Mdivi 1Selective DRP1/Dnm1 inhibitor, cell-permeable CAS# 338967-87-6 |
- Necrosulfonamide
Catalog No.:BCC7992
CAS No.:1360614-48-7
- DAPK Substrate Peptide
Catalog No.:BCC2400
CAS No.:386769-53-5
- Cesium chloride
Catalog No.:BCC2399
CAS No.:7647-17-8
- TLQP 21
Catalog No.:BCC2405
CAS No.:869988-94-3
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 338967-87-6 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 3825829 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C15H10Cl2N2O2S | M.Wt | 353.22 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Synonyms | Mitochondrial division inhibitor 1 | ||
| Solubility | DMSO : ≥ 32 mg/mL (90.60 mM) H2O : < 0.1 mg/mL (insoluble) *"≥" means soluble, but saturation unknown. | ||
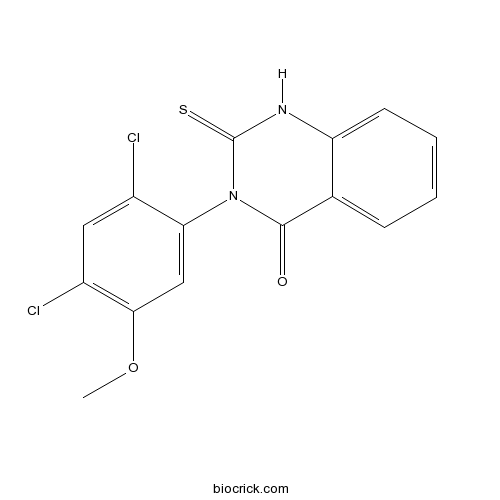
| Chemical Name | 3-(2,4-dichloro-5-methoxyphenyl)-2-sulfanylidene-1H-quinazolin-4-one | ||
| SMILES | COC1=C(C=C(C(=C1)N2C(=O)C3=CC=CC=C3NC2=S)Cl)Cl | ||
| Standard InChIKey | NZJKEVWTYMOYOR-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C15H10Cl2N2O2S/c1-21-13-7-12(9(16)6-10(13)17)19-14(20)8-4-2-3-5-11(8)18-15(19)22/h2-7H,1H3,(H,18,22) | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Selective inhibitor of Dnm1 GTPase (IC50 = 1 - 10 μM); attenuates Dnm1- and Drp1-mediated mitochondrial division. Inhibits mitochondrial outer membrane permeabilization (MOMP) and attenuates apoptosis. |

Mdivi 1 Dilution Calculator

Mdivi 1 Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.8311 mL | 14.1555 mL | 28.311 mL | 56.6219 mL | 70.7774 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.5662 mL | 2.8311 mL | 5.6622 mL | 11.3244 mL | 14.1555 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.2831 mL | 1.4155 mL | 2.8311 mL | 5.6622 mL | 7.0777 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0566 mL | 0.2831 mL | 0.5662 mL | 1.1324 mL | 1.4155 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0283 mL | 0.1416 mL | 0.2831 mL | 0.5662 mL | 0.7078 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
Mdivi-1 is a selective cell-permeable inhibitor of mitochondrial division DRP1 (dynamin-related GTPase) and mitochondrial division Dynamin I (Dnm1). DRP1, a member of the dynamin family of large GTPases, mediates mitochondrial fission.
In vitro: The most efficacious inhibitor, mdivi-1 attenuates mitochondrial division in yeast and mammalian cells by selectively inhibiting the mitochondrial Drp1-mediated division dynamin. Mdivi-1 potently blocks Bid-activated Bax/Bak-dependent cytochrome c release from mitochondria [1].
In vivo: Mdivi-1 treatment blocked apoptotic cell death in ischemic retina, and significantly increased RGC survival at 2 weeks after ischemia. Moreover, Mdivi-1 treatment did not change this increase of Drp1 protein expression but significantly decreased GFAP protein expression [2].
Clinical trial: Currently no clinical data are available.
References:
[1] Cassidy-Stone A, Chipuk JE, Ingerman E, Song C, Yoo C, Kuwana T, Kurth MJ, Shaw JT, Hinshaw JE, Green DR, Nunnari J. Chemical inhibition of the mitochondrial division dynamin reveals its role in Bax/Bak-dependent mitochondrial outer membrane permeabilization. Dev Cell. 2008;14(2):193-204.
[2] Park SW, Kim KY, Lindsey JD, Dai Y, Heo H, Nguyen DH, Ellisman MH, Weinreb RN, Ju WK. A selective inhibitor of drp1, mdivi-1, increases retinal ganglion cell survival in acute ischemic mouse retina. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2011;52(5):2837-43.
- Pabulenol
Catalog No.:BCC8347
CAS No.:33889-70-2
- Silychristin
Catalog No.:BCN2389
CAS No.:33889-69-9
- Demethyl tetrandrine
Catalog No.:BCN2624
CAS No.:33889-68-8
- LY 456236 hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC7347
CAS No.:338736-46-2
- CITCO
Catalog No.:BCC7749
CAS No.:338404-52-7
- Di-O-methylbergenin
Catalog No.:BCN5263
CAS No.:33815-57-5
- Methasterone
Catalog No.:BCC9027
CAS No.:3381-88-2
- H-D-Abu-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3202
CAS No.:338-69-2
- Deodarin
Catalog No.:BCN6874
CAS No.:33788-39-5
- Hederacholchiside E
Catalog No.:BCC8329
CAS No.:33783-82-3
- Androstanolone heptanoate
Catalog No.:BCC8827
CAS No.:33776-88-4
- Abieta-8,11,13-triene-7,15,18-triol
Catalog No.:BCN5262
CAS No.:337527-10-3
- Vandetanib trifluoroacetate
Catalog No.:BCC2029
CAS No.:338992-53-3
- 2,3,4'-Trihydroxy-3',5'-dimethoxypropiophenone
Catalog No.:BCN1455
CAS No.:33900-74-2
- Boc-Ala-OSu
Catalog No.:BCC3048
CAS No.:3392-05-0
- Boc-Gly-OSu
Catalog No.:BCC3397
CAS No.:3392-07-2
- Boc-Ile-Osu
Catalog No.:BCC2604
CAS No.:3392-08-3
- UBP1112
Catalog No.:BCC7033
CAS No.:339526-74-8
- Anamorelin Fumarate
Catalog No.:BCC1363
CAS No.:339539-92-3
- Thalrugosidine
Catalog No.:BCN7785
CAS No.:33954-34-6
- H-D-Phe(4-Cl)-OMe.HCl
Catalog No.:BCC3174
CAS No.:33965-47-8
- Z-Leu-Osu
Catalog No.:BCC2592
CAS No.:3397-35-1
- Triacetonamine hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCN5264
CAS No.:33973-59-0
- Pelargonidin-3-O-rutinosde chloride
Catalog No.:BCN3112
CAS No.:33978-17-5
Mdivi-1 Inhibits Astrocyte Activation and Astroglial Scar Formation and Enhances Axonal Regeneration after Spinal Cord Injury in Rats.[Pubmed:27807407]
Front Cell Neurosci. 2016 Oct 19;10:241.
After spinal cord injury (SCI), astrocytes become hypertrophic, and proliferative, forming a dense network of astroglial processes at the site of the lesion. This constitutes a physical and biochemical barrier to axonal regeneration. Mitochondrial fission regulates cell cycle progression; inhibiting the cell cycle of astrocytes can reduce expression levels of axon growth-inhibitory molecules as well as astroglial scar formation after SCI. We therefore investigated how an inhibitor of mitochondrial fission, Mdivi-1, would affect astrocyte proliferation, astroglial scar formation, and axonal regeneration following SCI in rats. Western blot and immunofluorescent double-labeling showed that Mdivi-1 markedly reduced the expression of the astrocyte marker glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP), and a cell proliferation marker, proliferating cell nuclear antigen, in astrocytes 3 days after SCI. Moreover, Mdivi-1 decreased the expression of GFAP and neurocan, a chondroitin sulfate proteoglycan. Notably, immunofluorescent labeling and Nissl staining showed that Mdivi-1 elevated the production of growth-associated protein-43 and increased neuronal survival at 4 weeks after SCI. Finally, hematoxylin-eosin staining, and behavioral evaluation of motor function indicated that Mdivi-1 also reduced cavity formation and improved motor function 4 weeks after SCI. Our results confirm that Mdivi-1 promotes motor function after SCI, and indicate that inhibiting mitochondrial fission using Mdivi-1 can inhibit astrocyte activation and astroglial scar formation and contribute to axonal regeneration after SCI in rats.
The Putative Drp1 Inhibitor mdivi-1 Is a Reversible Mitochondrial Complex I Inhibitor that Modulates Reactive Oxygen Species.[Pubmed:28350990]
Dev Cell. 2017 Mar 27;40(6):583-594.e6.
Mitochondrial fission mediated by the GTPase dynamin-related protein 1 (Drp1) is an attractive drug target in numerous maladies that range from heart disease to neurodegenerative disorders. The compound mdivi-1 is widely reported to inhibit Drp1-dependent fission, elongate mitochondria, and mitigate brain injury. Here, we show that mdivi-1 reversibly inhibits mitochondrial complex I-dependent O2 consumption and reverse electron transfer-mediated reactive oxygen species (ROS) production at concentrations (e.g., 50 muM) used to target mitochondrial fission. Respiratory inhibition is rescued by bypassing complex I using yeast NADH dehydrogenase Ndi1. Unexpectedly, respiratory impairment by mdivi-1 occurs without mitochondrial elongation, is not mimicked by Drp1 deletion, and is observed in Drp1-deficient fibroblasts. In addition, mdivi-1 poorly inhibits recombinant Drp1 GTPase activity (Ki > 1.2 mM). Overall, these results suggest that mdivi-1 is not a specific Drp1 inhibitor. The ability of mdivi-1 to reversibly inhibit complex I and modify mitochondrial ROS production may contribute to effects observed in disease models.
Mdivi-1 Alleviates Early Brain Injury After Experimental Subarachnoid Hemorrhage in Rats, Possibly via Inhibition of Drp1-Activated Mitochondrial Fission and Oxidative Stress.[Pubmed:28210956]
Neurochem Res. 2017 May;42(5):1449-1458.
Mdivi-1 is a selective inhibitor of mitochondrial fission protein, Drp1, and can penetrate the blood-brain barrier. Previous studies have shown that Mdivi-1 improves neurological outcomes after ischemia, seizures and trauma but it remains unclear whether Mdivi-1 can attenuate early brain injury after subarachnoid hemorrhage (SAH). We thus investigated the therapeutic effect of Mdivi-1 on early brain injury following SAH. Rats were randomly divided into four groups: sham; SAH; SAH + vehicle; and SAH + Mdivi-1. The SAH model was induced by standard intravascular perforation and all of the rats were subsequently sacrificed 24 h after SAH. Mdivi-1 (1.2 mg/kg) was administered to rats 30 min after SAH. We found that Mdivi-1 markedly improved neurologic deficits, alleviated brain edema and BBB permeability, and attenuated apoptotic cell death. Mdivi-1 also significantly reduced the expression of cleaved caspase-3, Drp1 and p-Drp1((Ser616)), attenuated the release of Cytochrome C from mitochondria, inhibited excessive mitochondrial fission, and restored the ultra-structure of mitochondria. Furthermore, Mdivi-1 reduced levels of MDA, 3-NT, and 8-OHdG, and improved SOD activity. Taken together, our data suggest that Mdivi-1 exerts neuroprotective effects against cell death induced by SAH and the underlying mechanism may be inhibition of Drp1-activated mitochondrial fission and oxidative stress.
Deciphering the late biosynthetic steps of antimalarial compound FR-900098.[Pubmed:20142041]
Chem Biol. 2010 Jan 29;17(1):57-64.
FR-900098 is a potent chemotherapeutic agent for the treatment of malaria. Here we report the heterologous production of this compound in Escherichia coli by reconstructing the entire biosynthetic pathway using a three-plasmid system. Based on this system, whole-cell feeding assays in combination with in vitro enzymatic activity assays reveal an unusual functional role of nucleotide conjugation and lead to the complete elucidation of the previously unassigned late biosynthetic steps. These studies also suggest a biosynthetic route to a second phosphonate antibiotic, FR-33289. A thorough understanding of the FR-900098 biosynthetic pathway now opens possibilities for metabolic engineering in E. coli to increase production of the antimalarial antibiotic and combinatorial biosynthesis to generate novel derivatives of FR-900098.
A chemical inhibitor of DRP1 uncouples mitochondrial fission and apoptosis.[Pubmed:18313377]
Mol Cell. 2008 Feb 29;29(4):409-10.
DRP1, a member of the dynamin family of large GTPases, mediates mitochondrial fission. In a recent issue of Developmental Cell, Cassidy-Stone et al. (2008) identified mdivi-1, a new DRP1 inhibitor that prevents mitochondria division and Bax-mediated mitochondrial outer membrane permeabilization during apoptosis.


