Polygalacin D2CAS# 66663-92-1 |
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 66663-92-1 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 53325781 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C63H102O32 | M.Wt | 1371.5 |
| Type of Compound | Triterpenoids | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | Soluble in Chloroform,Dichloromethane,Ethyl Acetate,DMSO,Acetone,etc. | ||
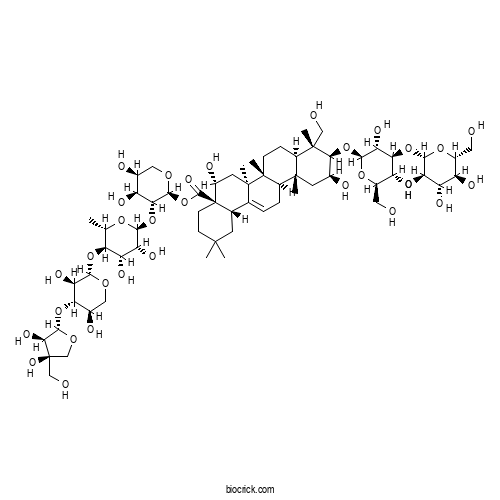
| Chemical Name | [(2S,3R,4S,5S)-3-[(2S,3R,4S,5R,6S)-5-[(2S,3R,4S,5R)-4-[(2S,3R,4R)-3,4-dihydroxy-4-(hydroxymethyl)oxolan-2-yl]oxy-3,5-dihydroxyoxan-2-yl]oxy-3,4-dihydroxy-6-methyloxan-2-yl]oxy-4,5-dihydroxyoxan-2-yl] (4aR,5R,6aR,6aS,6bR,8aR,9R,10R,11S,12aR,14bS)-10-[(2R,3R,4S,5R,6R)-3,5-dihydroxy-6-(hydroxymethyl)-4-[(2S,3R,4S,5S,6R)-3,4,5-trihydroxy-6-(hydroxymethyl)oxan-2-yl]oxyoxan-2-yl]oxy-5,11-dihydroxy-9-(hydroxymethyl)-2,2,6a,6b,9,12a-hexamethyl-1,3,4,5,6,6a,7,8,8a,10,11,12,13,14b-tetradecahydropicene-4a-carboxylate | ||
| SMILES | CC1C(C(C(C(O1)OC2C(C(COC2OC(=O)C34CCC(CC3C5=CCC6C(C5(CC4O)C)(CCC7C6(CC(C(C7(C)CO)OC8C(C(C(C(O8)CO)O)OC9C(C(C(C(O9)CO)O)O)O)O)O)C)C)(C)C)O)O)O)O)OC1C(C(C(CO1)O)OC1C(C(CO1)(CO)O)O)O | ||
| Standard InChIKey | DSHSDWSTXKYPEQ-DAANLMTCSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C63H102O32/c1-24-44(90-50-42(79)45(29(70)20-84-50)91-55-48(81)62(83,22-67)23-86-55)39(76)41(78)51(87-24)93-47-35(72)28(69)19-85-54(47)95-56(82)63-13-12-57(2,3)14-26(63)25-8-9-33-58(4)15-27(68)49(59(5,21-66)32(58)10-11-60(33,6)61(25,7)16-34(63)71)94-53-43(80)46(37(74)31(18-65)89-53)92-52-40(77)38(75)36(73)30(17-64)88-52/h8,24,26-55,64-81,83H,9-23H2,1-7H3/t24-,26-,27-,28-,29+,30+,31+,32+,33+,34+,35-,36+,37+,38-,39-,40+,41+,42+,43+,44-,45-,46-,47+,48-,49-,50-,51-,52-,53-,54-,55-,58-,59-,60+,61+,62+,63+/m0/s1 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Polygalacin D2 may have antimicrobial activity. | |||||

Polygalacin D2 Dilution Calculator

Polygalacin D2 Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 0.7291 mL | 3.6456 mL | 7.2913 mL | 14.5826 mL | 18.2282 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.1458 mL | 0.7291 mL | 1.4583 mL | 2.9165 mL | 3.6456 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.0729 mL | 0.3646 mL | 0.7291 mL | 1.4583 mL | 1.8228 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0146 mL | 0.0729 mL | 0.1458 mL | 0.2917 mL | 0.3646 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0073 mL | 0.0365 mL | 0.0729 mL | 0.1458 mL | 0.1823 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- Cimicifugic acid B
Catalog No.:BCN9806
CAS No.:205114-66-5
- Sennoside A1
Catalog No.:BCN9805
CAS No.:66575-30-2
- Gossypetin 3-methylether
Catalog No.:BCN9804
CAS No.:86749-51-1
- Stigmast-7-en-3-ol
Catalog No.:BCN9803
CAS No.:18525-35-4
- Quinidine sulfate
Catalog No.:BCN9802
CAS No.:50-54-4
- DL-2-Aminosuccinamic acid hydrate
Catalog No.:BCN9801
CAS No.:3130-87-8
- 4-Hydroxy-6-methylcoumarin
Catalog No.:BCN9800
CAS No.:13252-83-0
- 2-(2-Hydroxy-2-propyl)-5-methyl-5-vinyltetrahydrofuran
Catalog No.:BCN9799
CAS No.:60047-17-8
- beta-Glucogallin
Catalog No.:BCN9798
CAS No.:13405-60-2
- 2,4,6-Trihydroxybenzaldehyde
Catalog No.:BCN9797
CAS No.:487-70-7
- (1R)-Chrysanthemolactone
Catalog No.:BCN9796
CAS No.:14087-70-8
- Methyl trans-cinnamate
Catalog No.:BCN9795
CAS No.:1754-62-7
- DL-Phenylalanine
Catalog No.:BCN9808
CAS No.:150-30-1
- Isoedultin
Catalog No.:BCN9809
CAS No.:43043-08-9
- Quercetin 3-rutinoside 7-glucoside
Catalog No.:BCN9810
CAS No.:30311-61-6
- 3-Hydroxycoumarin
Catalog No.:BCN9811
CAS No.:939-19-5
- Norcamphor
Catalog No.:BCN9812
CAS No.:497-38-1
- 1,2,3-Tri-n-Octanoylglycerol
Catalog No.:BCN9813
CAS No.:538-23-8
- Vicinin 2
Catalog No.:BCN9814
CAS No.:90456-53-4
- 7-Ethoxy-4-methylcoumarin
Catalog No.:BCN9815
CAS No.:87-05-8
- 3-Aminocoumarin
Catalog No.:BCN9816
CAS No.:1635-31-0
- Withanoside V
Catalog No.:BCN9817
CAS No.:256520-90-8
- Tricetin
Catalog No.:BCN9818
CAS No.:520-31-0
- trans-Fertaric acid
Catalog No.:BCN9819
CAS No.:74282-22-7
Anti-Inflammatory Activities of Compounds Isolated from the Rhizome of Anemarrhena asphodeloides.[Pubmed:30322157]
Molecules. 2018 Oct 13;23(10). pii: molecules23102631.
Fifteen unreported compounds in Anemarrhena asphodeloides, iriflophene (3), hostaplantagineoside C (7), tuberoside G (8), spicatoside B (9), platycodin D (14), platycoside A (15), platycodin D2 (16), Polygalacin D2 (17), platycodin D3 (18), isovitexin (20), vitexin (21), 3,4-dihydroxyallylbenzene-3-O-alpha-l-rhamnopyranosyl(1-->6)-beta-d-glucopyranosi de (22), iryptophan (24), adenosine (25), alpha-d-Glucose monoallyl ether (26), together with eleven known compounds (1, 2, 4(-)6, 10(-)13, 19 and 23), were isolated from the rhizomes of Anemarrhena asphodeloides. The chemical structures of these compounds were characterized using HRMS and NMR. The anti-inflammatory activities of the compounds were evaluated by investigating their ability to inhibit LPS-induced NO production in N9 microglial cells. Timosaponin BIII (TBIII) and trans-hinokiresinol (t-HL) exhibited significant inhibitory effects on the NO production in a dose-dependent manner with IC50 values of 11.91 and 39.08 muM, respectively. Immunoblotting demonstrated that TBIII and t-HL suppressed NO production by inhibiting the expressions of iNOS in LPS-stimulated N9 microglial cells. Further results revealed that pretreatment of N9 microglial cells with TBIII and t-HL attenuated the LPS-induced expression tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-alpha and interleukin-6 (IL-6) at mRNAs and protein levels. Moreover, the activation of nuclear factor-kappaB (NF-kappaB) and phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K)/Akt signaling pathways were inhibited by TBIII and t-HL, respectively. Our findings indicate that the therapeutic implication of TBIII and t-HL for neurogenerative disease associated with neuroinflammation.
Influence of sulfur fumigation on glycoside profile in Platycodonis Radix (Jiegeng).[Pubmed:27385975]
Chin Med. 2016 Jul 6;11:32.
BACKGROUND: Over recent decades, sulfur fumigation is becoming abused in processing some freshly harvested herbs used as both medicine and food, although it has been questioned whether sulfur fumigation will change the efficacy and safety of the herbs. One of the herbs commonly processed by sulfur fumigation is Platycodonis Radix (Jiegeng in Chinese). Glycosides are the main bioactive components of Jiegeng. Up to the present, no study has been carried out to evaluate the impact of sulfur fumigation on glycoside profile of Jiegeng. METHODS: A rapid and versatile ultra-high performance liquid chromatography coupled with ultra-high resolution quadrupole time-of-flight mass spectrometry (UHPLC UHD Q-TOF MS/MS) method was developed for comprehensive analysis of the glycoside profiles of sulfur-fumigated and air-dried Jiegeng samples. RESULTS: Twenty-three glycosides were detected in air-dried and sulfur-fumigated Jiegeng samples. After sulfur fumigation, the peak heights of eight glycosides, namely platycogenin A, platycodin D, platycodin D2, platycodin D3, polygalacin D, Polygalacin D2, deapio-platycodin D and 3''-O-acetylplatycodin D2, remarkably decreased; while peak heights of five glycosides, namely syringin, lobetyolin, platycoside E, deapio-platycodin D2 and deapio-platycoside E, slightly increased; in addition, peaks of ten glycosides, platycodin A, platycodin C, platycodin V, platycoside C, 16-oxoplatycodin D, 2''-O-acetylpolygalacin D, 2''-O-acetylPolygalacin D2, 3''-O-acetylpolygalacin D, 3''-O-acetylPolygalacin D2, and platycogenic acid B, disappeared. CONCLUSION: Sulfur fumigation caused significant changes of glycoside components of Jiegeng. Further investigations are warranted to explore how these chemical changes occurred and whether these changes would affect the efficacy and safety of Jiegeng.
Simultaneous determination of multiple platycosides with a single reference standard in Platycodi Radix by high-performance liquid chromatography coupled with evaporative light scattering detection.[Pubmed:26331296]
J Sep Sci. 2015 Nov;38(21):3712-9.
A traditional external standard method using HPLC coupled with evaporative light scattering detection has been developed for fast and accurate determination of seven platycosides in Platycodi Radix. However, inevitable difficulties in reference standards preparation process, which are quite costly and time consuming, have made its application limited. To avoid this inconvenience, a simultaneous determination of multiple components with a single reference standard strategy, which could be realized by calibrating the standard curve with internal standard and response factors, was introduced to the HPLC coupled with evaporative light scattering detection method. This is the first time that an incorporation of these two methods has been realized. Among seven ingredients, platycodin D was selected as the internal standard for its relatively easy preparation and low cost. Moreover, according to the investigation on concentration-dependent effects over response factors and robustness test, platycoside E, deapioplatycodin D, platycodin D, and Polygalacin D2 were chosen to be the indicators for this novel method. The present method has not shown statistically significant differences with a traditional external standard method as verified sample analysis by the F-test (p = 95%, n = 6).
HPLC-ELSD analysis of 18 platycosides from balloon flower roots (Platycodi Radix) sourced from various regions in Korea and geographical clustering of the cultivation areas.[Pubmed:30634281]
Food Chem. 2011 Nov 15;129(2):645-651.
An effective HPLC method to analyse platycosides from the balloon flower root was developed using ELSD. The optimum resolution of the platycosides was achieved on an ODS column with gradient elution of eluent A, 30mM ammonium acetate buffer (pH 4.81): methanol: acetonitrile=75:5:20 (v/v/v), and B, 69:5:26 (v/v/v). Amongst 18 platycosides, platycoside E showed the highest content, followed by Polygalacin D2 and 3''-O-acetylplatyconic acid A. The sum of these three compounds was recommended for quality control of balloon flower root for medicinal purposes. The samples could be clustered into groups based on platycoside content. Group I, characterised by a high concentration of platycosides, was located near the west coast of Korea, whereas group II, characterised by a low concentration of platycosides, was located inland or in mountainous area. The method could be used to control the quality of balloon flower root.
Structure-function relationship of the saponins from the roots of Platycodon grandiflorum for hemolytic and adjuvant activity.[Pubmed:21945665]
Int Immunopharmacol. 2011 Dec;11(12):2047-56.
To assess the contribution of the aglycone and sugar chain to the biological activity of saponins from Platycodon grandiflorum, seven structurally consecutive saponins, platycodin D (PD), D2 (PD2), D3 (PD3), platycoside A (PA), E (PE), deapioplatycoside E (DPE), and Polygalacin D2 (PGD) were compared for their hemolytic activities and adjuvant potentials on the immune responses to Newcastle disease virus-based recombinant avian influenza vaccine (rL-H5) in mice. Among seven compounds, the order of the hemolytic activity was PGD approximately PD > PD2 > PA > PD3 > PE > DPE. PD, PD2, PA, and PGD significantly not only promoted concanavalin A (Con A)-, lipopolysaccharide (LPS)- and antigen-induced splenocyte proliferation, but enhanced the NK cell activity in mice immunized with rL-H5. PD and PD2 increased the antigen specific IgG, IgG1, IgG2a, and IgG2b antibody titers, while PA and PGD only induce the IgG and IgG1 antibody responses in the immunized mice. However, the other three saponins were not observed for adjuvant activity. The results suggested that the sugar chains attached to C-3, the glycidic moiety at C-28 of aglycone, as well as aglycone affect their biological activities. Interestingly, their hemolytic and adjuvant activities increased with the retention time by reverse phase HPLC analysis. The retention time may be useful for primary estimation of fundamental adjuvanticity of saponin with the same aglycone.
Platycodin D and 2''-O-acetyl-polygalacin D2 isolated from Platycodon grandiflorum protect ischemia/reperfusion injury in the gerbil hippocampus.[Pubmed:19433075]
Brain Res. 2009 Jul 7;1279:197-208.
Platycodi radix is used as a folk remedy for several conditions. In this study, we investigated the neuroprotective effects of five major extracts; deapioplatycoside E (DPE), platycoside E (PE), platyconic acid A (PA), platycodin D (PD) and 2''-o-acetyl-Polygalacin D2 (PD2) isolated from the P.radix in the hippocampal CA1 region (CA1) 4 or 10 days after ischemia/reperfusion (I/R). Each extract was administered into gerbils with intraperitoneal injection (5 mg/kg/day) 10 days before ischemic surgery and the gerbils were sacrificed 4 or 10 days after I/R. Fluoro-Jade B (F-J B, a marker for neurodegeneration) positive ((+)) neurons increased significantly in the stratum pyramidale of the CA1 region in the vehicle-treated group after I/R. A similar pattern was observed in the DPE-, PE- and PA-treated groups; however, in the PD- and PD2-treated groups, F-J B(+) neurons were small in number. We also observed that activations of astrocytes and microglia in the CA1 region after I/R were blocked by the PD- and PD2 treatments. In addition, we found that Cu,Zn-superoxide dismutase (SOD1) immunoreactivity in the pyramidal layer of the PD- and PD2-treated groups was similar to that of the sham group and COX-2(+) and NF-kappaB(+) cells were significantly lower in the PD- and PD2-treated group than those in the vehicle-treated group after I/R. These results suggest that PD and PD2 rescue neurons in the CA1 region from an ischemic damage.
Isolation of a new saponin and cytotoxic effect of saponins from the root of Platycodon grandiflorum on human tumor cell lines.[Pubmed:15971131]
Planta Med. 2005 Jun;71(6):566-8.
A novel triterpenoid saponin, deapioplatycoside E (1) was isolated from the root extract of Platycodon grandiflorum, together with the seven known saponins 2 - 8, i. e., platycoside E (2), deapioplatycodin D3 (3), platycodin D3 (4), Polygalacin D2 (5), platycodin D2 (6), deapioplatycodin D (7) and platycodin D (8). The structure of the new saponin 1 was determined on the basis of spectral analysis and chemical evidence. The crude saponin fraction (ED50: ca. 10 - 15 microg/mL) and compounds 6 - 8 (ED50: ca. 4 - 18 microg/mL) exhibited significant inhibition on the proliferation of five kinds of cultured human tumor cell lines, i. e., A549 (non-small cell lung), SK-OV-3 (ovary), SK-MEL-2 (melanoma), XF498 (central nerve system) and HCT-15 (colon), in vitro.


