, Sephadex LH-20, middle chromatogram isolated gel(MCI), octadecyl silica(ODS), and semi-preparative high performance liquid chromatography(HPLC). Their structures were elucidated by infrared spectroscopy(IR), ultraviolet spectroscopy(UV), high-resolution electrospray ionization mass spectrometry(HR-ESI-MS), nuclear magnetic re-sonance(NMR), and circular dichroism(CD) as(5S)-5,11-dihydroxy-3-methyl-5-pentylfuran-2(5H)-one(1), withaphysalin R(2), withaphysalin Q(3), withaphysanolide A(4), phaseic acid(5), Grasshopper ketone(6), 3S,5R-dihydroxy-6S,7-megastigmadien-9-one(7), vanillic acid(8), 2-trans,4-trans-abscisic acid(9), capillasterolide(10), 5,3'-dihydroxy-3,7,4'-trimethoxyflavone(11),(-)-loliolide(12), 4-hydroxyacetophenone(13), acetosyringone(14), and aurantiamide acetate(15). Compound 1 was a new butenolide, and compounds 5-7 and 10-12 were isolated from the Physalis for the first time. Compounds 4, 13, and 15 were isolated for the first time from P. minima. Moreover, their anti-inflammatory activity was evaluated in vitro. Compound 12 was found to possess an inhibitory effect on the transcription of an NF-kappaB-dependent reporter gene in LPS-induced 293 T/NF-kappaB-luc cells at 10 mumol.L~(-1), showing an inhibitory rate of 62.31%+/-4.8%.
Anti-Inflammatory Effects of Grasshopper Ketone from Sargassum fulvellum Ethanol Extract on Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Inflammatory Responses in RAW 264.7 Cells.[Pubmed:30982318]
J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2019 May 28;29(5):820-826.
This study evaluated the anti-inflammatory potential of a Grasshopper ketone (GK) isolated from the brown alga Sargassum fulvellum on lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced RAW 264.7 murine macrophage cell line. GK was isolated and purified from the n-hexane fraction and its structure was verified on the basis of NMR spectroscopic data. GK up to 100 mug/ml is not cytotoxic to RAW 264.7, and is an effective inhibitor of LPS-induced NO production in RAW 264.7 cells. The production of pro-inflammatory cytokines, including IL-6, IL-1beta, and TNF-alpha was found significantly reduced in 0.1-100 mug/ml dose ranges of GK treatment (p < 0.05). We confirmed the dose-dependent and significant inhibition of iNOS and COX-2 proteins expression. In addition, it has been shown that GK induces anti-inflammatory effects by inhibiting MAPKs (ERK, JNK, and p38) and NF-kappaB p65 phosphorylation. Our results show that the anti-inflammatory properties of GK may be due to the inhibition of the NF-kappaB and MAPKs pathways, which are associated with the attenuation of cytokine secretion.
[A new dimeric xanthanolide from fruits of Xanthium chinense].[Pubmed:29600618]
Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2018 Feb;43(3):532-536.
Through the methods of polyamide resin Sephadex LH-20 ODS column chromatography and preparative HPLC etc. 7 compounds were isolated from the 70% ethanol extract of the fruits of Xanthium chinense. Based on ESI-MS and NMR data the structures of these compounds were identified as pungiolide O(1) Grasshopper ketone(2) icariside F(2)(3) 7-[(beta-D-apiofuranosyl-(1-->6)-beta-D-glucopyranosyl)oxymethy]-88-dimethyl-48-d ihydrobenzo[14]thiazine-35-dione(4)(6R9S)-3-oxo-alpha-ionol beta-D-glucopyranoside(5) cryptochlorogenic acid methyl ester(6) and chlorogenic acid methyl ester(7). Among them compound 1 is a new compound.
[Chemical constituents from Murraya euchrestifolia].[Pubmed:29090551]
Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2017 May;42(10):1916-1921.
The open silica gel, ODS, and Sephadex LH-20 column chromatography, along with the semi-preparative HPLC was used to isolate and purify the chemical constituents from Murraya euchrestifolia. The structures of the isolates were elucidated by their physiochemical properties, NMR, and MS spectroscopic data, as well as comparison with literature data. Eighteen compounds were isolated from the CH2Cl2 fraction of the 95% aqueous EtOH extract of M. euchrestifolia, and their structures were identified as sakuranetin (1), eriodictyol-7,4'-dimethyl ether (2), isosakuranetin (3), 5-hydroxy-7,4'-dimethoxyflavanone (4), eriodictyol-7-methyl ether (5), lichexanthon (6), 5,6,7-trimethoxycoumarin (7), 5-hydroxy-6,8-dimethoxycoumarin (8), 8-hydroxy-6-methoxy-3-n-pentylisocoumarin (9), ethyl caffeate (10), 4-hydroxy-3,5- dimethoxycinnamic acid ethyl ester (11), methyl 3-(5'-hydroxyprenyl)-coumarate (12), (E)-coniferol (13), beta-hydroxypropiovanillone (14), 3-hydroxy-7,8-didehydro-beta-ionone (15), 3beta-hydroxy-5alpha, 6alpha-epoxy-7-megastigmen-9-one (16), Grasshopper ketone (17), and 4-hydroxy-3,5-dimethoxybenzaldehyde (18). Compounds 1-15 and 18 were first obtained from the plants of Murraya genus, and compounds 16 and 17 were isolated from M. euchrestifolia for the first time.
In vivo and in vitro inhibitory activity of an ethanolic extract of Sargassum fulvellum and its component grasshopper ketone on atopic dermatitis.[Pubmed:27608302]
Int Immunopharmacol. 2016 Nov;40:176-183.
The present study investigated the effect of Sargassum fulvellum ethanol extract (SFEE) on 2,4-dinitrochlorobenzene (DNCB)-induced atopic dermatitis (AD)-like skin lesions in BALB/c mice. The severity of skin dermatitis, production of cytokines, and total IgE content were measured, and the histopathological features were analyzed. SFEE decreased the severity of DNCB-induced dermatitis and suppressed the serum levels of total immunoglobulin E (IgE), tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-alpha, and interleukin (IL)-4. In addition, SFEE reduced the production of IL-4, IL-5, and IL-13 in mice splenocytes. However, the levels of IL-10 and interferon (IFN)-gamma significantly increased in mice sera and splenocytes. Histological examination revealed decreased dermal thickness and infiltration by mast cells after treatment with SFEE. Furthermore, Grasshopper ketone, a compound isolated from SFEE, was found to significantly decrease cytokine production in concanavalin A-stimulated splenocytes from BALB/c mice with no cytotoxicity. Taken together, these results indicate that SFEE and the isolated Grasshopper ketone have an inhibitory effect on AD by regulating immune mediators and cells and may be a potential effective alternative therapy for AD.
[Chemical Constituents of Ethyl Acetate Extract from Viola biflora].[Pubmed:30132649]
Zhong Yao Cai. 2016 May;39(5):1041-4.
Objective: To isolate the chemical constituents of ethyl acetate extract from Viola biflora. Methods: Isolation and purification were carried out on repeated silica gel column chromatography,PTLC,and Sephadex LH-20. The structures of these compounds were elucidated by physico-chemical properties and spectral analyses. Results: Twelve compounds were isolated from Viola biflora,which identified as aurantiamide acetate( 1),solalyratin B( 2),esculetin( 3),scopoletin( 4),lupeol( 5),132S-hydroxypheophytin a( 6),vomifoliol( 7),dibutyl phthalate( 8),(-)-dihydrovomifoliol( 9),Grasshopper ketone( 10),crassifol( 11) and beta-sitosterol( 12). Conclusion: All the compounds are isolated from Viola biflora for the first time. Compounds 2,7,9 ~ 11 are isolated from Viola genus for the first time.
[Sesquiterpenoids from Solanum lyratum].[Pubmed:24946547]
Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2014 Feb;39(3):453-6.
Ten compounds were isolated and purified by column chromatography over silica gel, preparative TLC, and Sephadex LH-20 from the whole plant of Solanum lyratum. The structures were elucidated on the basis of physico-chemical properties and spectral data as 1beta-hydroxy-1 ,2-dihydro-alpha-santonin (1) , boscialin (2) , blumenol C (3), 3beta-hydroxy-5alpha, 6alpha-epoxy-7-megastigmen-9-one(4), dehydrovomifoliol(5) , blumenol A(6), (1'S,2R,5S, 10R) -2-(1', 2'-dihydroxy-l1'-methylethyl) -6,10-dimethylspiro[4,5] dec-6-en-8-one(7) , (1'R,2R,5S,10R)-2-( 1',2'-dihydroxy-l '-methylethyl) -6,1 l0-dimethylspiro[4,5]dec-6-en-8-one( 8) , 2-(1',2'-dihydroxy-1 '-methylethyl) -6,1 0-dimethyl-9-hydroxyspiro [4,5] dec-6-en-8-one (9) , and Grasshopper ketone (10). Compounds 1-10 were isolated from this plant for the first time.
[Chemical constituents from Chenopodium ambrosioides].[Pubmed:24761641]
Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2014 Jan;39(2):254-7.
Twelve compounds were isolated from the herb of Chenopodium ambrosioides, and their structures were identified by spectroscopic methods as kaempferol-7-O-alpha-L-rhamnopyranoside (1), kaempferol-3,7-di-O-alpha-L-rhamnopyranoside (2), patuletin (3), quercetin-7-O-alpha-L-rhamnopyranoside (4), Grasshopper ketone (5), 4-hydroxy-4-methyl-2-cyclohexen-1-one (6), syringaresinol (7), benzyl beta-D-glucopyranoside (8), dendranthemoside B (9), N-trans-feruloyl tyramine (10), N-trans-feruloyl 4'-O-methyldopamine (11), and 4-hydroxy-N-[2-(4-hydroxyphenyl) ethyl] benzamide (12). Among them,compounds 3, 6-8,10, and 12 were isolated from the genus Chenopodium for the first time, and compounds 2-12 were isolated from this plant for the first time.
Grasshopper ketone 3-O-primveroside from Sinocrassula indica.[Pubmed:22530677]
J Asian Nat Prod Res. 2012;14(5):503-7.
A new megastigmane glycoside, Grasshopper ketone 3-O-primveroside (1), was isolated from the methanolic extract of the whole herbs of Sinocrassula indica (Crassulaceae). Its structure was elucidated on the basis of spectral and chemical evidence.
Identification of two phytotoxins, blumenol A and grasshopper ketone, in the allelopathic Japanese rice variety Awaakamai.[Pubmed:22364828]
J Plant Physiol. 2012 May 1;169(7):682-5.
Aqueous methanol extracts of the traditional rice (Oryza sativa) variety Awaakamai, which is known to have the greatest allelopathic activity among Japanese traditional rice varieties, inhibited the growth of roots and shoots of cress (Lepidium sativum), lettuce (Lactuca sativa), timothy (Phleum pratense), Digitaria sanguinalis, Lolium multiflorum and Echinochloa crus-galli. Increasing the extract concentration increased the inhibition, suggesting that the extract of Awaakamai contains growth inhibitory substances. The extract of Awaakamai was purified and two main growth inhibitory substances were isolated and determined by spectral data as blumenol A and Grasshopper ketone. Blumenol A and Grasshopper ketone, respectively, inhibited the growth of cress shoots and roots at concentrations greater than 10 and 30 mumol/L. The concentrations required for 50% growth inhibition on cress roots and shoots were 84 and 27 mumol/L, respectively, for blumenol A, and 185 and 76 mumol/L, respectively, for Grasshopper ketone. These results suggest that blumenol A and Grasshopper ketone may contribute to the growth inhibitory effect of Awaakamai and may play an important role in the allelopathy of Awaakamai.
Silvestrol and episilvestrol, potential anticancer rocaglate derivatives from Aglaia silvestris.[Pubmed:15132542]
J Org Chem. 2004 May 14;69(10):3350-8.
Two cytotoxic rocaglate derivatives possessing an unusual dioxanyloxy unit, silvestrol (1) and episilvestrol (2), were isolated from the fruits and twigs of Aglaia silvestris by bioassay-guided fractionation monitored with a human oral epidermoid carcinoma (KB) cell line. Additionally, two new baccharane-type triterpenoids, 17,24-epoxy-25-hydroxybaccharan-3-one (3) and 17,24-epoxy-25-hydroxy-3-oxobaccharan-21-oic acid (4), as well as eleven known compounds, 1beta,6alpha-dihydroxy-4(15)-eudesmene (5), ferulic acid (6), Grasshopper ketone (7), apigenin, cabraleone, chrysoeriol, 1beta,4beta-dihydroxy-6alpha,15alpha-epoxyeudesmane, 4-hydroxy-3-methoxyacetophenone, 4-hydroxyphenethyl alcohol, ocotillone, and beta-sitosterol 3-O-beta-D-glucopyranoside, were also isolated and characterized. The structures of compounds 1-4 were elucidated by spectroscopic studies and by chemical transformation. The absolute stereochemistry of silvestrol (1) was established by a X-ray diffraction study of its di-p-bromobenzoate derivative, and the structure of 3 was also confirmed by single-crystal X-ray diffraction. The isolates and chemical transformation products were evaluated for cytotoxicity against several human cancer cell lines, and silvestrol (1) and episilvestrol (2) exhibited potent in vitro cytotoxic activity. Silvestrol (1) was further evaluated in vivo in the hollow fiber test and in the murine P-388 leukemia model.
Aroma composition of Vitis vinifera Cv. tannat: the typical red wine from Uruguay.[Pubmed:12926890]
J Agric Food Chem. 2003 Aug 27;51(18):5408-13.
The free volatiles, as well as those released from the glycosidically bound forms by enzyme hydrolysis, have been analyzed to chracterize young Tannat wines from two successive vintages. The Tannat wine showed some aroma profile peculiarities detected in the free forms but, above all, in the bound fraction for the level and profile of the norisoprenoidic fraction. Among the free volatile compunds, a rather low content of C(6) alcohols with a prevalence of cis-3-hexen-1-ol on the trans form and sometimes a remarkable level of trans-2-hexen-1-ol seem to be typical for the variety. C(13)-norisoprenoidic and monoterpenic volatiles made up approximately 42% of the total level of the volatiles observed in the glycosidase enzyme-released fraction. The other volatiles were C(6) alcohols (6%) and benzenoid compounds (51%). The dominating monoterpene alcohols were the cis and trans isomers of 3,7-dimethyl-1,6-octadiene-3,8-diol (8-hydroxylinalool). The C(13)-norisoprenoid pattern was composed by 3-hydroxy-beta-damascone, 3-oxo-alpha-ionol, vomifoliol, 4-oxo-beta-ionol, 3-oxo-7,8-dihydro-alpha-ionol, 4-oxo-7,8-dihydro-beta-ionol, Grasshopper ketone, and 7,8-dihydrovomifoliol.


