PenthiopyradCarboxamide fungicide CAS# 183675-82-3 |
- Pentamidine
Catalog No.:BCC3836
CAS No.:100-33-4
- Pentamidine dihydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC5194
CAS No.:50357-45-4
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 183675-82-3 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 11388558 | Appearance | Powder |
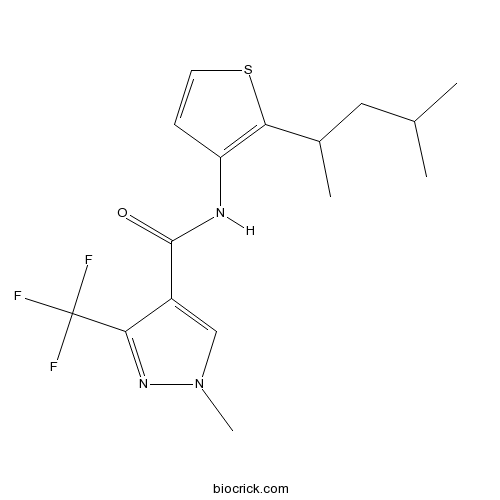
| Formula | C16H20F3N3OS | M.Wt | 359.41 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Synonyms | MTF-753 | ||
| Solubility | DMSO : ≥ 26 mg/mL (72.34 mM) *"≥" means soluble, but saturation unknown. | ||
| Chemical Name | 1-methyl-N-[2-(4-methylpentan-2-yl)thiophen-3-yl]-3-(trifluoromethyl)pyrazole-4-carboxamide | ||
| SMILES | CC(C)CC(C)C1=C(C=CS1)NC(=O)C2=CN(N=C2C(F)(F)F)C | ||
| Standard InChIKey | PFFIDZXUXFLSSR-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C16H20F3N3OS/c1-9(2)7-10(3)13-12(5-6-24-13)20-15(23)11-8-22(4)21-14(11)16(17,18)19/h5-6,8-10H,7H2,1-4H3,(H,20,23) | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Penthiopyrad(MTF-753) is a carboxamide fungicide used to control a broad spectrum of diseases on large variety of corps; inhibits fungal respiration by binding to mitochondrial respiratory complex II. |

Penthiopyrad Dilution Calculator

Penthiopyrad Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.7823 mL | 13.9117 mL | 27.8234 mL | 55.6468 mL | 69.5584 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.5565 mL | 2.7823 mL | 5.5647 mL | 11.1294 mL | 13.9117 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.2782 mL | 1.3912 mL | 2.7823 mL | 5.5647 mL | 6.9558 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0556 mL | 0.2782 mL | 0.5565 mL | 1.1129 mL | 1.3912 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0278 mL | 0.1391 mL | 0.2782 mL | 0.5565 mL | 0.6956 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
Penthiopyrad(MTF-753) is a carboxamide fungicide used to control a broad spectrum of diseases on large variety of corps; inhibits fungal respiration by binding to mitochondrial respiratory complex II.
- CYN 154806
Catalog No.:BCC5823
CAS No.:183658-72-2
- Cleroindicin A
Catalog No.:BCC8916
CAS No.:176598-06-4
- Apicidin
Catalog No.:BCC3599
CAS No.:183506-66-3
- CPPG
Catalog No.:BCC6872
CAS No.:183364-82-1
- Erlotinib
Catalog No.:BCC1557
CAS No.:183321-74-6
- OSI-420
Catalog No.:BCC4472
CAS No.:183320-51-6
- Erlotinib Hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC3645
CAS No.:183319-69-9
- 5-(1-Piperazinyl)benzofuran-2-carboxamide
Catalog No.:BCC8717
CAS No.:183288-46-2
- 2-Acetoxy-3-deacetoxycaesaldekarin E
Catalog No.:BCN7476
CAS No.:18326-06-2
- AM251
Catalog No.:BCC4412
CAS No.:183232-66-8
- 1,7-Dihydroxy-2,3-methylenedioxyxanthone
Catalog No.:BCN7543
CAS No.:183210-63-1
- Tipiracil hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC2001
CAS No.:183204-72-0
- 1,2,3,4,5,6-Hexabromocyclohexane
Catalog No.:BCC2437
CAS No.:1837-91-8
- MRS 1220
Catalog No.:BCC6972
CAS No.:183721-15-5
- Amyloid β-Protein (1-15)
Catalog No.:BCC1003
CAS No.:183745-81-5
- Cyanidin 3-sophoroside chloride
Catalog No.:BCN2611
CAS No.:18376-31-3
- Mithramycin A
Catalog No.:BCC2470
CAS No.:18378-89-7
- Ciproxifan
Catalog No.:BCC4539
CAS No.:184025-18-1
- Ciproxifan maleate
Catalog No.:BCC4049
CAS No.:184025-19-2
- sitaxsentan
Catalog No.:BCC1951
CAS No.:184036-34-8
- Dimeric coniferyl acetate
Catalog No.:BCN1148
CAS No.:184046-40-0
- Calystegine B4
Catalog No.:BCN1881
CAS No.:184046-85-3
- Isoleojaponin
Catalog No.:BCN7442
CAS No.:1840966-49-5
- Hautriwaic acid
Catalog No.:BCN4686
CAS No.:18411-75-1
Haptens, bioconjugates, and antibodies for penthiopyrad immunosensing.[Pubmed:25197742]
Analyst. 2014 Nov 7;139(21):5358-61.
Haptens, bioconjugates, and antibodies for highly sensitive immunochemical analysis of the new-generation fungicide Penthiopyrad are described. Two haptens with equivalent carboxylated linkers were prepared, and the purified active esters were efficiently coupled to proteins. The results revealed slightly different antibody-eliciting capacities for the two synthetic derivatives. All of the produced antibodies were specific for Penthiopyrad, and showed affinity values in the nanomolar range.
Molecular characterization of boscalid- and penthiopyrad-resistant isolates of Didymella bryoniae and assessment of their sensitivity to fluopyram.[Pubmed:22076736]
Pest Manag Sci. 2012 Apr;68(4):645-51.
BACKGROUND: Didymella bryoniae has a history of developing resistance to single-site fungicides. A recent example is with the succinate-dehydrogenase-inhibiting fungicide (SDHI) boscalid. In laboratory assays, out of 103 isolates of this fungus, 82 and seven were found to be very highly resistant (B(VHR) ) and highly resistant (B(HR) ) to boscalid respectively. Cross-resistance studies with the new SDHI Penthiopyrad showed that the B(VHR) isolates were only highly resistant to Penthiopyrad (B(VHR) -P(HR) ), while the B(HR) isolates appeared sensitive to Penthiopyrad (B(HR) -P(S) ). In this study, the molecular mechanism of resistance in these two phenotypes (B(VHR) -P(HR) and B(HR) -P(S) ) was elucidated, and their sensitivity to the new SDHI fluopyram was assessed. RESULTS: A 456 bp cDNA amplified fragment of the succinate dehydrogenase iron sulfur gene (DbSDHB) was initially cloned and sequenced from two sensitive (B(S) -P(S) ), two B(VHR) -P(HR) and one B(HR) -P(S) isolate of D. bryoniae. Comparative analysis of the DbSDHB protein revealed that a highly conserved histidine residue involved in the binding of SDHIs and present in wild-type isolates was replaced by tyrosine (H277Y) or arginine (H277R) in the B(VHR) -P(HR) and B(HR) -P(S) variants respectively. Further examination of the role and extent of these alterations showed that the H/Y and H/R substitutions were present in the remaining B(VHR) -P(HR) and B(HR) -P(S) variants respectively. Analysis of the sensitivity to fluopyram of representative isolates showed that both SDHB mutants were sensitive to this fungicide as the wild-type isolates. CONCLUSION: The genotype-specific cross-resistance relationships between the SDHIs boscalid and Penthiopyrad and the lack of cross-resistance between these fungicides and fluopyram should be taken into account when selecting SDHIs for gummy stem blight management.
Evaluation of dodine, fluopyram and penthiopyrad for the management of leaf spot and powdery mildew of tart cherry, and fungicide sensitivity screening of Michigan populations of Blumeriella jaapii.[Pubmed:23175430]
Pest Manag Sci. 2013 Jun;69(6):747-54.
BACKGROUND: Field trials were conducted on the tart cherry cultivar Montmorency to evaluate the efficacy of dodine and the succinate dehydrogenase inhibitor (SDHI) fungicides fluopyram and Penthiopyrad for control of cherry leaf spot (CLS) and powdery mildew (PM). The in vitro sensitivity of Blumeriella jaapii (CLS) to the same fungicides was also tested. RESULTS: Treatments with dodine or fluopyram were among the most effective for controlling CLS, while fluopyram or Penthiopyrad treatments were among the most effective for controlling PM. In vitro studies detected a wide range of minimum inhibitory concentrations (MICs) among the isolates (0.05-400 microg AI mL(-1) ) in response to dodine. Orchard isolates showed reduced sensitivity to dodine as compared with baseline isolates. B. jaapii was more sensitive to fluopyram (0.01-10.0 microg AI mL(-1) ) than to Penthiopyrad (0.01-25 microg AI mL(-1) ), and orchard isolates also showed a shift towards reduced sensitivity. CONCLUSION: The results indicate that dodine remains effective in CLS control. In addition, as Penthiopyrad and fluopyram become available to growers, this research establishes baseline information that will be important for future monitoring and analysis of B. jaapii population responses to exposure to dodine and these SDHI fungicides.
Effect of the new pyrazole carboxamide fungicide penthiopyrad on late leaf spot and stem rot of peanut.[Pubmed:18785218]
Pest Manag Sci. 2009 Jan;65(1):66-73.
BACKGROUND: Management of early leaf spot (Cercospora arachidicola Hori.), late leaf spot [Cercosporidium personatum (Berk. & MA Curtis) Deighton] and stem rot (Sclerotium rolfsii Sacc.) of peanut (Arachis hypogaea L.) in the southeastern USA is heavily dependent upon sterol biosynthesis inhibitor (SBI) and quinone outside inhibitor (QoI) fungicides. Effective new fungicides with different modes of action could improve overall disease control and extend the utility of the current fungicides. Penthiopryad is a pyrazole carboxamide fungicide being evaluated for use on peanut. Field experiments were conducted from 2004 to 2007 to determine the effect of a range of rates (0-0.36 kg AI ha(-1)) of Penthiopyrad on leaf spot and stem rot and the relative efficacy of Penthiopyrad and current fungicide standards chlorothalonil, tebuconazole and azoxystrobin. RESULTS: Leaf spot control in plots treated with Penthiopyrad at 0.20 kg AI ha(-1) or higher was similar to or better than that for the chlorothalonil standard. The incidence of stem rot for all Penthiopyrad treatments was usually less than that for the tebuconazole or azoxystrobin standard treatments. Pod yields for all Penthiopyrad treatments were similar to or higher than those for the respective standards. CONCLUSION: Penthiopyrad has excellent potential for management of late leaf spot and stem rot of peanut, and may complement current SBI and QoI fungicides.


