NiranthinCAS# 50656-77-4 |
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 50656-77-4 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 13989915 | Appearance | White powder |
| Formula | C24H32O7 | M.Wt | 432.5 |
| Type of Compound | Lignans | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | Soluble in chloroform; slightly soluble in water | ||
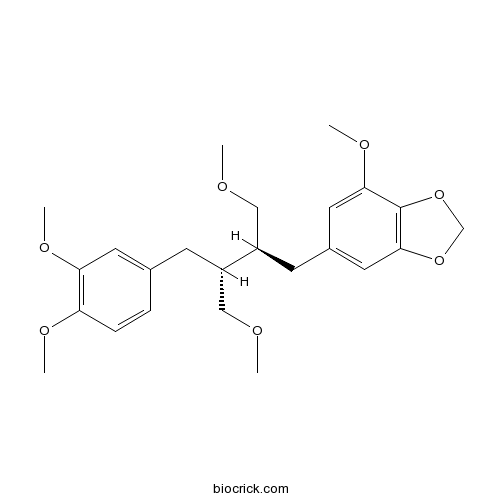
| Chemical Name | 6-[(2R,3R)-3-[(3,4-dimethoxyphenyl)methyl]-4-methoxy-2-(methoxymethyl)butyl]-4-methoxy-1,3-benzodioxole | ||
| SMILES | COCC(CC1=CC(=C(C=C1)OC)OC)C(CC2=CC3=C(C(=C2)OC)OCO3)COC | ||
| Standard InChIKey | RCFGIEPQSDGMJJ-OALUTQOASA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C24H32O7/c1-25-13-18(8-16-6-7-20(27-3)21(10-16)28-4)19(14-26-2)9-17-11-22(29-5)24-23(12-17)30-15-31-24/h6-7,10-12,18-19H,8-9,13-15H2,1-5H3/t18-,19-/m0/s1 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | 1. Niranthin exhibits anti-hepatitis B virus activity both in vitro and in vivo. 2. Niranthin exhibits antiinflammatory and antiallodynic actions which are probably mediated through its direct antagonistic action on the PAF receptor binding sites. 3. Niranthin is a potent anti-leishmanial agent, inhibits the relaxation activity of heterodimeric type IB topoisomerase of L. donovani and acts as a non-competitive inhibitor interacting with both subunits of the enzyme. |
| Targets | HBV | Topoisomerase | PAFR | Antifection |

Niranthin Dilution Calculator

Niranthin Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.3121 mL | 11.5607 mL | 23.1214 mL | 46.2428 mL | 57.8035 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.4624 mL | 2.3121 mL | 4.6243 mL | 9.2486 mL | 11.5607 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.2312 mL | 1.1561 mL | 2.3121 mL | 4.6243 mL | 5.7803 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0462 mL | 0.2312 mL | 0.4624 mL | 0.9249 mL | 1.1561 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0231 mL | 0.1156 mL | 0.2312 mL | 0.4624 mL | 0.578 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- Octacosanoic Acid
Catalog No.:BCN5395
CAS No.:506-48-9
- Nervonic acid
Catalog No.:BCN8374
CAS No.:506-37-6
- Arachidonic acid
Catalog No.:BCN2215
CAS No.:506-32-1
- Isojacareubin
Catalog No.:BCN6883
CAS No.:50597-93-8
- Columbianadin
Catalog No.:BCN1275
CAS No.:5058-13-9
- Fenspiride HCl
Catalog No.:BCC4659
CAS No.:5053-08-7
- 3-(Carboxymethylamino)propanoic acid
Catalog No.:BCN1791
CAS No.:505-72-6
- Homopiperazine
Catalog No.:BCC8995
CAS No.:505-66-8
- Araneosol
Catalog No.:BCN5613
CAS No.:50461-86-4
- GW441756
Catalog No.:BCC5093
CAS No.:504433-23-2
- Methyl 2alpha-hydroxyhardwickiate
Catalog No.:BCN7595
CAS No.:50428-93-8
- 1,5,6-Trihydroxyxanthone
Catalog No.:BCN7642
CAS No.:5042-03-5
- Alkaloid KD1
Catalog No.:BCN1898
CAS No.:50656-87-6
- Alkaloid C
Catalog No.:BCN1897
CAS No.:50656-88-7
- Vandrikidine
Catalog No.:BCN5615
CAS No.:50656-92-3
- Chasmanine
Catalog No.:BCN5409
CAS No.:5066-78-4
- Terfenadine
Catalog No.:BCC3866
CAS No.:50679-08-8
- Boc-Cys(Bzl)-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3376
CAS No.:5068-28-0
- Borneol
Catalog No.:BCN4964
CAS No.:507-70-0
- Pennogenin
Catalog No.:BCN2839
CAS No.:507-89-1
- Vecuronium Bromide
Catalog No.:BCC2498
CAS No.:50700-72-6
- 3-Cyano-6-isopropylchromone
Catalog No.:BCC8627
CAS No.:50743-32-3
- TPCA-1
Catalog No.:BCC2473
CAS No.:507475-17-4
- Polyphyllin D
Catalog No.:BCN2401
CAS No.:50773-41-6
Antiinflammatory and antiallodynic actions of the lignan niranthin isolated from Phyllanthus amarus. Evidence for interaction with platelet activating factor receptor.[Pubmed:16925995]
Eur J Pharmacol. 2006 Sep 28;546(1-3):182-8.
Previous studies have shown that the extracts obtained from Phyllanthus amarus, and some of the lignans isolated from it, exhibit pronounced antiinflammatory properties. In the present study, we have assessed whether the antiinflammatory actions of these lignans can be mediated by interaction with platelet activating factor (PAF) receptor or interference with the action of this lipid. The local administration of nirtetralin, phyltetralin or Niranthin (30 nmol/paw), similar to WEB2170 (a PAF receptor antagonist, 30 nmol/paw), significantly inhibited PAF-induced paw oedema formation in mice. The extracts of P. amarus (100 microg/ml) and Niranthin (30 microM), but not nirtetralin or phyltetralin (30 microM), decreased the specific binding of [(3)H]-PAF in mouse cerebral cortex membranes. Furthermore, both Niranthin and WEB2170 displaced, in a concentration-dependent manner, the [(3)H]-PAF binding sites. The mean IC(50) values from these effects were 6.5 microM and 0.3 microM, respectively. Additionally, both Niranthin and WEB2170 (30 nmol/paw) inhibited the increase of myeloperoxidase activity induced by PAF injection in the mouse paw. When assessed the mouse model of pleurisy induced by PAF, pretreatment with Niranthin (100 micromol/kg, p.o.) or WEB2170 (1.7 micromol/kg, i.p.) significantly inhibited PAF-induced protein extravasations. Moreover, in the rat model of PAF-induced allodynia, both Niranthin (30 nmol/paw) and WEB2170 (30 nmol/paw) treatment significantly inhibited PAF-induced allodynia. In addition, Niranthin had a rapid onset and long-lasting antiallodynic action when compared with WEB2170. Collectively, the present findings suggest that Niranthin exhibits antiinflammatory and antiallodynic actions which are probably mediated through its direct antagonistic action on the PAF receptor binding sites.
The lignan niranthin poisons Leishmania donovani topoisomerase IB and favours a Th1 immune response in mice.[Pubmed:23027614]
EMBO Mol Med. 2012 Oct;4(10):1126-43.
Niranthin, a lignan isolated from the aerial parts of the plant Phyllanthus amarus, exhibits a wide spectrum of pharmacological activities. In the present study, we have shown for the first time that Niranthin is a potent anti-leishmanial agent. The compound induces topoisomerase I-mediated DNA-protein adduct formation inside Leishmania cells and triggers apoptosis by activation of cellular nucleases. We also show that Niranthin inhibits the relaxation activity of heterodimeric type IB topoisomerase of L. donovani and acts as a non-competitive inhibitor interacting with both subunits of the enzyme. Niranthin interacts with DNA-protein binary complexes and thus stabilizes the 'cleavable complex' formation and subsequently inhibits the religation of cleaved strand. The compound inhibits the proliferation of Leishmania amastigotes in infected cultured murine macrophages with limited cytotoxicity to the host cells and is effective against antimony-resistant Leishmania parasites by modulating upregulated P-glycoprotein on host macrophages. Importantly, besides its in vitro efficacy, Niranthin treatment leads to a switch from a Th2- to a Th1-type immune response in infected BALB/c mice. The immune response causes production of nitric oxide, which results in almost complete clearance of the liver and splenic parasite burden after intraperitoneal or intramuscular administration of the drug. These findings can be exploited to develop Niranthin as a new drug candidate against drug-resistant leishmaniasis.
In vitro and in vivo anti-hepatitis B virus activities of the lignan niranthin isolated from Phyllanthus niruri L.[Pubmed:25009077]
J Ethnopharmacol. 2014 Sep 11;155(2):1061-7.
ETHNOPHARMACOLOGICAL RELEVANCE: Niranthin is a lignan isolated from Phyllanthus niruri L. This plant has long been used in folk medicine for liver protection and antihepatitis B in many Asian countries. This study was designed to evaluate the anti-hepatitis B virus activity of Niranthin using HepG2.2.15 cells and duck hepatitis B virus (DHBV) infected ducks as in vitro and in vivo models. MATERIALS AND METHODS: Niranthin was isolated from Phyllanthus niruri L. (Euphorbiaceae) by extraction and chromatographic procedures and the anti-hepatitis B virus activity was evaluated both in vitro and in vivo. The human HBV-transfected liver cell line HepG2.2.15 was used in vitro assay. And the in vivo anti-hepatitis B virus activity was evaluated on the expression of HBV replication, HBsAg, HBeAg, ALT and AST on day 0, 7, 14, 17 after Niranthin was dosed intragastricly (i.g.) once a day for 14 days at the dosages of 25, 50 and 100 mg/kg/day in the duck hepatitis B virus (DHBV) infected ducks. RESULTS: In the human HBV-transfected liver cell line HepG2.2.15, the secretion of HBsAg and HBeAg were significantly decreased after treatment with Niranthin for 144 h, with IC50 values for HBsAg of 15.6 microM, IC50 values for HBeAg of 25.1 microM. In DHBV-infected ducklings, Niranthin significantly reduced the serum DHBV DNA, HBsAg, HBeAg, ALT and AST. Furthermore, analysis of the liver pathological changes confirmed the hepatoprotective effect of Niranthin. CONCLUSION: The experimental data demonstrated that Niranthin exhibits anti-hepatitis B virus activity both in vitro and in vivo.


