LG 101506Selective RXR modulator CAS# 331248-11-4 |
- Leucovorin Calcium
Catalog No.:BCC1198
CAS No.:6035-45-6
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 331248-11-4 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 9845057 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C25H34F2O3 | M.Wt | 420.53 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Synonyms | LG 1506 | ||
| Solubility | Soluble to 100 mM in DMSO and to 50 mM in ethanol | ||
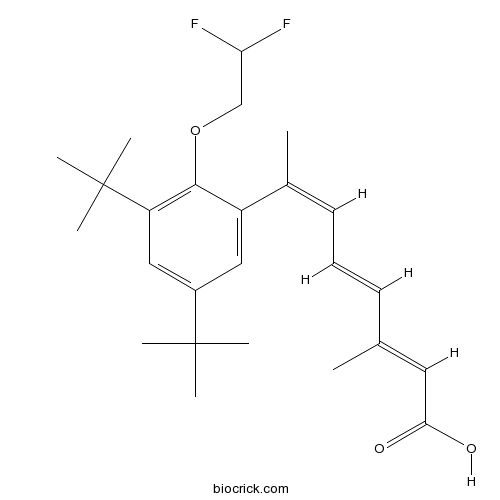
| Chemical Name | (2E,4E,6Z)-7-[3,5-ditert-butyl-2-(2,2-difluoroethoxy)phenyl]-3-methylocta-2,4,6-trienoic acid | ||
| SMILES | CC(=CC(=O)O)C=CC=C(C)C1=CC(=CC(=C1OCC(F)F)C(C)(C)C)C(C)(C)C | ||
| Standard InChIKey | BHIBZAZKKARFIM-XRYBSMBUSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C25H34F2O3/c1-16(12-22(28)29)10-9-11-17(2)19-13-18(24(3,4)5)14-20(25(6,7)8)23(19)30-15-21(26)27/h9-14,21H,15H2,1-8H3,(H,28,29)/b10-9+,16-12+,17-11- | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Selective RXR modulator (Ki values are 3, 9 and 11 for RXRα, RXRβ and RXRγ respectively). Displays poor binding affinity for RAR isoforms (Ki values are 2746, 3516 and >10,000 nM for RARα, RARβ and RARγ respectively). Binding to RXR results in selective activation of RXR:PPARγ, RXR:PPARα and RXR:PPARδ heterodimers. |

LG 101506 Dilution Calculator

LG 101506 Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.378 mL | 11.8898 mL | 23.7795 mL | 47.559 mL | 59.4488 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.4756 mL | 2.378 mL | 4.7559 mL | 9.5118 mL | 11.8898 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.2378 mL | 1.189 mL | 2.378 mL | 4.7559 mL | 5.9449 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0476 mL | 0.2378 mL | 0.4756 mL | 0.9512 mL | 1.189 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0238 mL | 0.1189 mL | 0.2378 mL | 0.4756 mL | 0.5945 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- BAM7
Catalog No.:BCC1397
CAS No.:331244-89-4
- Stephavanine
Catalog No.:BCN5253
CAS No.:33116-33-5
- PT 1
Catalog No.:BCC7846
CAS No.:331002-70-1
- IQ 1
Catalog No.:BCC7965
CAS No.:331001-62-8
- Caffeic acid
Catalog No.:BCN5979
CAS No.:331-39-5
- AS 1269574
Catalog No.:BCC7878
CAS No.:330981-72-1
- Betrixaban
Catalog No.:BCC5118
CAS No.:330942-05-7
- Amitraz
Catalog No.:BCC8816
CAS No.:33089-61-1
- MRT 10
Catalog No.:BCC7950
CAS No.:330829-30-6
- PCI 29732
Catalog No.:BCC4100
CAS No.:330786-25-9
- Avanafil
Catalog No.:BCC2288
CAS No.:330784-47-9
- Paclitaxel
Catalog No.:BCN4650
CAS No.:33069-62-4
- Boc-D-Phg-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3315
CAS No.:33125-05-2
- Etomidate
Catalog No.:BCC1150
CAS No.:33125-97-2
- trans-2,3,4-Trimethoxycinnamic acid
Catalog No.:BCN5035
CAS No.:33130-03-9
- CFM 4
Catalog No.:BCC8017
CAS No.:331458-02-7
- AZ 10417808
Catalog No.:BCC2356
CAS No.:331645-84-2
- DMPO
Catalog No.:BCC7684
CAS No.:3317-61-1
- Bisdemethoxycurcumin
Catalog No.:BCN5975
CAS No.:33171-05-0
- 10-Demethoxy-10-(diethylamino)colchicine
Catalog No.:BCC8164
CAS No.:6962-03-4
- ZM 447439
Catalog No.:BCC2169
CAS No.:331771-20-1
- 2-(N,N-Dimethylamino)acetophenone
Catalog No.:BCN1747
CAS No.:3319-03-7
- 2',4'-Dihydroxy-7-methoxy-8-prenylflavan
Catalog No.:BCN6844
CAS No.:331954-16-6
- I2906
Catalog No.:BCC1637
CAS No.:331963-29-2
Transferable Reactive Force Fields: Extensions of ReaxFF-lg to Nitromethane.[Pubmed:28177629]
J Phys Chem A. 2017 Mar 9;121(9):2001-2013.
Transferable ReaxFF-lg models of nitromethane that predict a variety of material properties over a wide range of thermodynamic states are obtained by screening a library of approximately 6600 potentials that were previously optimized through the Multiple Objective Evolutionary Strategies (MOES) approach using a training set that included information for other energetic materials composed of carbon, hydrogen, nitrogen, and oxygen. Models that best match experimental nitromethane lattice constants at 4.2 K and 1 atm are evaluated for transferability to high-pressure states at room temperature and are shown to better predict various liquid- and solid-phase structural, thermodynamic, and transport properties as compared to the existing ReaxFF and ReaxFF-lg parametrizations. Although demonstrated for an energetic material, the library of ReaxFF-lg models is supplied to the scientific community to enable new research explorations of complex reactive phenomena in a variety of materials research applications.
Loading of halloysite nanotubes with BSA, alpha-Lac and beta-Lg: a Fourier transform infrared spectroscopic and thermogravimetric study.[Pubmed:28029112]
Nanotechnology. 2017 Feb 3;28(5):055706.
Halloysite nanotubes (HNTs) are considered as ideal materials for biotechnological and medical applications. An important feature of halloysite is that it has a different surface chemistry on the inner and outer sides of the tubes. This property means that negatively-charged molecules can be selectively loaded inside the halloysite nanoscale its lumen. Loaded HNTs can be used for the controlled or sustained release of proteins, drugs, bioactive molecules and other agents. We studied the interaction between HNTs and bovine serum albumin, alpha lactalbumin and beta -lactoglobulin loaded into HTNs using Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy and thermogravimetry. These techniques enabled us to study the protein conformation and thermal stability, respectively, and to estimate the amount of protein loaded into the HNTs. TEM images confirmed the loading of proteins into HTNs.
A GLABRA1 ortholog on LG A9 controls trichome number in the Japanese leafy vegetables Mizuna and Mibuna (Brassica rapa L. subsp. nipposinica L. H. Bailey): evidence from QTL analysis.[Pubmed:28258381]
J Plant Res. 2017 May;130(3):539-550.
Brassica rapa show a wide range of morphological variations. In particular, the leaf morphologies of the Japanese traditional leafy vegetables Mizuna and Mibuna (Brassica rapa L. subsp. nipposinica L. H. Bailey) are distinctly different, even though they are closely related cultivars that are easy to cross. In addition to the differences in the gross morphology of leaves, some cultivars of Mibuna (Kyo-nishiki) have many trichomes on its leaves, whereas Mizuna (Kyo-mizore) does not. To identify the genes responsible for the different number of trichomes, we performed a quantitative trait loci (QTL) analysis of Mizuna and Mibuna. To construct linkage maps for these cultivars, we used RNA-seq data to develop cleaved amplified polymorphic sequence (CAPS) markers. We also performed a restriction site-associated DNA sequencing (RAD-seq) analysis to detect single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs). Two QTL analyses were performed in different years, and both analyses indicated that the largest effect was found on LG A9. Expression analyses showed that a gene homologous to GLABRA1 (GL1), a transcription factor implicated in trichome development in Arabidopsis thaliana, and the sequences 3'-flanking (downstream) of BrGL1, differed considerably between Mizuna (Kyo-mizore) and Mibuna (Kyo-nishiki). These results indicate that BrGL1 on LG A9 is one of the candidate genes responsible for the difference in trichome number between Mizuna and Mibuna. Detecting genes that are responsible for morphological variations allows us to better understand the breeding history of Mizuna and Mibuna.
The LG/J murine strain exhibits near-normal tendon biomechanical properties following a full-length central patellar tendon defect.[Pubmed:27552106]
Connect Tissue Res. 2016 Nov;57(6):496-506.
PURPOSE OF THE STUDY: Identifying biological success criteria is needed to improve therapies, and one strategy for identifying them is to analyze the RNA transcriptome for successful and unsuccessful models of tendon healing. We have characterized the MRL/MpJ murine strain and found improved mechanical outcomes following a central patellar tendon (PT) injury. In this study, we evaluate the healing of the LG/J murine strain, which comprises 75% of the MRL/MpJ background, to determine if the LG/J also exhibits improved biomechanical properties following injury and to determine differentially expressed transcription factors across the C57BL/6, MRL/MpJ and the LG/J strains during the early stages of healing. MATERIALS AND METHODS: A full-length, central PT defect was created in 16-20 week old MRL/MpJ, LG/J, and C57BL/6 murine strains. Mechanical properties were assessed at 2, 5, and 8 weeks post surgery. Transcriptomic expression was assessed at 3, 7, and 14 days following injury using a novel clustering software program to evaluate differential expression of transcription factors. RESULTS: Average LG/J structural properties improved to 96.7% and 97.2% of native LG/J PT stiffness and ultimate load by 8 weeks post surgery, respectively. We found the LG/J responded by increasing expression of transcription factors implicated in the inflammatory response and collagen fibril organization. CONCLUSIONS: The LG/J strain returns to normal structural properties by 8 weeks, with steadily increasing properties at each time point. Future work will characterize the cell populations responding to injury and investigate the role of the differentially expressed transcription factors during healing.
Therapeutic potential of retinoid x receptor modulators for the treatment of the metabolic syndrome.[Pubmed:17497022]
PPAR Res. 2007;2007:94156.
The increasing prevalence of obesity is a fundamental contributor to the growing prevalence of the metabolic syndrome. Rexinoids, a class of compounds that selectively bind and activate RXR, are being studied as a potential option for the treatment of metabolic syndrome. These compounds have glucose-lowering, insulin-sensitizing, and antiobesity effects in animal models of insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes. However, undesirable side effects such as hypertriglyceridemia and suppression of the thyroid hormone axis also occur. This review examines and compares the effects of four RXR-selective ligands: LGD1069, LG100268, AGN194204, and LG101506, a selective RXR modulator. Similar to selective modulators of other nuclear receptors such as the estrogen receptor (SERMs), LG101506 binding to RXR selectively maintains the desirable characteristic effects of rexinoids while minimizing the undesirable effects. These recent findings suggest that, with continued research efforts, RXR-specific ligands with improved pharmacological profiles may eventually be available as additional treatment options for the current epidemic of obesity, insulin resistance, type 2 diabetes, and all of the associated metabolic sequelae.
Biological characterization of a heterodimer-selective retinoid X receptor modulator: potential benefits for the treatment of type 2 diabetes.[Pubmed:16269450]
Endocrinology. 2006 Feb;147(2):1044-53.
Specific retinoid X receptor (RXR) agonists, such as LG100268 (LG268), and the thiazolidinedione (TZD) PPARgamma agonists, such as rosiglitazone, produce insulin sensitization in rodent models of insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes. In sharp contrast to the TZDs that produce significant increases in body weight gain, RXR agonists reduce body weight gain and food consumption. Unfortunately, RXR agonists also suppress the thyroid hormone axis and generally produce hypertriglyceridemia. Heterodimer-selective RXR modulators have been identified that, in rodents, retain the metabolic benefits of RXR agonists with reduced side effects. These modulators bind specifically to RXR with high affinity and are RXR homodimer partial agonists. Although RXR agonists activate many heterodimer partners, these modulators selectively activate RXR:PPARalpha and RXR:PPARgamma, but not RXR:RARalpha, RXR:LXRalpha, RXR:LXRbeta, or RXR:FXRalpha. We report the in vivo characterization of one RXR modulator, LG101506 (LG1506). In Zucker fatty (fa/fa) rats, LG1506 is a potent insulin sensitizer that also enhances the insulin-sensitizing activities of rosiglitazone. Administration of LG1506 reduces both body weight gain and food consumption and blocks the TZD-induced weight gain when coadministered with rosiglitazone. LG1506 does not significantly suppress the thyroid hormone axis in rats, nor does it elevate triglycerides in Sprague Dawley rats. However, LG1506 produces a unique pattern of triglycerides elevation in Zucker rats. LG1506 elevates high-density lipoprotein cholesterol in humanized apolipoprotein A-1-transgenic mice. Therefore, selective RXR modulators are a promising approach for developing improved therapies for type 2 diabetes, although additional studies are needed to understand the strain-specific effects on triglycerides.
Novel (2E,4E,6Z)-7-(2-alkoxy-3,5-dialkylbenzene)-3-methylocta-2,4,6-trienoic acid retinoid X receptor modulators are active in models of type 2 diabetes.[Pubmed:12801232]
J Med Chem. 2003 Jun 19;46(13):2683-96.
Previous data have shown that RXR-selective agonists (e.g., 3 and 4) are insulin sensitizers in rodent models of non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus (NIDDM). Unfortunately, they also produce dramatic increases in triglycerides and profound suppression of the thyroid hormone axis. Here we describe the design and synthesis of new RXR modulators that retain the insulin-sensitizing activity of RXR agonists but produce substantially reduced side effects. These molecules bind selectively and with high affinity to RXR and, unlike RXR agonists, do not activate RXR homodimers. To further evaluate the antidiabetic activity of these RXR modulators, we have designed a concise and systematic structure-activity relationship around the 2E,4E,6Z-7-aryl-3-methylocta-2,4,6-trienoic acid scaffold. Selected compounds have been evaluated using insulin-resistant rodents (db/db mice) to characterize effects on glucose homeostasis. Our studies demonstrate the effectiveness of RXR modulators in lowering plasma glucose in the db/db mouse model.


