Soyasapogenol ACAS# 508-01-0 |
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 508-01-0 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 160495 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C30H50O4 | M.Wt | 474.7 |
| Type of Compound | Triterpenoids | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Synonyms | Soyasapogenin A | ||
| Solubility | Soluble in chloroform and methan | ||
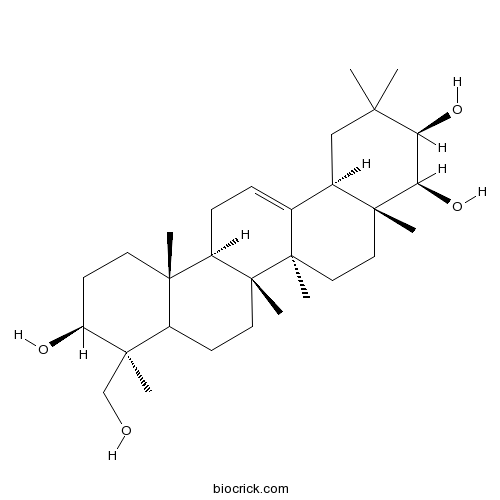
| Chemical Name | (3R,4S,4aR,6aR,6aS,6bR,9S,10S,12aR,14bR)-9-(hydroxymethyl)-2,2,4a,6a,6b,9,12a-heptamethyl-1,3,4,5,6,6a,7,8,8a,10,11,12,13,14b-tetradecahydropicene-3,4,10-triol | ||
| SMILES | CC1(CC2C3=CCC4C5(CCC(C(C5CCC4(C3(CCC2(C(C1O)O)C)C)C)(C)CO)O)C)C | ||
| Standard InChIKey | CDDWAYFUFNQLRZ-POFPXMCLSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C30H50O4/c1-25(2)16-19-18-8-9-21-27(4)12-11-22(32)28(5,17-31)20(27)10-13-30(21,7)29(18,6)15-14-26(19,3)24(34)23(25)33/h8,19-24,31-34H,9-17H2,1-7H3/t19-,20?,21-,22+,23+,24-,26-,27+,28-,29-,30-/m1/s1 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | 1. Soyasapogenol A and soyasapogenol B concentrated extracts show a greater ability to inhibit proliferation of cultured Hep-G2 when compared to a total soyasaponin extract that did not contain any soyasapogenols. 2. Soyasapogenol A directly prevents apoptosis of hepatocytes, and secondly, inhibits the elevation of plasma TNF-α, which consequently resulted in the prevention of liver damage in the concanavalin A-induced hepatitis model. 3. Soyasapogenol A shows estrogenic activities. |
| Targets | TNF-α |

Soyasapogenol A Dilution Calculator

Soyasapogenol A Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.1066 mL | 10.533 mL | 21.0659 mL | 42.1319 mL | 52.6648 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.4213 mL | 2.1066 mL | 4.2132 mL | 8.4264 mL | 10.533 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.2107 mL | 1.0533 mL | 2.1066 mL | 4.2132 mL | 5.2665 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0421 mL | 0.2107 mL | 0.4213 mL | 0.8426 mL | 1.0533 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0211 mL | 0.1053 mL | 0.2107 mL | 0.4213 mL | 0.5266 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- Polyphyllin B
Catalog No.:BCN2833
CAS No.:50773-42-7
- Polyphyllin D
Catalog No.:BCN2401
CAS No.:50773-41-6
- TPCA-1
Catalog No.:BCC2473
CAS No.:507475-17-4
- 3-Cyano-6-isopropylchromone
Catalog No.:BCC8627
CAS No.:50743-32-3
- Vecuronium Bromide
Catalog No.:BCC2498
CAS No.:50700-72-6
- Pennogenin
Catalog No.:BCN2839
CAS No.:507-89-1
- Borneol
Catalog No.:BCN4964
CAS No.:507-70-0
- Boc-Cys(Bzl)-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3376
CAS No.:5068-28-0
- Terfenadine
Catalog No.:BCC3866
CAS No.:50679-08-8
- Chasmanine
Catalog No.:BCN5409
CAS No.:5066-78-4
- Vandrikidine
Catalog No.:BCN5615
CAS No.:50656-92-3
- Alkaloid C
Catalog No.:BCN1897
CAS No.:50656-88-7
- Oleanolic acid
Catalog No.:BCN5616
CAS No.:508-02-1
- 13(18)-Oleanen-3-ol
Catalog No.:BCN5617
CAS No.:508-04-3
- Glutinone
Catalog No.:BCN5618
CAS No.:508-09-8
- N-acetylanonaine
Catalog No.:BCN2666
CAS No.:5894-74-6
- Ouabagenin
Catalog No.:BCC8227
CAS No.:508-52-1
- Rosenonolactone
Catalog No.:BCN5621
CAS No.:508-71-4
- Convallatoxin
Catalog No.:BCC8155
CAS No.:508-75-8
- Hellebrigenol
Catalog No.:BCN8238
CAS No.:508-79-2
- Vasicinol
Catalog No.:BCN5812
CAS No.:5081-51-6
- Astrophylline
Catalog No.:BCN2151
CAS No.:5081-53-8
- Hastatoside
Catalog No.:BCN6898
CAS No.:50816-24-5
- Suchilactone
Catalog No.:BCN6752
CAS No.:50816-74-5
Effect of soyasapogenol A and soyasapogenol B concentrated extracts on HEP-G2 cell proliferation and apoptosis.[Pubmed:18361499]
J Agric Food Chem. 2008 Apr 23;56(8):2603-8.
The growth inhibition and the induction of apoptosis brought about by soyasaponins extracted from soy flour ( Glycine max (L.)) and concentrated for soyasapogenols A and B formed by hydrolysis were tested for cytoactivity in the human hepatocellular carcinoma cell line Hep-G2. Concentrated Soyasapogenol A (SG-A) and soyasapogenol B (SG-B) extracts contained approximately 69.3% and 46.2% of their respective aglycones (soyasapogenols) assessed by HPLC and ESI-MS, while the soyasaponin extract (TS), derived from crude methanol extraction, did not contain any detectable amounts of SG-A or SG-B. An MTT viability assay showed that all three extracts had an effect on Hep-G2 proliferation in a dose-response manner with 72 h LC50 values of 0.594+/-0.021 mg/mL for TS, 0.052+/-0.011 mg/mL for SG-A, and 0.128+/-0.005 mg/mL for SG-B. Apoptotic cells were determined by flow cytometry cell cycle analysis and confocal laser scanning microscopy (CLSM). Cell cycle analysis indicated a significant ( P< 0.05) greater sub-G1 buildup of apoptotic cells at 24 h (25.63+/-2.1%) and 72 h (47.1+/-3.5%) for the SG-A extract compared to SG-B, whereas the TS extract produced only a minor buildup of sub-G1 cells. CLSM confirmed a morphological change of all treatments after 24 h, at the respective LC50 concentrations. These results show that the samples that contained mainly soyasapogenols A and B showed a greater ability to inhibit proliferation of cultured Hep-G2 when compared to a total soyasaponin extract that did not contain any soyasapogenols.
Protective effects of soyasapogenol A on liver injury mediated by immune response in a concanavalin A-induced hepatitis model.[Pubmed:10720649]
Eur J Pharmacol. 2000 Mar 10;391(1-2):175-81.
The present study was carried out to analyze the effects of Soyasapogenol A on the liver injury mediated by the immune response in concanavalin A-induced hepatitis in mice. Soyasapogenol A reduced the number of infiltrating inflammatory cells in the liver and significantly lowered the elevated level of plasma tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-alpha) 2 h after concanavalin A treatment, and then markedly reduced the elevated plasma alanine aminotransferase activity and decreased the number of apoptotic bodies in the liver parenchymal cells but not in the sinusoidal cells at 24 h. Since the effect of Soyasapogenol A on the elevated plasma TNF-alpha level was not appreciable compared to the preventive effect of Soyasapogenol A on the elevated plasma alanine aminotransferase level, these results suggest that Soyasapogenol A directly prevents apoptosis of hepatocytes, and secondly, inhibits the elevation of plasma TNF-alpha, which consequently resulted in the prevention of liver damage in the concanavalin A-induced hepatitis model.
Estrogenic and antiproliferative properties of soy sapogenols in human breast cancer cells in vitro.[Pubmed:12419690]
Food Chem Toxicol. 2002 Dec;40(12):1767-74.
Two soy sapogenols, Soyasapogenol A (SA) and soyasapogenol B (SB) were tested for their estrogenic activities in estrogen responsive MCF-7 or estrogen-insensitive MDA-MB-231 (MDA) human breast cancer cells. SB and SA had differential actives on cell proliferation with 10 microM SB being growth inhibitory to MDA cells with no significant effect at any concentration on MCF-7 cells. SA also inhibited MDA cell proliferation at 10 micro, but at this same dose stimulated a 2.5-fold increase in MCF-7 proliferation. SA (0.1-10 microM) induced pS2 mRNA levels and the induction was blocked by co-treatment of cells with the anti-estrogen ICI 182,780. SA also induced the formation of an ER-ERE DNA complex measured by electrophoretic mobility shift assay. In summary, these results show that Soyasapogenol A is estrogenic, whereas soyasapogenol B is growth inhibitory.


