TricetinCAS# 520-31-0 |
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 520-31-0 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 5281701 | Appearance | Powder |
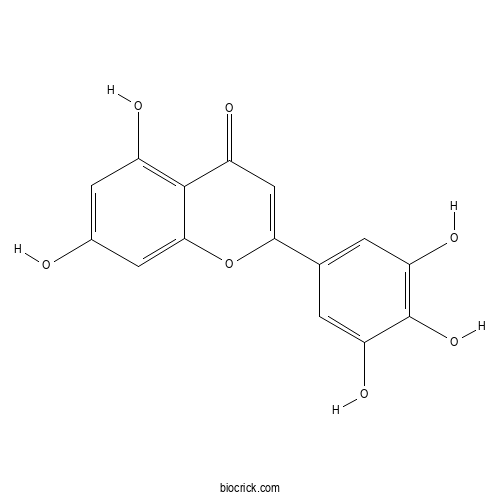
| Formula | C15H10O7 | M.Wt | 302.2 |
| Type of Compound | Flavonoids | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | Soluble in Chloroform,Dichloromethane,Ethyl Acetate,DMSO,Acetone,etc. | ||
| Chemical Name | 5,7-dihydroxy-2-(3,4,5-trihydroxyphenyl)chromen-4-one | ||
| SMILES | C1=C(C=C(C(=C1O)O)O)C2=CC(=O)C3=C(C=C(C=C3O2)O)O | ||
| Standard InChIKey | ARSRJFRKVXALTF-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C15H10O7/c16-7-3-8(17)14-9(18)5-12(22-13(14)4-7)6-1-10(19)15(21)11(20)2-6/h1-5,16-17,19-21H | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Tricetin, a dietary flavonoid, inhibits proliferation of human breast adenocarcinoma mcf-7 cells by blocking cell cycle progression and inducing apoptosis. It possesses the anti‐metastatic activity of osteosarcoma cells by transcriptionally repressing MMP‐9 via p38 and Akt signaling pathways. Tricetin also may be a promising chemopreventive agent against human breast cancer. | |||||

Tricetin Dilution Calculator

Tricetin Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 3.3091 mL | 16.5453 mL | 33.0907 mL | 66.1813 mL | 82.7267 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.6618 mL | 3.3091 mL | 6.6181 mL | 13.2363 mL | 16.5453 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.3309 mL | 1.6545 mL | 3.3091 mL | 6.6181 mL | 8.2727 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0662 mL | 0.3309 mL | 0.6618 mL | 1.3236 mL | 1.6545 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0331 mL | 0.1655 mL | 0.3309 mL | 0.6618 mL | 0.8273 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- Withanoside V
Catalog No.:BCN9817
CAS No.:256520-90-8
- 3-Aminocoumarin
Catalog No.:BCN9816
CAS No.:1635-31-0
- 7-Ethoxy-4-methylcoumarin
Catalog No.:BCN9815
CAS No.:87-05-8
- Vicinin 2
Catalog No.:BCN9814
CAS No.:90456-53-4
- 1,2,3-Tri-n-Octanoylglycerol
Catalog No.:BCN9813
CAS No.:538-23-8
- Norcamphor
Catalog No.:BCN9812
CAS No.:497-38-1
- 3-Hydroxycoumarin
Catalog No.:BCN9811
CAS No.:939-19-5
- Quercetin 3-rutinoside 7-glucoside
Catalog No.:BCN9810
CAS No.:30311-61-6
- Isoedultin
Catalog No.:BCN9809
CAS No.:43043-08-9
- DL-Phenylalanine
Catalog No.:BCN9808
CAS No.:150-30-1
- Polygalacin D2
Catalog No.:BCN9807
CAS No.:66663-92-1
- Cimicifugic acid B
Catalog No.:BCN9806
CAS No.:205114-66-5
- trans-Fertaric acid
Catalog No.:BCN9819
CAS No.:74282-22-7
- beta-Citronellol
Catalog No.:BCN9820
CAS No.:106-22-9
- Cimicifugic acid F
Catalog No.:BCN9821
CAS No.:220618-91-7
- Eclalbasaponin II
Catalog No.:BCN9822
CAS No.:78285-90-3
- Morindin
Catalog No.:BCN9823
CAS No.:60450-21-7
- Acetic acid hexyl ester
Catalog No.:BCN9824
CAS No.:142-92-7
- Grayanotoxin I
Catalog No.:BCN9825
CAS No.:4720-09-6
- Vaccarin E
Catalog No.:BCN9826
CAS No.:2252345-81-4
- 6-Hydroxyflavone
Catalog No.:BCN9827
CAS No.:6665-83-4
- Picrotoxinin
Catalog No.:BCN9828
CAS No.:17617-45-7
- 4,4'-Dimethoxychalcone
Catalog No.:BCN9829
CAS No.:2373-89-9
- Urushiol (15:1)
Catalog No.:BCN9830
CAS No.:35237-02-6
Identification of Anti-Inflammatory Compounds from Hawaiian Noni (Morinda citrifolia L.) Fruit Juice.[Pubmed:33121016]
Molecules. 2020 Oct 27;25(21). pii: molecules25214968.
Noni (Morinda citrifolia L.) fruit juice has been used in Polynesia as a traditional folk medicine and is very popular worldwide as a functional food supplement. In this study, compounds present in Hawaiian Noni fruit juice, with anti-inflammatory activity in lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-stimulated RAW 264.7 cells were identified. Five compounds were isolated using a bioassay-driven technique and phytochemical analysis of noni fruit juice: asperulosidic acid (1), rutin (2), nonioside A (3), (2E,4E,7Z)-deca-2,4,7-trienoate-2-O-beta-d-glucopyranosyl-beta-d-glucopyranoside (4), and Tricetin (5). The structures of these five compounds were determined via NMR spectroscopy and LC/MS. In an anti-inflammatory assay, compounds 1-5 inhibited the production of nitric oxide (NO), which is a proinflammatory mediator, in LPS-stimulated macrophages. Moreover, the mechanisms underlying the anti-inflammatory effects of compounds 1-5 were investigated. Parallel to the inhibition of NO production, treatment with compounds 1-5 downregulated the expression of IKKalpha/beta, I-kappaBalpha, and NF-kappaB p65 in LPS-stimulated macrophages. Furthermore, treatment with compounds 1-5 downregulated the expression of nitric oxide synthase and cyclooxygenase-2. Thus, these data demonstrated that compounds 1-5 present in noni fruit juice, exhibited potential anti-inflammatory activity; these active compounds may contribute preventively and therapeutically against inflammatory diseases.
Antioxidant action of deprotonated flavonoids: Thermodynamics of sequential proton-loss electron-transfer.[Pubmed:33022536]
Phytochemistry. 2020 Dec;180:112528.
Despite the intensive research on radical scavenging action of flavonoids, a systematic study of the thermochemistry for their mono-deprotonated species in aqueous solution is still missing. In this work, reaction enthalpies related to Sequential Proton-Loss Electron-Transfer (SPLET) mechanism were theoretically investigated for all mono-deprotonated forms of nine flavonoids: apigenin, luteolin, fisetin, kaempferol, quercetin, taxifolin, Tricetin, tricin and cyanidin. Differences in reaction enthalpies of the first and the second deprotonation can be lower than 10 kJ mol(-1), when two successive deprotonations occur in different aromatic rings of the molecule. For neutral flavonoids, thermodynamically preferred deprotonation sites are 4'-OH and 7-OH groups. In cyanidin (cation in native form), preferred second deprotonation site is 5-OH group. In the case of the formation of the preferred dianions, reaction enthalpies of the second proton loss are not affected by the structural distinctions between the flavonoids. In aqueous solution, deprotonated flavonoids show higher tendency to enter SPLET mechanism in comparison to Hydrogen Atom Transfer (HAT) or electron transfer.
Tricetin Suppresses Migration and Presenilin-1 Expression of Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma through Akt/GSK-3beta Pathway.[Pubmed:32668971]
Am J Chin Med. 2020;48(5):1203-1220.
Lymph node migration results in poor prognoses for nasopharyngeal carcinoma (NPC) patients. Tricetin, a flavonoid derivative, regulates tumorigenesis activity through its antiproliferative and antimetastatic properties. However, the molecular mechanism of Tricetin affecting the migration and invasion of NPC cells remains poorly understood. In this paper, we examined the antimetastatic properties of Tricetin in human NPC cells. Our results demonstrated that Tricetin at noncytotoxic concentrations (0-80 3M) noticeably reduced the migration and invasion of NPC cells (HONE-1, NPC-39, and NPC-BM). Moreover, Tricetin suppressed the indicative protease, presenilin-1 (PS-1), as indicated by protease array. PS-1 was transcriptionally inhibited via the Akt signaling pathway but not mitogen-activated protein kinase pathways, such as the JNK, p38, and ERK1/2 pathways. In addition to upregulating GSK-3[Formula: see text] phosphorylation through Akt suppression, Tricetin may downregulate the activity of PS-1. Overall, our study provides new insight into the role of Tricetin-induced molecular regulation in the suppression of NPC metastasis and suggests that Tricetin has prospective therapeutic applications for patients with NPC.
Natural flavone tricetin suppresses oxidized LDL-induced endothelial inflammation mediated by Egr-1.[Pubmed:31991371]
Int Immunopharmacol. 2020 Mar;80:106224.
Atherosclerosis is the primary cause of many cardiovascular diseases. Endothelial dysfunction is recognized as a crucial early event in atherosclerotic lesion formation. Tricetin is a natural flavonoid derivative that has demonstrated a wide range of therapeutic properties. This study investigates the protective effect of Tricetin in cultured endothelial cells. The results of our study show that Tricetin suppressed oxidized low-density lipoprotein (ox-LDL)-induced expression of pro-inflammatory monocyte chemotactic protein-1 (MCP-1) and interleukin-1beta (IL-1beta), as well as the generation of reactive oxygen species (ROS). Furthermore, our findings indicate that Tricetin suppressed ox-LDL-induced expression of intercellular adhesion molecule-1 (ICAM-1) and vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 (VCAM-1). At the cellular level, the presence of Tricetin inhibited ox-LDL-induced monocyte adhesion to endothelial cells. Mechanistically, we showed that Tricetin suppressed the induction of the endothelial receptor for ox-LDL, lectin-like ox-LDL receptor-1 (LOX-1), and the transcriptional factor early growth response 1 (Egr-1) as well as extracellular signal-regulated protein kinase 1 and 2 (ERK1/2) activation. These data demonstrate that Tricetin is a natural protective agent in vascular endothelial cells, indicating that Tricetin could have a potentially beneficial effect in the modulation of atherosclerosis.
Gold nanoparticles synthesised by flavonoid tricetin as a potential antibacterial nanomedicine to treat respiratory infections causing opportunistic bacterial pathogens.[Pubmed:31843547]
Microb Pathog. 2020 Feb;139:103928.
In this study, flavonoid Tricetin was used as a reducing and capping agent for the synthesis of gold nanoparticles (AuNPs). Further, the antibacterial efficacy of the synthesised AuNPs was evaluated against the opportunistic bacterial pathogens that cause respiratory infections. The optimum levels for the synthesis of AuNPs were found to be pH 8, temperature 30 degrees C, Tricetin 125 muM and chloroauric acid 250 muM. The Tricetin synthesised AuNPs exhibited in spherical shape with an average size of 12 nm. FT-IR results confirmed that the hydroxyl (OH) and carbonyl (CO) groups of Tricetin were mainly participated in the synthesis of AuNPs. The opportunistic bacterial pathogens isolated from immunocompromised patients suffering with different respiratory infections were identified as Staphylococcus aureus, Enterobacter xiangfangensis, Bacillus licheniformis, Escherichia fergusonii, Acinetobacter pittii, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Aeromonas enteropelogenes and Proteus mirabilis. The antibacterial studies confirmed the broad-spectrum antibacterial activity of AuNPs against the tested Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria. The synthesised AuNPs showed high biocompatibility on primary normal human dermal fibroblast (NHDF-c) cells up to 50 muM mL(-1). Best of our knowledge, this is the first report on the synthesis of AuNPs using Tricetin, which may be a potential antibacterial nanomedicine to treat bacterial infections.
Tricetin Protects Rat Chondrocytes against IL-1beta-Induced Inflammation and Apoptosis.[Pubmed:31231454]
Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2019 Apr 28;2019:4695381.
Tricetin is a well-studied flavonoid with a wide range of pharmacological activities in cancer and inflammation. However, the ability of Tricetin to ameliorate the inflammation that occurs in osteoarthritis (OA) has not been determined. This study explored the effects of Tricetin on interleukin- (IL-) 1beta-induced rat chondrocytes. Chondrocytes harvested from rat cartilage were incubated in vitro with Tricetin in the presence of IL-1beta. The expression of matrix metalloproteinase- (MMP-) 1, MMP-3, MMP-13, nitric oxide (NO), prostaglandin E2 (PGE2), Bax, and Bcl-2 was evaluated by real-time-PCR, ELISA, Griess reaction, and western blotting. Caspase-3 activity in chondrocytes was determined using a caspase-3 activity assay and MAPK pathway activity by western blotting. Tricetin decreased the expression of MMP-1, MMP-3, and MMP-13 at both the gene and protein level in IL-1beta-induced rat chondrocytes. It also inhibited IL-1beta-induced NO and PGE2 production, by modulating inducible NO synthase and cyclooxygenase 2 gene expression. An antiapoptotic role of Tricetin involving the Bax/Bcl-2/caspase-3 pathway was also determined. The chondroprotective effect of Tricetin was shown to be partly related to the suppression of the MAPK signaling pathway. The results of this study demonstrate the chondroprotective role of Tricetin, based on its anticatabolic, anti-inflammatory, and antiapoptotic effects in chondrocytes. The therapeutic potential of Tricetin in OA patients should be explored in future studies.
Tricetin protects against 6-OHDA-induced neurotoxicity in Parkinson's disease model by activating Nrf2/HO-1 signaling pathway and preventing mitochondria-dependent apoptosis pathway.[Pubmed:31176653]
Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2019 Sep 1;378:114617.
Apoptosis of DA neurons is a contributing cause of disability and death for Parkinson's disease (PD). In this experiment, the neuroprotective effect of Tricetin was examined in PD models both in vitro and in vivo. The results suggested that 6-OHDA-induced cytotoxicity was accompanied by an increase in ROS generation, an increase in caspase-3 protein activity, an increase in Lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) release and an increase in the ratio of Bax/Bcl-2, but the pretreatment with Tricetin significantly improved cell viability and suppressed mitochondria-mediated apoptosis. Moreover, Tricetin also induced the protein expression of Nuclear factor (erythroid-derived 2)-like 2 (Nrf2) and its transcriptional activation, resulting in the up-regulated expression of heme oxygenase-1 (HO-1), which conferred neuroprotection against 6-OHDA-induced oxidative damage. Results from molecular docking indicated that Tricetin could be a potent competitive inhibitor of the Keap1-Nrf2 Protein Protein Interaction (PPI). Finally, in vivo findings were confirmed in the 6-OHDA-PD C. elegans model. Thus, Tricetin may be an attractive therapeutic candidate for the neuroprotection.
Network pharmacology-based analysis on bioactive anti-diabetic compounds in Potentilla discolor bunge.[Pubmed:31022565]
J Ethnopharmacol. 2019 Sep 15;241:111905.
ETHNOPHARMACOLOGICAL RELEVANCE: Potentilla discolor Bunge (PDB) is a commonly used herbal for alleviating diabetes mellitus and its complications. Although accumulating evidences show the anti-diabetic efficacy of PDB, the vital anti-diabetic compounds and their functional targets remain elusive. AIM OF THE STUDY: To investigate the anti-diabetic ingredients and their functional mechanisms in PDB, gas chromatograph-mass spectrometry analysis was performed on PDB extract and 21 were testified as anti-diabetic compounds. MATERIALS AND METHODS: Subsequently their potential protein targets were also identified. The bioinformatics analysis was implemented by network pharmacology-based approaches. STRING analysis was performed to reveal enrichment of these target proteins, protein-protein interactions, pathways and related diseases. Cytoscape was used to determine the potential protein targets for these components in PDB, indicating that 21 anti-diabetic compounds in PDB regulate 33 diabetes-related proteins in 28 signal pathways and involve 21 kinds of diabetes-related diseases. Among the 21 potential anti-diabetic components predicted by network analysis, Tricetin was firstly experimentally validated at the molecular and cellular level. RESULTS: Results indicated that this active small-molecule compound may have beneficial effects on improving glucose uptake. CONCLUSIONS: We envisage that network analysis will be useful in screening bioactive compounds of medicinal plants.
Characterization of a heat responsive UDP: Flavonoid glucosyltransferase gene in tea plant (Camellia sinensis).[Pubmed:30475819]
PLoS One. 2018 Nov 26;13(11):e0207212.
Tea plant (Camellia sinensis) accumulates abundant flavonoid glycosides that are the major bioactive ingredients in tea. Biosynthesis of flavonoid glycosides are catalyzed by UDP-glucosyltransferases (UGTs) that are widely present in plants. Among one hundred and seventy-eight UGTs genes that we have previously identified in tea plant, few of them have been functionally characterized. In the present study, we further identified UGT73A17 gene that is responsible for the biosynthesis of a broad range of flavonoid glycosides. Sequence analysis revealed that the deduced UGT73A17 protein showed high identity with 7-O-glycosyltransferases at amino acid level and it was clustered into the clade containing several 7-O-glycosyltransferases from other plant species. Enzymatic assays revealed that the recombinant UGT73A17 protein (rUGT73A17) exhibited activity toward flavonols (kaempferol, quercetin, and myricetin), flavones (apigenin, luteolin, and Tricetin), flavanone (naringenin), isoflavones (genistein) and epicatechin gallate, yielding 7-O-glucosides as the major in vitro products. In particular, rUGT73A17 displayed higher activity at high temperatures (eg. 50 degrees C) than at low temperatures, which was consistent with its relatively high expression level at high temperatures. Two amino acid substitutions at I296L and V466A improved the enzymatic activity of rUGT73A17. Our study demonstrated that UGT73A17 is responsible for the biosynthesis of a broad range of flavonoid glucosides, which is also involved in heat response and quality of tea plant.
PgUGT95B2 preferentially metabolizes flavones/flavonols and has evolved independently from flavone/flavonol UGTs identified in Arabidopsis thaliana.[Pubmed:30419412]
Phytochemistry. 2019 Jan;157:184-193.
UDP-dependent glycosyltransferases (UGTs) convert aglycones into more stable, bioactive, and structurally diverse glycosylated derivatives. Pomegranate (Punica granatum L.) produces various glycosylated phenolic metabolites, e.g. hydrolyzable tannins (HTs), anthocyanins, and flavonoids, and constitutes an excellent system for investigating the corresponding UGT activities. Here we report the cloning and functional characterization of a pomegranate UGT, PgUGT95B2, which is highly active towards flavones and flavonols and can glycosylate at more than one position in the substrate molecule. Particularly, PgUGT95B2 has the strongest activity towards Tricetin (flavone with a tri-hydroxylated B-ring) and can act at the 4'-O position of its B-ring. In addition, PgUGT95B2 was able to glycosylate flavones present in pomegranate metabolite extracts. Conversely, PgUGT95B2 did not produce a galloylglucose ester (precursor for HT biosynthesis) or anthocyanins in enzyme assays. Our phylogenetic analysis suggested an independent evolution of PgUGT95B2 and flavone/flavonol UGTs identified in the model plant Arabidopsis thaliana through convergent evolution or gene loss.
Molecular docking and two-dimensional quantitative structure-activity relationship studies of synthetic flavonoids on horseradish peroxidase compounds (I, II, and III).[Pubmed:30230144]
J Biochem Mol Toxicol. 2018 Dec;32(12):e22222.
For the first time, the enzymatic inhibition activity of 13 synthetic flavonoids was assessed by quantitative structure-activity relationship (QSAR) modeling and molecular docking with the three states of the enzyme horseradish peroxidase (HRP). The results show that apigenin, quercetin, kaempferol, fisetin, Tricetin, and luteolin exerted a high competitive inhibition on HRP (Ki between 0.14 and 1.74 mM) compared with other flavonoids. The QSAR model of enzymatic activity (R(2) = 0.95, RMSE = 5.48) showed that Ghose-Crippen octanol-water partition coefficient (Alog P) and lowest unoccupied molecular orbital's energy (epsilonlumo ) correlated with 0.65 and 0.17, respectively, with Ki values. According to the docking results using Molegro Virtual Docker program, all the flavonoids have shown great binding affinity towards peroxidase. Apigenin has the largest MolDock score in the three states of HRP noting an increased affinity of these flavonoids between compound I and compound II by 2.26%. However, these affinities strongly decrease between compound II and compound III by 28.43% especially for luteolin whose MolDock score decreased by 74.7%. With the results of docking, the affinities of the flavonoids tested and translated by their Ki values are much more presentative of the inhibition of the first reaction states of HRP because their inhibitory effect is important.
Analysis of mulberry leaf components in the treatment of diabetes using network pharmacology.[Pubmed:29782863]
Eur J Pharmacol. 2018 Aug 15;833:50-62.
Mulberry leaves are one of the most commonly used medicinal and herbaceous traditional Chinese medicines that are currently considered for the treatment of diabetes mellitus and its complications. The alkaloids, flavonoids, and polysaccharides in mulberry leaves impart regulatory effects on blood sugar levels. To identify the hypoglycemia-related active components in mulberry leaves and their targets, the present study conducted gas chromatography-mass spectrometer (GC/MS), which identified 202 components of mulberry leaf, of which 22 components may have significant curative effects on diabetes mellitus and its complications and chronic inflammation. The network-based pharmacological analysis platform was used to identify target proteins related to diabetes. Finally, the interaction networks of these target proteins were identified using STRING and Cytoscape. The results showed that mulberry leaf powder contains Tricetin, gallic acid, chlorogenic acid, and other drug components that can regulate tumor necrosis factor (TNF), peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma (PPARG), glycogen synthase kinase-3 beta (GSK3B), insulin receptor substrate 1 (IRS1), interleukin 6 (IL-6) and other proteins, which are related to the insulin and inflammatory signaling pathways, glucose metabolism and other related pathways, chronic inflammatory diseases, obesity, diabetic nephropathy, non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus and other diseases.
Chemical characterization complemented with chemometrics for the botanical origin identification of unifloral and multifloral honeys from India.[Pubmed:29580480]
Food Res Int. 2018 May;107:216-226.
Chemical fingerprints based on FTIR spectra, phenolics and volatiles were studied for a total of 30 honey types of eight different botanical origin i.e. litchi, neem, ginger, eucalyptus, lemon (unifloral) and Kashmiri white, BR Hills & Pan India honey (Multifloral). Chemometrics based on principal component analysis (PCA) was used as a complementary tool for chemical fingerprint of honey. ATR-FTIR had a good predictive capability to discriminate among honey when conjugated with chemometric tools, providing the rapid first-line of classification for honey. The specific phenolic compounds identified were homovanillic acid for neem, zingerone and gingerol for ginger, Tricetin for eucalyptus, hesperitin and naringenin for lemon honey. Analysis of volatiles led to identification of odor active compounds such as azadirachtin for neem and zingiberene in ginger honey for the first time, whereas cis-rose oxide for litchi, 2-hydroxycineole for eucalyptus and methyl anthranilate & limonene diol for lemon honey as per previous studies which were well correlated with PCA of phenolics and volatiles.
A new flavone glucoside together with known ellagitannins and flavones with anti-diabetic and anti-obesity activities from the flowers of pomegranate (Punica granatum).[Pubmed:29502447]
Nat Prod Res. 2019 Jan;33(2):252-257.
A new flavone glucoside Tricetin 4'-O-beta-glucopyranoside (1) and four known ellagitannins and flavones Tricetin (2), luteolin (3), ellagic acid (4), and granatin B (5) were isolated from the flowers of Punica granatum L. (Lythraceae). Their structures were established by 1D and 2D NMR as well as mass spectrometry analyses. Among all tested compounds, Tricetin (2) exhibited the strongest alpha-glucosidase inhibitory activity that was comparable to the anti-diabetic drug acarbose. Comparative structure-function analysis of tri-, tetra-, and pentahydroxy flavones [apigenin, luteolin (3), and Tricetin (2), respectively] suggested that a greater number of hydroxyl groups on the flavone molecule enhanced its suppression of alpha-glucosidase, alpha-amylase, and lipase activities.
A large-scale multiomics analysis of wheat stem solidness and the wheat stem sawfly feeding response, and syntenic associations in barley, Brachypodium, and rice.[Pubmed:29470681]
Funct Integr Genomics. 2018 May;18(3):241-259.
The wheat stem sawfly (WSS), Cephus cinctus Norton (Hymenoptera: Cephidae), is an important pest of wheat and other cereals, threatening the quality and quantity of grain production. WSS larvae feed and develop inside the stem where they are protected from the external environment; therefore, pest management strategies primarily rely on host plant resistance. A major locus on the long arm of wheat chromosome 3B underlies most of the variation in stem solidness; however, the impact of stem solidness on WSS feeding has not been completely characterized. Here, we used a multiomics approach to examine the response to WSS in both solid- and semi-solid-stemmed wheat varieties. The combined transcriptomic, proteomic, and metabolomic data revealed that two important molecular pathways, phenylpropanoid and phosphate pentose, are involved in plant defense against WSS. We also detected a general downregulation of several key defense transcripts, including those encoding secondary metabolites such as DIMBOA, Tricetin, and lignin, which suggested that the WSS larva might interfere with plant defense. We comparatively analyzed the stem solidness genomic region known to be associated with WSS tolerance in wild emmer, durum, and bread wheats, and described syntenic regions in the close relatives barley, Brachypodium, and rice. Additionally, microRNAs identified from the same genomic region revealed potential regulatory pathways associated with the WSS response. We propose a model outlining the molecular responses of the WSS-wheat interactions. These findings provide insight into the link between stem solidness and WSS feeding at the molecular level.


