Cimicifugic acid BCAS# 205114-66-5 |
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 205114-66-5 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 6449880 | Appearance | Light yellow powder |
| Formula | C21H20O11 | M.Wt | 448.4 |
| Type of Compound | Phenols | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | Soluble in methan | ||
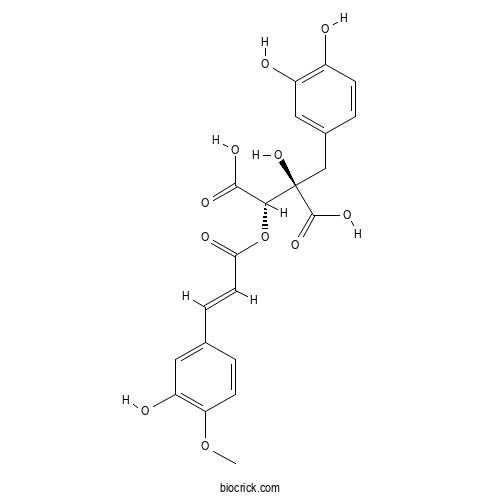
| Chemical Name | (2R,3S)-2-[(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)methyl]-2-hydroxy-3-[(E)-3-(3-hydroxy-4-methoxyphenyl)prop-2-enoyl]oxybutanedioic acid | ||
| SMILES | COC1=C(C=C(C=C1)C=CC(=O)OC(C(=O)O)C(CC2=CC(=C(C=C2)O)O)(C(=O)O)O)O | ||
| Standard InChIKey | YVHLLZXSGPDXOA-ZHBFVYIWSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C21H20O11/c1-31-16-6-3-11(8-15(16)24)4-7-17(25)32-18(19(26)27)21(30,20(28)29)10-12-2-5-13(22)14(23)9-12/h2-9,18,22-24,30H,10H2,1H3,(H,26,27)(H,28,29)/b7-4+/t18-,21-/m1/s1 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Cimicifugic acid B shows inhibitory collagenolytic activity. | |||||

Cimicifugic acid B Dilution Calculator

Cimicifugic acid B Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.2302 mL | 11.1508 mL | 22.3015 mL | 44.603 mL | 55.7538 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.446 mL | 2.2302 mL | 4.4603 mL | 8.9206 mL | 11.1508 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.223 mL | 1.1151 mL | 2.2302 mL | 4.4603 mL | 5.5754 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0446 mL | 0.223 mL | 0.446 mL | 0.8921 mL | 1.1151 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0223 mL | 0.1115 mL | 0.223 mL | 0.446 mL | 0.5575 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- Sennoside A1
Catalog No.:BCN9805
CAS No.:66575-30-2
- Gossypetin 3-methylether
Catalog No.:BCN9804
CAS No.:86749-51-1
- Stigmast-7-en-3-ol
Catalog No.:BCN9803
CAS No.:18525-35-4
- Quinidine sulfate
Catalog No.:BCN9802
CAS No.:50-54-4
- DL-2-Aminosuccinamic acid hydrate
Catalog No.:BCN9801
CAS No.:3130-87-8
- 4-Hydroxy-6-methylcoumarin
Catalog No.:BCN9800
CAS No.:13252-83-0
- 2-(2-Hydroxy-2-propyl)-5-methyl-5-vinyltetrahydrofuran
Catalog No.:BCN9799
CAS No.:60047-17-8
- beta-Glucogallin
Catalog No.:BCN9798
CAS No.:13405-60-2
- 2,4,6-Trihydroxybenzaldehyde
Catalog No.:BCN9797
CAS No.:487-70-7
- (1R)-Chrysanthemolactone
Catalog No.:BCN9796
CAS No.:14087-70-8
- Methyl trans-cinnamate
Catalog No.:BCN9795
CAS No.:1754-62-7
- 2-Propylpyridine
Catalog No.:BCN9794
CAS No.:622-39-9
- Polygalacin D2
Catalog No.:BCN9807
CAS No.:66663-92-1
- DL-Phenylalanine
Catalog No.:BCN9808
CAS No.:150-30-1
- Isoedultin
Catalog No.:BCN9809
CAS No.:43043-08-9
- Quercetin 3-rutinoside 7-glucoside
Catalog No.:BCN9810
CAS No.:30311-61-6
- 3-Hydroxycoumarin
Catalog No.:BCN9811
CAS No.:939-19-5
- Norcamphor
Catalog No.:BCN9812
CAS No.:497-38-1
- 1,2,3-Tri-n-Octanoylglycerol
Catalog No.:BCN9813
CAS No.:538-23-8
- Vicinin 2
Catalog No.:BCN9814
CAS No.:90456-53-4
- 7-Ethoxy-4-methylcoumarin
Catalog No.:BCN9815
CAS No.:87-05-8
- 3-Aminocoumarin
Catalog No.:BCN9816
CAS No.:1635-31-0
- Withanoside V
Catalog No.:BCN9817
CAS No.:256520-90-8
- Tricetin
Catalog No.:BCN9818
CAS No.:520-31-0
Cytotoxic caffeic acid derivatives from the rhizomes of Cimicifuga heracleifolia.[Pubmed:23054712]
Arch Pharm Res. 2012 Sep;35(9):1559-65.
Activity profiling of the n-BuOH extract from Cimicifuga heracleifolia rhizomes led to the identification of three cytotoxic caffeic acid derivatives, carboxymethyl isoferulate (2), cimicifugic acid A (3), and Cimicifugic acid B (4) together with a series of structurally related inactive compounds. The extract was separated by time-based fractionation in a gradient HPLC condition, and cytotoxicity of each fraction was evaluated using HCT116 colon cancer cells in vitro. HPLChyphenated spectroscopy including LC/NMR and LC/PDA/MS provided structural information for phenolic compounds contained in the extract, and further preparative isolation of active compounds 2-4 was achieved by semi-preparative HPLC. Compounds 2-4 showed cytotoxic activity against cancer cells in a dose-dependent manner at the concentrations of 2.5-40 muM, and western blotting analysis showed that these compounds increased expression of cleaved poly ADP ribose polymerase (PARP), a critical apoptosis marker.
Polyphenolic constituents of Actaea racemosa.[Pubmed:16562825]
J Nat Prod. 2006 Mar;69(3):314-8.
A new lignan, actaealactone (1), and a new phenylpropanoid ester derivative, cimicifugic acid G (2), together with 15 known polyphenols, protocatechuic acid, protocatechualdehyde, p-coumaric acid, caffeic acid, methyl caffeate, ferulic acid, ferulate-1-methyl ester, isoferulic acid, 1-isoferuloyl-beta-d-glucopyranoside, fukinolic acid, and cimicifugic acids A, B, and D-F, were isolated from an extract of the rhizomes and roots of black cohosh (Actaea racemosa). The structures of the new compounds were determined on the basis of NMR spectroscopic analysis. Compounds 1 and 2 displayed antioxidant activity in the 1,1-diphenyl-2-picrylhydrazyl (DPPH) free-radical assay with IC(50) values of 26 and 37 microM, respectively. Other antioxidants identified from A. racemosa include cimicifugic acid A (3), Cimicifugic acid B (4), and fukinolic acid (5). Compounds 1 and 2 also exhibited a small stimulating effect on the growth of MCF-7 breast cancer cell proliferation 1.24-fold (14 microM) and 1.14-fold (10 microM), respectively, compared to untreated cells.
Identification of caffeic acid derivatives in Actea racemosa (Cimicifuga racemosa, black cohosh) by liquid chromatography/tandem mass spectrometry.[Pubmed:12717772]
Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom. 2003;17(9):978-82.
Caffeic acid derivatives occurring in black cohosh [Cimicifuga racemosa (L.) Nutt., Actaea racemosa (Ranunculaceae)], some of which may have pharmacological activity, were analyzed using high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) electrospray ionization tandem mass spectrometry (ESI-MS/MS) with the aim of developing a methodology for their rapid identification in a complex plant matrix. Based on these studies, structurally characteristic product ions and neutral molecule losses were identified, which were then used during LC/MS/MS with product ion scanning, precursor scanning and constant neutral loss scanning to detect caffeic acid derivatives in a crude extract of black cohosh. Several caffeic acid derivatives were detected, and the identification of six of them were confirmed by comparison with authentic standards including caffeic acid, ferulic acid, isoferulic acid, fukinolic acid, cimicifugic acid A, and Cimicifugic acid B. Four other compounds were detected that appeared to be caffeic acid derivatives based on LC/MS/MS retention times, molecular weights, and fragmentation patterns during MS/MS. Since standards were unavailable for these four compounds, they were tentatively identified using LC/MS/MS as cimicifugic acid E, cimicifugic acid F, dehydrocimicifugic acid A, and dehydroCimicifugic acid B. Dehydrocimicifugic acid A and dehydroCimicifugic acid B have not been reported previously to be constituents of black cohosh.
Black cohosh (Cimicifuga racemosa L.) protects against menadione-induced DNA damage through scavenging of reactive oxygen species: bioassay-directed isolation and characterization of active principles.[Pubmed:12428954]
J Agric Food Chem. 2002 Nov 20;50(24):7022-8.
The roots/rhizomes of Cimicifuga racemosa L. (Nutt.) (black cohosh) have traditionally been used to treat menopausal symptoms through an unknown mechanism of action. In an effort to determine if black cohosh had additional health benefits, methanol extracts were investigated for their potential to scavenge reactive oxygen species and to protect against menadione-induced DNA damage. These extracts effectively scavenged 1,1-diphenyl-2-picrylhydrazyl (DPPH) free radicals. In addition, the extracts showed dose-dependent decreases in DNA single-strand breaks and oxidized bases induced by the quinone menadione using the comet (single-cell gel electrophoresis assay) and fragment length associated repair enzyme assays, respectively. Bioassay-directed fractionation of the methanolic extracts using the DPPH assay as a monitor led to the isolation of nine antioxidant active compounds: caffeic acid (1), methyl caffeate (2), ferulic acid (3), isoferulic acid (4), fukinolic acid (5), cimicifugic acid A (6), Cimicifugic acid B (7), cimicifugic acid F (8), cimiracemate A (9), and cimiracemate B (10). Six of these antioxidants were found to reduce menadione-induced DNA damage in cultured S30 breast cancer cells with the following order of potency: methyl caffeate (2) > caffeic acid (1) > ferulic acid (3) > cimiracemate A (9) > cimiracemate B (10) > fukinolic acid (5). These data suggest that black cohosh can protect against cellular DNA damage caused by reactive oxygen species by acting as antioxidants.


