HomatropineCAS# 87-00-3 |
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 87-00-3 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 73707487 | Appearance | Powder |
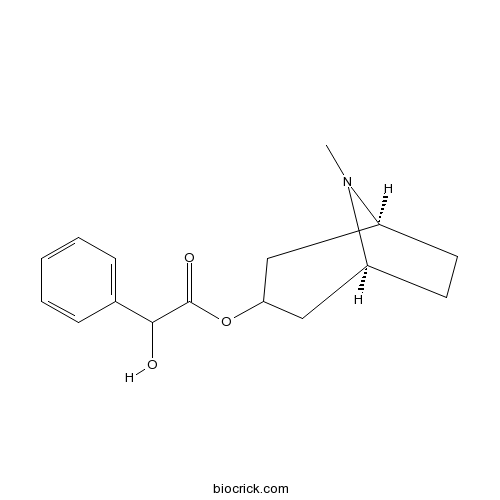
| Formula | C16H21NO3 | M.Wt | 275.4 |
| Type of Compound | Alkaloids | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | Soluble in Chloroform,Dichloromethane,Ethyl Acetate,DMSO,Acetone,etc. | ||
| Chemical Name | [(1S,5S)-8-methyl-8-azabicyclo[3.2.1]octan-3-yl] 2-hydroxy-2-phenylacetate | ||
| SMILES | CN1C2CCC1CC(C2)OC(=O)C(C3=CC=CC=C3)O | ||
| Standard InChIKey | ZTVIKZXZYLEVOL-QNIGDANOSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C16H21NO3/c1-17-12-7-8-13(17)10-14(9-12)20-16(19)15(18)11-5-3-2-4-6-11/h2-6,12-15,18H,7-10H2,1H3/t12-,13-,15?/m0/s1 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||

Homatropine Dilution Calculator

Homatropine Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 3.6311 mL | 18.1554 mL | 36.3108 mL | 72.6216 mL | 90.7771 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.7262 mL | 3.6311 mL | 7.2622 mL | 14.5243 mL | 18.1554 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.3631 mL | 1.8155 mL | 3.6311 mL | 7.2622 mL | 9.0777 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0726 mL | 0.3631 mL | 0.7262 mL | 1.4524 mL | 1.8155 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0363 mL | 0.1816 mL | 0.3631 mL | 0.7262 mL | 0.9078 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- Merepoxine
Catalog No.:BCN8946
CAS No.:115777-94-1
- Indicine hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCN8945
CAS No.:1195140-94-3
- Heliosupine N-oxide
Catalog No.:BCN8943
CAS No.:31701-88-9
- Glucoraphenin
Catalog No.:BCN8942
CAS No.:108844-81-1
- 6-Hydroxytropinone
Catalog No.:BCN8940
CAS No.:5932-53-6
- Glucohesperin
Catalog No.:BCN8939
CAS No.:33049-17-1
- Sceleratine N-oxide
Catalog No.:BCN8938
CAS No.:103184-92-5
- Senecivernine N-oxide
Catalog No.:BCN8937
CAS No.:101687-28-9
- Riddelline N-oxide
Catalog No.:BCN8936
CAS No.:75056-11-0
- 7-O-Acetyllycopsamine N-oxide
Catalog No.:BCN8935
CAS No.:685132-58-5
- Merenskine N-oxide
Catalog No.:BCN8934
CAS No.:96657-95-3
- Merenskine
Catalog No.:BCN8933
CAS No.:96657-94-2
- Echimidine N-oxide
Catalog No.:BCN8950
CAS No.:41093-89-4
- Lycopsamine N-oxide
Catalog No.:BCN8951
CAS No.:95462-15-0
- Usaramine N-oxide
Catalog No.:BCN8952
CAS No.:117020-54-9
- Scopolamine N-oxide hydrobromide
Catalog No.:BCN8953
CAS No.:6106-81-6
- Noratropine
Catalog No.:BCN8955
CAS No.:16839-98-8
- Glucoraphasatin
Catalog No.:BCN8957
CAS No.:28463-23-2
- Glucobrassicin
Catalog No.:BCN8958
CAS No.:143231-38-3
- Glucocheirolin
Catalog No.:BCN8959
CAS No.:15592-36-6
- Sinalbin potassium salt
Catalog No.:BCN8960
CAS No.:16411-05-5
- Gluconasturtiin
Catalog No.:BCN8961
CAS No.:18425-76-8
- Glucohirsutin
Catalog No.:BCN8962
CAS No.:21973-60-4
- Glucoraphasatin potassium salt
Catalog No.:BCN8963
CAS No.:245550-64-5
Case Report: Corneal Ulceration from Bilateral Ectropion Due to Congenital Ichthyosis.[Pubmed:31479026]
Optom Vis Sci. 2019 Sep;96(9):706-709.
SIGNIFICANCE: Ichthyosis is a group of heterogenous inherited skin disorders characterized by abnormal cornification and keratinization of the skin. Autosomal recessive congenital ichthyosis presents with severe lagophthalmos and cicatricial ectropion of both upper and lower lids. Chronic corneal exposure from lid abnormalities may lead to ulcerative keratitis or corneal perforation. PURPOSE: The case highlights a rarely seen condition that presents with potentially serious ocular complications and vision loss. Corneal complications may be avoided or managed with moisture goggles, corneal vaulting with scleral lenses, topical therapeutics, amniotic membrane, and surgical lid repair. CASE REPORT: A 25-year-old woman presented with a painful right eye for 1 week. She had a medical history of autosomal recessive congenital ichthyosis. Her ocular adnexa revealed bilateral lagophthalmos and cicatricial ectropion of both upper and lower lids. The slit lamp of examination revealed an injected eye with corneal ulcer with hypopyon in the right eye and quiet eye with corneal scarring in the left eye. The patient was treated with topical moxifloxacin and polymyxin B sulfate/trimethoprim as well as in-office Homatropine 5% in the right eye. The keratitis was treated to resolution, and the patient referred for consultation on lid repair. CONCLUSIONS: Chronic corneal exposure from autosomal recessive congenital ichthyosis may lead to severe dry eye, ulcerative keratitis, or perforation. Patients should be monitored carefully for corneal disease, educated on methods and devices to protect the corneal surface, and referred for surgical repair if indicated. Although rare, this condition presents unique findings that may be visually devastating. Awareness of the condition, as well as the various clinical presentations and appropriate management necessary, will prove beneficial to the patient.
Ocular surface histopathological insult following sarin and VX exposure and potential treatments in the rat model.[Pubmed:31408696]
Toxicol Lett. 2019 Oct 10;314:153-163.
Eye exposure to organophosphate (OP) chemical warfare irreversible acetylcholinesterase inhibitors, results in long-term miosis and impaired visual function. In contrast to the well-documented miotic and ciliary muscle spasm observed following chemical warfare, OP ocular exposure, little is known regarding the ocular surface histopathological insult. The aim of the present study was to determine the degree of the ocular surface insult following sarin or VX ocular exposure and to evaluate potential anti-cholinergic treatments in counteracting this insult. Rats that were whole body exposed to various sarin concentrations (0.049-43mug/L; 5min exposure), showed a dose-dependent miotic response and light reflex impairment. Following whole body sarin exposure, a dose dependent ocular surface histopathological insult was developed. A week following exposure to a low concentration of 0.05mug/L, conjunctival pathology was observed, while corneal insult was noticed only following exposure to a concentration of 0.5mug/L and above. Both tissues presented poorer outcomes when exposed to higher sarin concentrations. In contrast, eyes topically exposed to 1mug sarin demonstrated no ocular insult a week following exposure. On the contrary, topical exposure to 1mug VX resulted in a significant corneal insult. Anticholinergic treatments such as 0.1% atropine or 2% Homatropine, given shortly following VX exposure, counteracted this insult. The results of this study show that not only do anti-cholinergic treatments counteract the miotic response, but also prevent the histopathological insult observed when given shortly following OP exposure.
Oral malignant melanoma of alveolar ridge.[Pubmed:31154344]
BMJ Case Rep. 2019 May 31;12(5). pii: 12/5/e227456.
Malignancy of melanocytes, a pigment-producing cell, is referred as malignant melanoma (MM) which occur basically on skin and oral mucous membrane, but as well found in ears, eyes, gastrointestinal tract and genital mucosa. Oral melanomas has propensity to metastasise and invade more voluntarily than other malignant counterparts. Here we present a case of 52-year-old male patient with a chief symptom of blackening of gums in the upper front tooth region. In dental history, the patient revealed history of faulty artificial prosthesis fixed in the same region since 6 months. On the basis of a through clinical assessment, a provisional opinion of oral malignant melanoma, was prepared. On histopathological and immunohistochemical analysis with S-100 and Homatropine methylbromide 45 the diagnosis of MM was confirmed.
Systemic toxicity of topical corticosteroids.[Pubmed:30900600]
Indian J Ophthalmol. 2019 Apr;67(4):559-561.
Corticosteroids are known to cause many ocular and systemic side effects when administered by oral or parenteral routes. Corticosteroid induced systemic toxicity secondary to topical steroid eye drops is rare. A 6-week-old, male infant was brought to our tertiary eye care center with bilateral congenital cataracts. The child underwent phacoaspiration with primary posterior capsulotomy without intraocular lens implantation in both eyes at an interval of 6 weeks. Child was initiated on topical betamethsone 0.1% eight times a day, tobramycin 0.3% six times a day, Homatropine 2% twice a day, and carboxymethylcellulose 0.5% four times a day. Two and four weeks later he underwent surgical membranectomy in the right and left eye respectively followed by frequent use of topical steroids, initially given 1 hourly and then tapered weekly in the follow-up period. The patient showed increase in intraocular pressure and gain in body weight along with development of cushingoid habitus nearly 6 to 8 weeks after starting topical steroids. These side effects started weaning off following the reduction in dose of topical steroids, suggesting the role of the corticosteroid-related systemic side effects. This case highlights the serious systemic side effects secondary to increased frequency and duration of topical corticosteroid use in infancy. Hence, dosage of topical steroids should be adjusted in its therapeutic range to prevent their ocular and systemic side effects. Therefore, close monitoring is advocated for children using topical corticosteroids to prevent serious ocular and systemic side effects.
Complexation of tropane alkaloids by cyclodextrins.[Pubmed:30732827]
Carbohydr Polym. 2019 Apr 1;209:74-81.
Complexes of atropine, Homatropine, scopolamine, and ipratropium with cyclodextrins were investigated by NMR and capillary electrophoresis. It has been demonstrated that tropane alkaloids form complexes with beta- and gamma-cyclodextrins of 1:1 stoichiometry. NMR measurements indicate the formation of complexes where both aliphatic and aromatic parts of tropane alkaloids interact with beta-cyclodextrin. The stability constants of the investigated alkaloids with beta- and gamma-cyclodextrins were determined by capillary electrophoresis. It has been found that beta-cyclodextrin forms ten times more stable complexes than gamma-cyclodextrin. Moreover, the analysis of the obtained crystal structure of beta-cyclodextrin/(-)-hyoscyamine complex reveals that two molecules of (-)-hyoscyamine oriented in head-to-tail mode are tightly fitted inside head-to-head beta-cyclodextrin dimer. Conformation of (-)-hyoscyamine as well as scopolamine changes substantially upon complexation adapting to the cavity of beta-cyclodextrin as shown by X-ray analysis, NMR and DFT calculations data.
Amniotic Membrane Transplantation in Acute Severe Ocular Chemical Injury: A Randomized Clinical Trial.[Pubmed:30419194]
Am J Ophthalmol. 2019 Mar;199:209-215.
PURPOSE: To compare the outcomes of conventional medical treatment vs combined medical treatment and amniotic membrane transplantation (AMT) in the management of patients with Roper-Hall grade IV ocular chemical injury. DESIGN: Randomized, parallel-controlled clinical trial. METHODS: Setting: Single tertiary referral hospital. PATIENTS: Sixty eyes of 60 patients with Roper-Hall grade IV ocular chemical injury with a minimum follow-up of 12 months were enrolled in the study. INTERVENTION: Patients were randomly assigned to 2 groups: Group 1 (30 eyes) received topical preservative-free lubricating gel and drops, chloramphenicol, betamethasone, Homatropine, oral vitamin C, and doxycycline; Group 2 (30 eyes) received amniotic membrane transplant (AMT) on the entire ocular surface in addition to the medical treatment provided in Group 1. OUTCOME MEASURES: The main outcome measure was time to complete corneal epithelialization. Secondary outcome measures were best-corrected visual acuity (BCVA) and neovascularization in the central 5 mm of the cornea. RESULTS: Mean follow-up time was 20.3 +/- 2.5 months (range 13-24 months). Corneal epithelial defects healed within 72.6 +/- 30.4 (21-180) days in Group 1 vs 75.8 +/- 29.8 (46-170) days in Group 2 (P = .610). Mean BCVA was 2.06 +/- 0.67 (0.4-2.6) logMAR vs 2.06 +/- 0.57 (1-2.9) logMAR in Groups 1 and 2, respectively (P = .85). Group 1 developed more central corneal neovascularization (22 eyes; 73.3%) compared to Group 2 (16 eyes; 53.3%); however, it was not statistically significant (P = .108). CONCLUSIONS: In comparison to conventional medical therapy, combined amniotic membrane transplantation and medical therapy does not accelerate corneal epithelialization or affect final visual acuity in severe chemical injuries.
Determination of thermodynamic binding constants by affinity capillary electrophoresis.[Pubmed:30348416]
Talanta. 2019 Jan 15;192:448-454.
A strategy to study thermodynamic binding constants by affinity capillary electrophoresis (ACE) is presented. In order to simplify mathematical treatment, analogy with acid-base dissociation equilibrium is proposed: instead of ligand concentration [X], negative logarithm of ligand concentration (or activity), pX=-log[X], is used. On this base, and taking into account ionic activities, a general procedure for obtaining thermodynamic binding constants is proposed. In addition, the method provides electrophoretic mobilities of the free analyte and analyte-ligand complex, even when binding constants are low and thus, the complexed analyte fraction is also low. This is useful as a base to rationally analyze a diversity of situations, i.e., different mathematical dependencies are obtained when analytes and ligands with different charges are combined. Practical considerations are given for carrying out a full experimental design. Enantiomeric ACE separation based on the use of chiral selectors is addressed. 2-hydroxypropyl-beta-cyclodextrin was chosen as a model ligand, and both enantiomeric forms of four pharmaceutical drugs (propranolol, pindolol, oxprenolol and Homatropine methylbromide) were considered as model analytes. Practical aspects are detailed and thermodynamic binding constants as well as free and complexed analytes mobilities are determined.
A novel one-pot strategy to prepare beta-cyclodextrin functionalized capillary monoliths for enantioseparation of basic drugs.[Pubmed:30086947]
Talanta. 2018 Nov 1;189:458-466.
With native beta-cyclodextrin (beta-CD) added into the polymerization mixture directly, a novel, convenient and low-cost one-pot strategy was developed to prepare the beta-CD functionalized organic polymer monolithic capillary column. Diazabicyclo[5.4.0]undec-7-ene (DBU) as a basic catalyst for the ring opening reaction between beta-CD and glycidyl methacrylate (GMA) was introduced into the polymerization system for the first time. Thereby, two consecutive reactions namely the in situ methacrylation of beta-CD and copolymerization reaction can be achieved in one pot. The preparation conditions including the type and composition of porogensthe ratio of functional monomer to crosslinker and amount of 2-acrylamido-2-methyl propane sulfonic acid (AMPS) were optimized. The specific surface area and morphology of the prepared monolith were characterized using scanning electron microscopy (SEM) and nitrogen adsorption analysis, respectively. Raman spectroscopy and nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy confirmed that beta-CD was covalently bonded onto the monolith successfully. Then, the monolithic column was applied to enantioseparation of six basic drugs in capillary electrochromatography (CEC). Under the optimal conditions, tropicamide, Homatropine, Homatropine methylbromide, brompheniramine, chlorpheniramine and clorprenaline were all totally separated with the resolution (Rs) values of 2.84, 4.70, 4.61, 3.01, 2.57 and 2.33, respectively. Furthermore, the column demonstrated satisfactory stability and repeatability of retention time and enantioselectivity using Homatropine as model analyte.
Effect of Cycloplegia on Optical Biometry in Pediatric Eyes.[Pubmed:29809268]
J Pediatr Ophthalmol Strabismus. 2018 Jul 1;55(4):260-265.
PURPOSE: To study the effect of cycloplegia on optical biometry parameters in pediatric eyes using the Lenstar LS 900 (Haag-Streit, Koeniz, Switzerland). METHODS: In this observational and comparative study, 56 normal eyes and 20 cataractous eyes in children between 5 and 15 years of age were included. Measurements were taken before and after cycloplegia using 2% Homatropine drops. Parameters studied were axial length, central corneal thickness, keratometry, anterior chamber depth, and lens thickness. The Wilcoxon test was used to compare the effects of cycloplegia on all parameters. RESULTS: Cycloplegia resulted in a statistically significant decrease in axial length (P < .05), central corneal thickness (P < .05), and lens thickness (P < .001) and an increase in the anterior chamber depth (P < .001) in normal eyes. In the cataract group, cycloplegia resulted in an increase in anterior chamber depth (P < .001) and decrease in lens thickness (P < .001). CONCLUSIONS: Biometry measurements have to be carefully interpreted in pediatric eyes where cycloplegia is an important part of the examination. [J Pediatr Ophthalmol Strabismus. 2018;55(4):260-265.].
Screening of drugs and homeopathic products from Atropa belladonna seed extracts: Tropane alkaloids determination and untargeted analysis.[Pubmed:29808589]
Drug Test Anal. 2018 Oct;10(10):1579-1589.
Homeopathic products are still a controversial issue in modern medicine, understood as complementary or alternative medicine (CAM). In this particular case, homeopathic products prepared from Atropa belladonna extracts may present specific problems due to the effects derived from its components. This article applies a simple, rapid, reliable method to the analysis of different homeopathic products obtained from Atropa belladonna; drugs containing high concentration of plant extracts; and Atropa belladonna seeds. The method was based on a simple solid-phase preconcentration method followed by ultra-high pressure liquid chromatography (UHPLC) coupled to high resolution mass spectrometry using Exactive-Orbitrap as an analyser. An in-house database was set and atropine and scopolamine were the compounds detected at highest concentrations in homeopathic products from Atropa belladonna extracts (4.57 and 2.56 mug/kg, respectively), in Belladonna ointment (4007 and 1139 mug/kg, respectively) and Belladonna seeds (338 and 32.1 mg/kg, respectively). Other tropane alkaloids such as tropine, apoatropine, aposcopolamine, tropinone, Homatropine, and anisodamine were detected at lower concentrations (0.04-1.36 mug/kg). When untargeted analysis was performed, other tropane alkaloids were identified in the tested samples, such as ecgonine (0.003 mug/kg), benzoylecgonine (0.56 mug/kg), calystegines A (19.6 mug/kg), B (33.1 mug/kg), and C (1.01 mug/kg). Finally other compounds present in the homeopathic products, such as sugars (fructose, glucose, and lactose) or amino acids (valine, ornithine, leucine, and phenylalanine), were identified.
The interaction between homatropine and optical blur on choroidal thickness.[Pubmed:29691923]
Ophthalmic Physiol Opt. 2018 May;38(3):257-265.
PURPOSE: To analyse the short-term interaction between a short period of myopic and hyperopic defocus and the muscarinic antagonist Homatropine upon the choroidal thickness and ocular biometrics of healthy subjects. METHODS: Thirty young adults (15 myopes and 15 emmetropes) aged 18-35 years had subfoveal choroidal thickness (ChT) and ocular biometry measurements taken before, 30 min, and 60 min following the introduction of monocular optical blur (0.00 D, +3.00 D and -3.00 D) combined with administration of either 2% Homatropine or placebo (total of six conditions). Each combination of optical blur and drug was tested on different days, 2 days apart, in randomised order. For choroidal thickness, we captured three SD OCT images (5 mm, cross scans centred at the fovea with 999 A-scans and 50 B-scans) with the Copernicus SOCT HR instrument (www.optopol.com). A masked observer manually segmented the average B-scan images to derive subfoveal choroidal thickness measurements from each measurement session. RESULTS: The choroid exhibited significant thinning after imposing hyperopic defocus (-3.00 D) combined with placebo (-11 +/- 3 mum, p < 0.001). Homatropine prevented the significant choroidal thinning response with hyperopic defocus (+3 +/- 2 mum), and the magnitude of ChT change was significantly different to placebo and hyperopic defocus (p < 0.001). There was a significant increase in ChT after the introduction of myopic defocus (+3.00 D) with placebo (+12 +/- 3 mum, p < 0.0001) and Homatropine combined with myopic defocus also caused a similar increase in ChT (+11 +/- 3 mum; p < 0.001). Eyes treated with Homatropine alone exhibited a significant increase in ChT (+14 +/- 3 mum, p < 0.0001). There was no evidence of differences in choroidal response between refractive groups. Axial length also underwent small but significant changes (all p < 0.01 except Homatropine/hyperopic blur and placebo) that were of similar magnitude, but of opposite direction to the changes in choroidal thickness. CONCLUSIONS: Homatropine appears to block the thinning effect of hyperopic defocus on choroidal thickness but did not enhance the thickening effect of myopic defocus. The changes in the choroid may relate to the different pathways in the eye's response to myopic and hyperopic blur or reflect an upper limit on the capacity of the choroid to thicken in the short-term.
Primary sinonasal mucosal melanoma simulated as cystic lesions: a case report.[Pubmed:29535967]
J Korean Assoc Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2018 Feb;44(1):29-33.
Sinonasal mucosal melanoma (SNMM) in the maxillary sinus is a rare disease condition. Compared to oral mucosal melanoma, SNMM has a bulky, exophytic, and polypoid appearance, is weakly pigmented, and associated with unspecific symptoms. Due to these features, SNMM in the maxillary sinus has been misdiagnosed as nasal polyps and chronic sinusitis. In this case report, we described SNMM occurring in the right maxillary sinus simulated as a cystic or benign lesion. Cortical bone thinning and expansion were observed around the mass. The excised soft mass was encapsulated and weakly pigmented. The mass was clearly excised and covered with a pedicled buccal fat pad graft. Diagnosis using immunohistochemistry with S-100 and Homatropine methylbromide-45 (HMB-45) is critical for proper treatment.
Optimization of the Ocular Treatment Following Organophosphate Nerve Agent Insult.[Pubmed:28903494]
Toxicol Sci. 2017 Sep 1;159(1):50-63.
Eye exposure to organophosphate (OP) irreversible acetylcholinesterase inhibitors, results in long-term miosis and impaired visual function. The aim of this study was to find an anticholinergic antidote, which would counteract miosis and visual impairment induced by the nerve agents sarin and VX with minimal untoward side-effects. Rat pupil width and light reflex were evaluated from 15 min up to 2 weeks following topical OP exposure with or without topical ocular treatment of atropine or Homatropine or with a combined intramuscular treatment of trimedoxime (TMB-4) and atropine (TA). Visual function following insult and treatment was assessed using a cued Morris water maze task. Topical VX exposure showed a dose-dependent miosis with a significant reduction in visual function similar to the effect seen following sarin exposure. Homatropine (2%; w/v) and atropine (0.1%; w/v) treatment ameliorated both sarin and VX-induced miosis and the resulting visual impairment. TA treatment was sufficient in ameliorating the sarin-induced ocular impairment while an additional ocular treatment with either 0.1% atropine or 2% Homatropine was necessary following VX exposure. To conclude the use of 0.1% atropine or 2% Homatropine was beneficial in ameliorating the ocular insult following VX or sarin ocular exposure and thus should be considered as universal treatments against this intoxication. The findings also emphasize the necessity of additional ocular treatment to the systemic treatment in visually impaired casualties following VX exposure.


