ColumbianadinCAS# 5058-13-9 |
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 5058-13-9 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 6436246 | Appearance | White cryst. |
| Formula | C19H20O5 | M.Wt | 328.36 |
| Type of Compound | Coumarins | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | DMSO : 33.33 mg/mL (101.50 mM; Need ultrasonic) H2O : < 0.1 mg/mL (insoluble) | ||
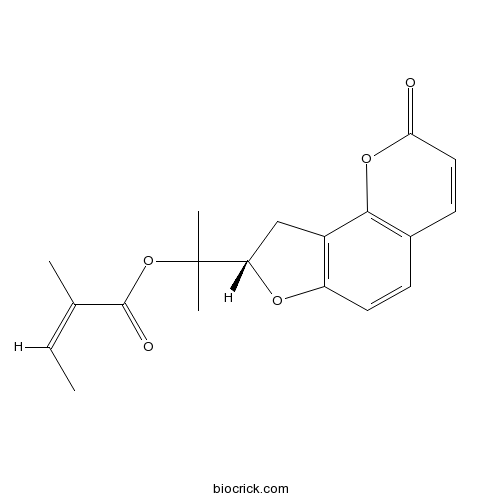
| Chemical Name | 2-[(8S)-2-oxo-8,9-dihydrofuro[2,3-h]chromen-8-yl]propan-2-yl (Z)-2-methylbut-2-enoate | ||
| SMILES | CC=C(C)C(=O)OC(C)(C)C1CC2=C(O1)C=CC3=C2OC(=O)C=C3 | ||
| Standard InChIKey | JRIBPWOXWIRQOQ-GHAIFCDISA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C19H20O5/c1-5-11(2)18(21)24-19(3,4)15-10-13-14(22-15)8-6-12-7-9-16(20)23-17(12)13/h5-9,15H,10H2,1-4H3/b11-5-/t15-/m0/s1 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Columbianadin has analgesic, anti-inflammatory, calcium-channel blocking, and platelet aggregation inhibiting functions. It can effectively suppress the growth of colon cancer cells, the induction of apoptosis was correlated with the modulation of caspase-9, caspase-3, Bax, Bcl-2, RIP-3, and caspase-8, Bim and Bid. |
| Targets | Caspase | Bcl-2/Bax | ROS | IL Receptor | NO | Calcium Channel | RIP-3 | SOD | GPx-1 |
| In vitro | Biotransformation of columbianadin by rat hepatic microsomes and inhibition of biotransformation products on NO production in RAW 264.7 cells in vitro.[Pubmed: 22784551]Phytochemistry. 2012 Sep;81:109-16.Columbianadin (CBN, 1), 1-[(8S)-8,9-dihydro-2-oxo-2H-furo[2,3-h]-1-benzopyran-8-yl]-1-methylethyl-[(2Z)-2-methyl-2-butenoic acid]ester is a coumarin-type compound and one of the main bioactive constituents of the underground part of Angelica pubescens Maxim. f. biserrata Shan et Yuan.
Although numerous investigations have been undertaken to study the biological activities of Columbianadin, such as analgesic, anti-inflammatory, calcium-channel blocking, and platelet aggregation inhibiting functions, little attention has been paid to its metabolism and/or biotransformation.
|
| In vivo | Inhibition of airway inflammation by the roots of Angelica decursiva and its constituent, columbianadin.[Pubmed: 25068578]J Ethnopharmacol. 2014 Sep 11;155(2):1353-61.The roots of Angelica decursiva Fr. Et Sav (Umbelliferae) have been frequently used in traditional medicine as anti-inflammatory, antitussive, analgesic agents and expectorant, especially for treating cough, asthma, bronchitis and upper respiratory tract infections. To establish the scientific rationale for the clinical use of Angelica decursiva and to identify new agents for treating inflammatory lung disorders, pharmacological evaluation of the roots of Angelica decursiva and the isolated constituents was performed.
|
| Kinase Assay | The furanocoumarin columbianadin inhibits depolarization induced Ca2+ uptake in rat pituitary GH3 cells.[Pubmed: 2162545 ]Planta Med. 1990 Feb;56(1):127-9.The furanocoumarin Columbianadin inhibits depolarization induced Ca2+ uptake in rat pituitary GH3 cells. |
| Cell Research | Columbianadin Inhibits Cell Proliferation by Inducing Apoptosis and Necroptosis in HCT116 Colon Cancer Cells.[Pubmed: 27098859 ]Biomol Ther (Seoul). 2016 May 1;24(3):320-7.Columbianadin (CBN), a natural coumarin from Angelica decursiva (Umbelliferae), is known to have various biological activities including anti-inflammatory and anti-cancer effects.
|
| Animal Research | Protective effects of the roots of Angelica decursiva and its active compound, columbianadin in lung inflammation[Reference: WebLink]Planta Med., 2014,.80 - P2O53.
|

Columbianadin Dilution Calculator

Columbianadin Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 3.0454 mL | 15.2272 mL | 30.4544 mL | 60.9088 mL | 76.1359 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.6091 mL | 3.0454 mL | 6.0909 mL | 12.1818 mL | 15.2272 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.3045 mL | 1.5227 mL | 3.0454 mL | 6.0909 mL | 7.6136 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0609 mL | 0.3045 mL | 0.6091 mL | 1.2182 mL | 1.5227 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0305 mL | 0.1523 mL | 0.3045 mL | 0.6091 mL | 0.7614 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
Columbianadin, a natural coumarin from, is known to have various biological activities including anti-inflammatory and anti-cancer effects.
In Vitro:Columbianadin (CBN) effectively suppresses the growth of colon cancer cells. Low concentration (up to 25 μM) of Columbianadin induces apoptosis, and high concentration (50 μM) of Columbianadin induces necroptosis. The induction of apoptosis by Columbianadin is correlated with the modulation of caspase-9, caspase-3, Bax, Bcl-2, Bim and Bid, and the induction of necroptosis is related with RIP-3, and caspase-8. In addition, Columbianadin induces the accumulation of ROS and imbalance in the intracellular antioxidant enzymes such as SOD-1, SOD-2, catalase and GPx-1. Columbianadin shows the most effective growth inhibitory activity against human colorectal cancer cells. Accordingly, further study is performed using HCT116 cells to give the detailed growth-inhibitory mechanism of action mediated by Columbianadin. The cells treated with various concentrations of Columbianadin (0-100 μM) exhibit a dose- and time-dependent growth inhibition with an IC50 value of 47.2 and 32.4 μM after 48 and 72 h incubation, respectively. Treatment of various concentrations (12.5, 25, and 50 μM) of Columbianadin for 48 h in HCT116 cells decreases the number of cells and increases the floating cells. Apparent morphological changes with round-shape and dying cells are also observed at 25 and 50 μM Columbianadin -treated cells[1].
In Vivo:The analysis method is successfully applied to a tissue distribution study of Columbianadin (CBN) and Columbianetin (CBT) after intravenous administration of Columbianadin to rats. The results of this study indicated that Columbianadin can be detected in all of the selected tissues after i.v. administration. Columbianadin is distributed to rat tissues rapidly and can be metabolized to CBT in most detected tissues. Of the detected tissues, heart had the highest uptake of Columbianadin, which suggests that heart might be one of the main target tissues of Columbianadin [2].
References:
[1]. Kang JI, et al. Columbianadin Inhibits Cell Proliferation by Inducing Apoptosis and Necroptosis in HCT116 Colon Cancer Cells. Biomol Ther (Seoul). 2016 May 1;24(3):320-7.
[2]. Zhang YB, et al. Tissue distribution study of columbianadin and its active metabolite columbianetin in rats. Biomed Chromatogr. 2016 Feb;30(2):256-62.
- Fenspiride HCl
Catalog No.:BCC4659
CAS No.:5053-08-7
- 3-(Carboxymethylamino)propanoic acid
Catalog No.:BCN1791
CAS No.:505-72-6
- Homopiperazine
Catalog No.:BCC8995
CAS No.:505-66-8
- Araneosol
Catalog No.:BCN5613
CAS No.:50461-86-4
- GW441756
Catalog No.:BCC5093
CAS No.:504433-23-2
- Methyl 2alpha-hydroxyhardwickiate
Catalog No.:BCN7595
CAS No.:50428-93-8
- 1,5,6-Trihydroxyxanthone
Catalog No.:BCN7642
CAS No.:5042-03-5
- Isorhamnetin-3-O-beta-D-Glucoside
Catalog No.:BCN1247
CAS No.:5041-82-7
- Isoliquiritin
Catalog No.:BCN5945
CAS No.:5041-81-6
- Juglanin
Catalog No.:BCN6505
CAS No.:5041-67-8
- 3-Nitropropionic acid
Catalog No.:BCC6303
CAS No.:504-88-1
- DL-Homocysteic acid
Catalog No.:BCN2233
CAS No.:504-33-6
- Isojacareubin
Catalog No.:BCN6883
CAS No.:50597-93-8
- Arachidonic acid
Catalog No.:BCN2215
CAS No.:506-32-1
- Nervonic acid
Catalog No.:BCN8374
CAS No.:506-37-6
- Octacosanoic Acid
Catalog No.:BCN5395
CAS No.:506-48-9
- Niranthin
Catalog No.:BCN5614
CAS No.:50656-77-4
- Alkaloid KD1
Catalog No.:BCN1898
CAS No.:50656-87-6
- Alkaloid C
Catalog No.:BCN1897
CAS No.:50656-88-7
- Vandrikidine
Catalog No.:BCN5615
CAS No.:50656-92-3
- Chasmanine
Catalog No.:BCN5409
CAS No.:5066-78-4
- Terfenadine
Catalog No.:BCC3866
CAS No.:50679-08-8
- Boc-Cys(Bzl)-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3376
CAS No.:5068-28-0
- Borneol
Catalog No.:BCN4964
CAS No.:507-70-0
Inhibition of airway inflammation by the roots of Angelica decursiva and its constituent, columbianadin.[Pubmed:25068578]
J Ethnopharmacol. 2014 Sep 11;155(2):1353-61.
ETHNOPHARMACOLOGICAL RELEVANCE: The roots of Angelica decursiva Fr. Et Sav (Umbelliferae) have been frequently used in traditional medicine as anti-inflammatory, antitussive, analgesic agents and expectorant, especially for treating cough, asthma, bronchitis and upper respiratory tract infections. To establish the scientific rationale for the clinical use of Angelica decursiva and to identify new agents for treating inflammatory lung disorders, pharmacological evaluation of the roots of Angelica decursiva and the isolated constituents was performed. METHODS: In vitro study was carried out using two lung cells, lung epithelial cells (A549) and alveolar macrophages (MH-S). The inflammatory markers such as IL-6 and nitric oxide (NO) for each cell line were examined. For in vivo study, a mouse model of lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced acute lung injury was used and the effects on lung inflammation were established by measuring the cell numbers in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid (BALF) and by histological observation. RESULTS: Water and 70% ethanol extracts of the roots of Angelica decursiva showed considerable inhibitory activity against LPS-induced lung inflammation in mice following oral administration at a dose of 400 mg/kg. Five coumarin derivatives including Columbianadin, umbelliferone, umbelliferone 6-carboxylic acid, nodakenin and nodakenetin were isolated. Among the isolated compounds, Columbianadin was found to possess strong inhibitory activity against the inflammatory response of IL-1beta-treated A549 cells and LPS-treated MH-S cells. Columbianadin was found to inhibit NO production by down-regulation of inducible NO synthase. Moreover, Columbianadin was also proved to possess significant inhibitory activity against LPS-induced lung inflammation following oral administration at a dose of 20-60 mg/kg. CONCLUSIONS: The roots of Angelica decursiva were proved to be effective in the treatment of lung inflammation. Columbianadin can be a potential new agent for treating inflammatory lung disorders.
Columbianadin Inhibits Cell Proliferation by Inducing Apoptosis and Necroptosis in HCT116 Colon Cancer Cells.[Pubmed:27098859]
Biomol Ther (Seoul). 2016 May 1;24(3):320-7.
Columbianadin (CBN), a natural coumarin from Angelica decursiva (Umbelliferae), is known to have various biological activities including anti-inflammatory and anti-cancer effects. In this study, the anti-proliferative mechanism of actions mediated by CBN was investigated in HCT-116 human colon cancer cells. CBN effectively suppressed the growth of colon cancer cells. Low concentration (up to 25 microM) of CBN induced apoptosis, and high concentration (50 microM) of CBN induced necroptosis. The induction of apoptosis by CBN was correlated with the modulation of caspase-9, caspase-3, Bax, Bcl-2, Bim and Bid, and the induction of necroptosis was related with RIP-3, and caspase-8. In addition, CBN induced the accumulation of ROS and imbalance in the intracellular antioxidant enzymes such as SOD-1, SOD-2, catalase and GPx-1. These findings demonstrate that CBN has the potential to be a candidate in the development of anti-cancer agent derived from natural products.
Biotransformation of columbianadin by rat hepatic microsomes and inhibition of biotransformation products on NO production in RAW 264.7 cells in vitro.[Pubmed:22784551]
Phytochemistry. 2012 Sep;81:109-16.
Columbianadin (CBN, 1), 1-[(8S)-8,9-dihydro-2-oxo-2H-furo[2,3-h]-1-benzopyran-8-yl]-1-methylethyl-[(2Z)-2 -methyl-2-butenoic acid]ester is a coumarin-type compound and one of the main bioactive constituents of the underground part of Angelica pubescens Maxim. f. biserrata Shan et Yuan. Although numerous investigations have been undertaken to study the biological activities of CBN, such as analgesic, anti-inflammatory, calcium-channel blocking, and platelet aggregation inhibiting functions, little attention has been paid to its metabolism and/or biotransformation. Biotransformation of CBN by rat liver microsomes in vitro was studied, and thirteen biotransformation products including eight hitherto unknown compounds [columbianadiratimetins A-H (3-10)] and five known compounds [Columbianadin oxide (2), (+)-2,3-dihydro-4-hydroxy-2-(1-hydroxy-1-methylethyl)-5-benzofurancarboxaldehyde (11), oroselol (12), columbianetin (13), and vaginol (14)] were produced by liver microsomes from rats pre-treated with sodium phenobarbital. The structures of these compounds were elucidated on the basis of extensive spectroscopic analyses which included IR, UV, EIMS, HRESIMS, 1D NMR and 2D NMR, respectively. The inhibition of CBN and its main biotransformation products on nitric oxide production induced by lipopolysaccharide was assayed in RAW 264.7 cells at concentrations ranging from 10 to 200 muM to evaluate the biological significance of biotransformation.


