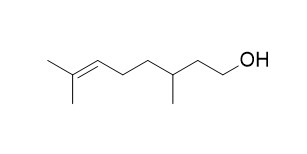
beta-CitronellolCAS# 106-22-9 |
Quality Control & MSDS
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 106-22-9 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | N/A | Appearance | Oil |
| Formula | C10H20O | M.Wt | 156.2 |
| Type of Compound | Monoterpenoids | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | Soluble in Chloroform,Dichloromethane,Ethyl Acetate,DMSO,Acetone,etc. | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | beta-Citronellol can controll Dermatophagoides farinae and D. pteronyssinus, it could be useful for managing populations of D. farinae and D. pteronyssinus. | |||||

beta-Citronellol Dilution Calculator

beta-Citronellol Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 6.402 mL | 32.0102 mL | 64.0205 mL | 128.041 mL | 160.0512 mL |
| 5 mM | 1.2804 mL | 6.402 mL | 12.8041 mL | 25.6082 mL | 32.0102 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.6402 mL | 3.201 mL | 6.402 mL | 12.8041 mL | 16.0051 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.128 mL | 0.6402 mL | 1.2804 mL | 2.5608 mL | 3.201 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.064 mL | 0.3201 mL | 0.6402 mL | 1.2804 mL | 1.6005 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- trans-Fertaric acid
Catalog No.:BCN9819
CAS No.:74282-22-7
- Tricetin
Catalog No.:BCN9818
CAS No.:520-31-0
- Withanoside V
Catalog No.:BCN9817
CAS No.:256520-90-8
- 3-Aminocoumarin
Catalog No.:BCN9816
CAS No.:1635-31-0
- 7-Ethoxy-4-methylcoumarin
Catalog No.:BCN9815
CAS No.:87-05-8
- Vicinin 2
Catalog No.:BCN9814
CAS No.:90456-53-4
- 1,2,3-Tri-n-Octanoylglycerol
Catalog No.:BCN9813
CAS No.:538-23-8
- Norcamphor
Catalog No.:BCN9812
CAS No.:497-38-1
- 3-Hydroxycoumarin
Catalog No.:BCN9811
CAS No.:939-19-5
- Quercetin 3-rutinoside 7-glucoside
Catalog No.:BCN9810
CAS No.:30311-61-6
- Isoedultin
Catalog No.:BCN9809
CAS No.:43043-08-9
- DL-Phenylalanine
Catalog No.:BCN9808
CAS No.:150-30-1
- Cimicifugic acid F
Catalog No.:BCN9821
CAS No.:220618-91-7
- Eclalbasaponin II
Catalog No.:BCN9822
CAS No.:78285-90-3
- Morindin
Catalog No.:BCN9823
CAS No.:60450-21-7
- Acetic acid hexyl ester
Catalog No.:BCN9824
CAS No.:142-92-7
- Grayanotoxin I
Catalog No.:BCN9825
CAS No.:4720-09-6
- Vaccarin E
Catalog No.:BCN9826
CAS No.:2252345-81-4
- 6-Hydroxyflavone
Catalog No.:BCN9827
CAS No.:6665-83-4
- Picrotoxinin
Catalog No.:BCN9828
CAS No.:17617-45-7
- 4,4'-Dimethoxychalcone
Catalog No.:BCN9829
CAS No.:2373-89-9
- Urushiol (15:1)
Catalog No.:BCN9830
CAS No.:35237-02-6
- 28-Homobrassinolide
Catalog No.:BCN9831
CAS No.:82373-95-3
- Ethyl caproate
Catalog No.:BCN9832
CAS No.:123-66-0
The impact that beta-citronellol isomers have on the biofilm formation of Candida yeasts.[Pubmed:32975125]
Nat Prod Res. 2020 Sep 25:1-5.
Infections associated with biofilms developed by Candida spp. are becoming a great problem due to its resistance against the immune response of the host and the action of antifungal agents. Hence, finding substances that can inhibit the development of biofilms increases the likelihood that these compounds one day can become good antifungals applied in the clinic. The aim of this study was to evaluate the effect of beta-Citronellol enantiomers on the biofilm formation by Candida albicans and Candida tropicalis isolated from bloodstream infections. Inhibition was evaluated by reading microplates treated with different concentrations of R-(+)-beta-Citronellol, S-(-)-beta-Citronellol and amphotericin B, compared to negative control, in spectrophotometer at 590 nm. All tested concentrations of beta-Citronellol enantiomers inhibited the biofilm formation of Candida. However, it is still necessary to evaluate the behavior of these isomers on mature biofilms, so that they can become more viable as antifungal therapeutical agents.
Influence of Rosa damascena hydrosol on skin flora (contact culture) after hand-rubbing.[Pubmed:32974119]
GMS Hyg Infect Control. 2020 Sep 7;15:Doc21.
Aim and Introduction: Rosa damascena is one of the most well-known species of the Rosaceae family and is widely used in the food and perfume industry. Rose hydrosol is a product which is produced by distillation of rose petals. There is very little research about the antimicrobial effect of rose hydrosol. In this study, we aimed to investigate the antibacterial effect of Rosa damascena hydrosol in vivo. Method: 45 adult volunteers who were not healthcare workers were included in this study. Exclusion criteria included existing skin disorders or lacerations, pregnancy, presence of nail polish, recent handwashing or use of antiseptic lotion/soap in the last week, and antibiotic use in the last 3 months. At baseline, each subject was asked to rub the fingertips of the dominant hand on a sheep-blood agar plate. The subjects were randomly divided into two groups: one group rubbed their hands with 3 mL of alcohol-based hand antiseptic and the other group with 3 mL of rose hydrosol. Following sample collection, the subjects were asked to rub their hands according to the World Health Organization's (WHO) "How to Hand Rub" technique. After the hand-rubbing sequence, the hands were allowed to air-dry and fingertip sampling was performed. Culture plates were evaluated by a microbiologist blinded to group assignment. Rose hydrosol was analysed by gas chromatography/mass spectrometry. Results: The main components of rose hydrosol are phenyl ethyl alcohol, beta-Citronellol and geraniol. Of the total of 45 participants, 23 were included in rose hydrosol group and 22 in the alcohol-based hand-rub group. The colony counts decreased significantly in the alcohol-based solution group after hand-rubbing, whereas there was no significant reduction in the rose hydrosol group. Conclusion: A number of studies have shown good antimicrobial activity in rose products, especially in rose oil, but we found no antibacterial effect of rose hydrosol after hand-rubbing. However, it must be borne in mind that the amount and types of rose hydrosol components are highly influenced by the given agro-meteorological conditions and technological production methods.
Chemosensory and Behavioural Responses of Ixodes scapularis to Natural Products: Role of Chemosensory Organs in Volatile Detection.[Pubmed:32759735]
Insects. 2020 Aug 4;11(8). pii: insects11080502.
Blacklegged ticks, Ixodes scapularis, represent a significant public health concern due to their vectoring of tick-borne disease. Despite their medical importance, there is still limited knowledge of the chemosensory system of this species, and thus a poor understanding of host-seeking behaviour and chemical ecology. We investigated the electrophysiological sensitivity of adult female blacklegged ticks to attractants and plant-derived compounds via an electrode inserted into the scutum. The response of female ticks to binary mixtures with a constant concentration of a selected attractant (butyric acid) and increasing concentration of volatile organic compounds (VOCs) (geraniol, phenethyl alcohol, beta-Citronellol, and citral) was recorded. A strict relationship between increasing volatile concentration and a decreasing response was observed for each VOC. Y-tube bioassays confirmed that tick attraction towards butyric acid decreased with the presence of a VOC, which exerted a deterrent effect. To determine the specific role of sensory appendages involved in the detection of attractant chemical stimuli, we tested tick electrophysiological response after removing appendages that house chemosensory sensilla (foretarsi, pedipalps, or both). The chemosensory response was related to the molecular structure of attractant odorant, and the lack of pedipalps significantly reduced olfactory responses, suggesting they play an important role in detecting attractants. This study provides new insight into the neurophysiological mechanisms underlying tick olfaction and the potential for interactions between attractant and deterrent chemical detection.
The Efficacy of Geraniol and ss-Citronellol against Freshwater and Marine Monogeneans.[Pubmed:32506710]
J Aquat Anim Health. 2020 Sep;32(3):127-132.
Monogeneans are parasitic flatworms that may be a threat for finfish aquaculture. In this study, the anthelmintic activity of two terpenes, geraniol and beta-Citronellol, was tested in vitro against ancyrocephalin and diplectanid monogeneans. Experiments were performed in both water and a culture medium. We observed that monogeneans in culture medium may be more tolerant to treatments compared with bioassays performed only in water. Concentrations of 300 mg/L of both compounds were required to kill 100% of monogeneans at 1 h postexposure. The toxicity of beta-Citronellol to fish was not evaluated. However, geraniol at 300 mg/L and 150 mg/L killed juvenile Nile Tilapia Oreochromis niloticus and White Snook Centropomus viridis, respectively, after a few minutes. Therefore, the present work suggests that other alternatives should be studied for use against monogeneans in aquaculture.
Oenological Characteristics of Fermented Apple Musts and Volatile Profile of Brandies Obtained from Different Apple Cultivars.[Pubmed:32503312]
Biomolecules. 2020 Jun 3;10(6). pii: biom10060853.
Volatile profile of spirits is the most important factor, because it can contribute to pleasant flavor. The aim of the study was to determine the impact of dessert apple cultivar used for fermentation on the concentration of volatile compounds in apple spirits. SPME-GC-MS (solid-phase microextraction- gas chromatography- mass spectrometry) method enables the detection of 69 substances and GC-FID (gas chromatography - flame ionization detector) 31 compounds. Characteristic volatiles for brandies obtained from Topaz were limonene, myrcene, methyl valerate and 1,1-diethoxy-propane, from Rubin-beta-Citronellol and isopropyl acetate, Elise-limonene, myrcene benzyl acetate and isopropyl acetate, Szampion-beta-Citronellol, Idared-1,1-diethoxy-propane and Jonagored-ethyl trans-4-decanoate. Of the ten analyzed apple spirits, those obtained from Topaz, Rubin and Elise cultivars demonstrated the most diverse profile of volatile compounds. Moreover, their oenological parameters that are the most important in the production of alcoholic beverages were the most favorable. On the other hand, the content of sugars was relatively low in Elise must, while it was highest in Topaz must, which later on translated into differences in alcohol content. Brandies obtained from Gloster contained the smallest concentrations of esters and terpenes. Results of the sensory analysis showed that highest rated brandies were obtained from Topaz, Rubin, Elise and Florina.
Increased anxiety-related behavior in mice following beta-citronellol inhalation.[Pubmed:32475228]
Libyan J Med. 2020 Dec;15(1):1767275.
beta-Citronellol is a monoterpene alcohol found in essential oils of various aromatic plant species. The physiological effects of beta-Citronellol inhalation on the central nervous system remain unclear. We investigated the effects of beta-Citronellol inhalation on mouse behavior. First, we examined whether the odor of beta-Citronellol was attractive or repellent to mice. Then, following 30 minutes of beta-Citronellol inhalation, a series of behavioral tests (elevated plus maze, open field, Y-maze, tail suspension, and forced swim tests) were performed. Mice were neither attracted to nor repelled by beta-Citronellol. Mice that inhaled beta-Citronellol showed an increase in anxiety-like behavior in the elevated plus maze and open field tests. Performance in the Y-maze and forced swim tests was not affected. These results indicate that beta-Citronellol acts on the central nervous system of mice following inhalation and increases anxiety. Essential oils and cosmetics containing beta-Citronellol should be used with caution.
Influence of Different Modalities of Grape Withering on Volatile Compounds of Young and Aged Corvina Wines.[Pubmed:32375272]
Molecules. 2020 May 3;25(9). pii: molecules25092141.
Withering is a practice traditionally used in various regions to produce sweet or dry wines. During withering there is an increase in sugar content but also a modification in volatile compound profiles. Controlling metabolic changes through the dehydration process to obtain wines with desired characteristics is therefore a challenging opportunity. The effects of two different withering technologies, post-harvest or on-vine with blocked sap vessel flow, on the volatile profile of young and aged Corvina red wines was investigated. The results showed that modulation of wine aroma due to the withering process is associated with fermentative metabolites, such as esters, higher alcohols, and acids, as well as grape-related compounds such as C6 alcohols, terpenes and norisoprenoids. Significant differences were also found by comparing the two withering techniques. Post-harvest in a traditional "fruttaio" warehouse wines showed higher content of ethyl acetate, ethyl butanoate, beta-Citronellol and 3-oxo-alpha-ionol, whereas post-harvest withering on-vine increased beta-damascenone in wines. The type of withering technique has an influence on the evolution of some aroma compounds during the aging of wine, among them linalool, (E)-1-(2,3,6-trimethylphenyl)buta-1,3-diene (TPB), n-hexyl acetate, ethyl acetate, ethyl 3-methylbutanoate, 3-oxo-alpha-ionol and beta-damascenone.
Fate of Grape-Derived Terpenoids in Model Systems Containing Active Yeast Cells.[Pubmed:32153191]
J Agric Food Chem. 2020 Nov 25;68(47):13294-13301.
Terpenes are important contributors to wine aroma. Free and glycosidically bound terpenes are primarily formed in grapes. During fermentation, they undergo important transformation catalyzed by yeast, so that the terpene profile of grape is substantially different from that of the corresponding wine. The present paper assessed the ability of a Saccharomyces cerevisiae strain to transform 17 different terpenes. Biotransformation was performed by placing target compounds in incubation with resting cells. Volatile compounds produced were extracted by solid-phase extraction and analyzed by gas chromatography-mass spectrometry. Geranyl acetate, neryl acetate, citronellyl acetate, and menthyl acetate were formed from the corresponding terpene alcohols. beta-Citronellol was the main product of geraniol transformation; geranial, an intermediate of this pathway, has also been detected. Limonene was hydroxylated by yeast to form carveol, trans-2,8-menthadien-1-ol, and cis-2,8-menthadien-1-ol. Moreover, yeast cells were found to be able to adsorb a significant portion of the terpenes present in the reaction batches, with the extent of this phenomenon being linked to terpene hydrophobicity.
(R)-(+)-beta-Citronellol and (S)-(-)-beta-Citronellol in Combination with Amphotericin B against Candida Spp.[Pubmed:32150884]
Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Mar 5;21(5). pii: ijms21051785.
The enantiomers (R)-(+)-beta-Citronellol and (S)-(-)-beta-Citronellol are present in many medicinal plants, but little is understood about their bioactivity against Candida yeasts. This study aimed to evaluate the behavior of positive and negative enantiomers of beta-Citronellol on strains of Candida albicans and C. tropicalis involved in candidemia. The minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) and minimum fungicide concentration (MFC) were determined. The evaluation of growth kinetics, mechanism of action, and association studies with Amphotericin B (AB) using the checkerboard method was also performed. R-(+)-beta-Citronellol and S-(-)-beta-Citronellol presented a MIC50% of 64 microg/mL and a MFC50% of 256 microg/mL for C. albicans strains. For C. tropicalis, the isomers exhibited a MIC50% of 256 microg/mL and a MFC50% of 1024 microg/mL. In the mechanism of action assay, both substances displayed an effect on the fungal membrane but not on the fungal cell wall. Synergism and indifference were observed in the association of R-(+)-beta-Citronellol and AB, while the association between S-(-)-beta-Citronellol and AB displayed synergism, additivity, and indifference. In conclusion, both isomers of beta-Citronellol presented a similar profile of antifungal activity. Hence, they can be contemplated in the development of new antifungal drugs providing that further research is conducted about their pharmacology and toxicity.
Chemical composition of hydrosol volatiles of flowers from ten Paeonia x suffruticosa Andr. cultivars from Luoyang, China.[Pubmed:31928365]
Nat Prod Res. 2020 Jan 13:1-5.
Hydrosol volatiles from flowers of ten Paeonia x suffruticosa Andr. cultivars were analysed by gas chromatography-mass spectrometry (GC-MS) and GC-flame ionisation detector (GC-FID) for the first time. Fifty components were identified representing 97.6-99.8% of total composition, in which oxygenated compounds (87.4-99.8%) predominated. Hydrosol volatiles of five and two cultivars presented chemotypes of 2-phenylethanol (48.0-79.5%) and 1,3,5-trimethoxybenzene (72.8%, 50.2%), respectively. Hydrosol volatiles of 'XYTH' rich in beta-Citronellol (57.2%) probably represented a newly defined chemotype with beta-Citronellol percentage over 50%. 'GFCC' hydrosol volatiles presented a balanced profile with 1,3,5-trimethoxybenzene (31.9%), beta-Citronellol (31.5%) and 2-phenylethanol (23.0%). 'LHZL' hydrosol volatiles were distinct from others due to occurrence of 6,9-heptadecadiene (2.0%), 2-heptanol (1.8%), pentadecane (1.5%), (Z)-3-nonen-1-ol (1.1%) and geraniol (15.7%). Chemotype characterisation of P. x suffruticosa Andr. hydrosols was of significance considering numerous cultivars of the species and potential applications of the hydrosols.
Geraniol targets KV1.3 ion channel and exhibits anti-inflammatory activity in vitro and in vivo.[Pubmed:31669719]
Fitoterapia. 2019 Nov;139:104394.
Naturally occurring monoterpenes are known for their various pharmacological activities including anti-inflammation. KV1.3 ion channel is a voltage-gated potassium channel and has been validated as a drug target for autoimmune and chronic inflammatory diseases like psoriasis. Here we experimentally test the direct interaction between monoterpenes and KV1.3 ion channel. Our electrophysiological analysis determined that monoterpenes (geraniol, nerol, beta-Citronellol, citral and linalool) have inhibitory effects on KV1.3 ion channel. Representatively, geraniol reversibly blocked KV1.3 currents in a voltage-dependent manner with an IC50 of 490.50+/-1.04muM at +40mV in HEK293T cells. At the effective concentrations, geraniol also inhibited cytokine secretion of activated human T cells, including IL-2, TNF-alpha and IFN-gamma. In an imiquimod-induced psoriasis-like animal model, geraniol administration significantly reduced psoriasis area and severity index scores, ameliorated the deteriorating histopathology and decreased the degree of splenomegaly. Together, our findings not only suggest that monoterpenes may serve as lead molecules for the development of KV1.3 inhibitors, but also indicate that geraniol could be considered as a promising therapeutic candidate to treat autoimmune diseases.
[Cloning and characterization of a monoterpene synthase gene from Tripterygium wilfordii].[Pubmed:31602927]
Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2019 Aug;44(16):3588-3593.
Tripterygium wilfordii is a medicinal plant commonly used in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis,and with pharmacological activities in anti-tumor and obesity treatment. The known active ingredients in T. wilfordii are mainly terpenoids,but with very low content. Therefore,the analysis of the biosynthesis pathway of terpenoids in T. wilfordii has become a research hotspot to solve the problem of its resources. Terpenoid synthase( TPS) is a key enzyme that catalyzes the formation of a wide variety of terpenoid skeletons. In this study,a gene fragment with an ORF of 1 785 bp was cloned from T. wilfordii. Bioinformatics analysis was performed using NCBI's BLASTP,ProtParam and Interpro online tools and MEGA 6.0 software. The response of this gene to methyl jasmonate was also detected by real-time fluorescent quantitative PCR,and its catalytic function was verified by prokaryotic expression and in vitro enzymatic assay. Bioinformatics analysis indicated that the amino acid sequence encoded by this gene had both N-terminal domain and C-terminal domain of TPS,as well as the DDxx D conserved domain of the class I of TPS family. And Tw MTS gathered together with TPS-b subfamily in the Neighbor-Joining Tree constructed with known homologous TPSs. The results of RT-PCR showed that 50 mumol.L-1 MeJA 12 h could increase the expression of Tw MTS to 735 times in the control group at 12 h,and 1 644 times at 24 h. In addition,in vitro enzymatic reaction results showed that Tw MTS can catalyze the production of beta-Citronellol with GPP as substrate,indicating that Tw MTS was a monoterpene synthase. The above results provided a new element for the synthetic biology database of T. wilfordii terpenoids,and laid the foundation for future biosynthesis research.
Potential of hydrocarbon and oxygenated monoterpenes against Culex pipiens larvae: Toxicity, biochemical, pharmacophore modeling and molecular docking studies.[Pubmed:31378352]
Pestic Biochem Physiol. 2019 Jul;158:156-165.
Culex pipiens is a main vector for Bancroftian filariasis, Rift Valley Fever and diseases caused by other viruses, leaving several peoples with disabilities. In recent years, plant derived compounds have received much attention as potential alternatives to synthetic chemicals due to their low toxicity to mammals and environmental persistence. Twenty-one monoterpenes from different chemical groups (hydrocarbons and oxygenated products) were evaluated against Culex pipiens larvae. In addition, in vivo biochemical studies including effects on acetylcholine esterase (AChE), acid and alkaline phosphatases (ACP and ALP), total adenosine triphosphatase (ATPase) and gamma-aminobutyric acid transaminase (GABA-T) were investigated. Furthermore, in silico studies including pharmacophore elucidation, ADMET analysis and molecular docking of these compounds were performed. Among all tested monoterpenes, hydrocarbons [p-cymene, (R)-(+)-limonene and (+)-alpha-pinene], acetates (cinnamyl acetate, citronellyl acetate, eugenyl acetate and terpinyl acetate), alcohols [(+/-)-beta-Citronellol and terpineol], aldehydes [citral and (1R)-(-)-myrtenal] and ketone [(R)-(+)-pulegone] exhibited the highest larval toxicity with LC50=14.88, 27.97, 26.13, 2.62, 3.81, 2.74, 21.65, 1.64, 21.70, 21.76, 1.68 and 1.90mg/L after 48h of exposure, respectively. The compounds proved a significant inhibition of all tested enzymes except total ATPase. The biochemical and molecular docking studies proved that AChE and GABA-T were the main targets for the tested monoterpenes.
Release of Fragrances from Cotton Functionalized with Carbohydrate-Binding Module Proteins.[Pubmed:31283162]
ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2019 Aug 7;11(31):28499-28506.
Perspiration as a response to daily activity and physical exercise results in unpleasant odors that cause social unrest and embarrassment. To tackle it, functional textiles incorporating fragrances could be an effective clothing deodorizing product. This work presents two strategies for the release of beta-Citronellol from functionalized cotton with carbohydrate-binding module (CBM)-based complexes (OBP::GQ20::CBM/beta-Citronellol-approach 1 and CBM::GQ20::SP-DS3-liposome/beta-Citronellol-approach 2). CBM from Cellulomonas fimi was fused with the odorant-binding protein (OBP::GQ20::CBM) and with an anchor peptide with affinity to the liposome membrane (CBM::GQ20::SP-DS3). In approach 1, OBP fusion protein served as a fragrance container, whereas in approach 2, the fragrance was loaded into liposomes with a higher cargo capacity. The two strategies showed a differentiated beta-Citronellol release profile triggered by an acidic sweat solution. OBP::GQ20::CBM complex revealed a fast release (31.9% and 25.8% of the initial amount, after 1.5 and 24 h of exposure with acidic sweat solution, respectively), while the CBM::GQ20::SP-DS3-liposome complex demonstrated a slower and controlled release (5.9% and 10.5% of the initial amount, after 1.5 and 24 h of exposure with acidic sweat solution, respectively). Both strategies revealed high potential for textile functionalization aimed at controlled release of fragrances. The OBP::GQ20::CBM/beta-Citronellol complex is ideal for applications requiring fast release of a high amount of fragrance, whereas the CBM::GQ20::SP-DS3-liposome/beta-Citronellol complex is more suitable for prolonged and controlled release of a lower amount of beta-Citronellol.


