Soyasapogenol BCAS# 595-15-3 |
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 595-15-3 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 115012 | Appearance | White powder |
| Formula | C30H50O3 | M.Wt | 458.7 |
| Type of Compound | Triterpenoids | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Synonyms | Soyasapogenin B; Soyasapogenol I | ||
| Solubility | Soluble in chloroform and methan | ||
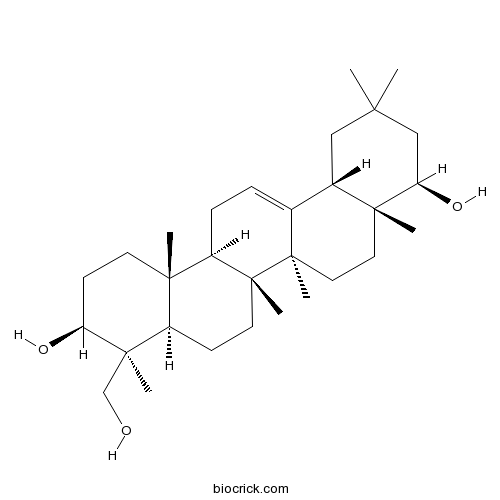
| Chemical Name | (3S,4S,4aR,6aR,6bS,8aR,9R,12aS,14aR,14bR)-4-(hydroxymethyl)-4,6a,6b,8a,11,11,14b-heptamethyl-1,2,3,4a,5,6,7,8,9,10,12,12a,14,14a-tetradecahydropicene-3,9-diol | ||
| SMILES | CC1(CC2C3=CCC4C5(CCC(C(C5CCC4(C3(CCC2(C(C1)O)C)C)C)(C)CO)O)C)C | ||
| Standard InChIKey | YOQAQNKGFOLRGT-UXXABWCISA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C30H50O3/c1-25(2)16-20-19-8-9-22-27(4)12-11-23(32)28(5,18-31)21(27)10-13-30(22,7)29(19,6)15-14-26(20,3)24(33)17-25/h8,20-24,31-33H,9-18H2,1-7H3/t20-,21+,22+,23-,24+,26+,27-,28+,29+,30+/m0/s1 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Soyasapogenol B has anti-cancer, hypocholesterolemic, anticomplementary, hepatoprotective effects, it inhibits proliferation of cultured Hep-G2. |
| Targets | PKC |
| In vitro | Hepatoprotective constituents in plants. 14. Effects of soyasapogenol B, sophoradiol, and their glucuronides on the cytotoxicity of tert-butyl hydroperoxide to HepG2 cells.[Pubmed: 12951488]Biol Pharm Bull. 2003 Sep;26(9):1357-60.The effects of Soyasapogenol B, sophoradiol, their glucuronides, and glycyrrhizin on the hepatotoxicity of tert-butyl hydroperoxide (t-BuOOH) in a human-liver-derived cell line (HepG2 cells) were investigated. Effect of soyasapogenol A and soyasapogenol B concentrated extracts on HEP-G2 cell proliferation and apoptosis.[Pubmed: 18361499]J Agric Food Chem. 2008 Apr 23;56(8):2603-8.The growth inhibition and the induction of apoptosis brought about by soyasaponins extracted from soy flour ( Glycine max (L.)) and concentrated for soyasapogenols A and B formed by hydrolysis were tested for cytoactivity in the human hepatocellular carcinoma cell line Hep-G2. |
| Cell Research | Soyasaponin I, III, and Soyasapogenol B Inhibit Proliferation and Modulate PKC Expression in Caco-2 Human Colon Cancer Cells.[Reference: WebLink]J. Food Res., 2013, 2(4):81-7.Group B saponins, the predominant form of saponins in heat-treated soy products, have been shown to possess hypocholesterolemic, antimutagenic, and anticarcinogenic properties. Previous studies have evaluated crude mixtures of soyasaponins, but studies evaluating a single purified soyasaponin as an anticarcinogenic agent are limited. |
| Structure Identification | Pest Manag Sci. 2011 Aug;67(8):1015-22.Soyasapogenol B and trans-22-dehydrocam- pesterol from common vetch (Vicia sativa L.) root exudates stimulate broomrape seed germination.[Pubmed: 21480462]Orobanche and Phelipanche species (the broomrapes) are root parasitic plants, some of which represent serious weed problems causing severe yield losses on important crops. Control strategies have largely focused on agronomic practices, resistant crop varieties and herbicides, albeit with marginal success. An alternative control method is the induction of suicidal seed germination with natural substances isolated from root exudates of host and non-host plants.
|

Soyasapogenol B Dilution Calculator

Soyasapogenol B Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.1801 mL | 10.9004 mL | 21.8007 mL | 43.6015 mL | 54.5019 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.436 mL | 2.1801 mL | 4.3601 mL | 8.7203 mL | 10.9004 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.218 mL | 1.09 mL | 2.1801 mL | 4.3601 mL | 5.4502 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0436 mL | 0.218 mL | 0.436 mL | 0.872 mL | 1.09 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0218 mL | 0.109 mL | 0.218 mL | 0.436 mL | 0.545 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- Calycanthine
Catalog No.:BCN7823
CAS No.:595-05-1
- Testosterone undecanoate
Catalog No.:BCC9173
CAS No.:5949-44-0
- Citric acid monohydrate
Catalog No.:BCN8492
CAS No.:5949-29-1
- Z-D-Glu(OBzl)-OH
Catalog No.:BCC2772
CAS No.:59486-73-6
- Tafamidis
Catalog No.:BCC5268
CAS No.:594839-88-0
- NSC 146109 hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC2410
CAS No.:59474-01-0
- Dihydropyrocurzerenone
Catalog No.:BCN8061
CAS No.:59462-26-9
- Nimbin
Catalog No.:BCN4617
CAS No.:5945-86-8
- Monotropein
Catalog No.:BCN6280
CAS No.:5945-50-6
- 1-Methyl-2-undecylquinolin-4(1H)-one
Catalog No.:BCN6591
CAS No.:59443-02-6
- 1F-Fructofuranosylnystose
Catalog No.:BCN8287
CAS No.:59432-60-9
- Boc-HoSer(Bzl)-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3244
CAS No.:59408-74-1
- Megestrol Acetate
Catalog No.:BCC4365
CAS No.:595-33-5
- Boc-Ser-OBzl
Catalog No.:BCC3440
CAS No.:59524-02-6
- H-D-Ala-OtBu.HCl
Catalog No.:BCC2849
CAS No.:59531-86-1
- Carnosol
Catalog No.:BCN1055
CAS No.:5957-80-2
- 3-Amino-2-naphthoic acid
Catalog No.:BCC8607
CAS No.:5959-52-4
- H-D-Gln-OH
Catalog No.:BCC2920
CAS No.:5959-95-5
- Glycopyrrolate
Catalog No.:BCC4275
CAS No.:596-51-0
- Alpha-Obscurine
Catalog No.:BCN6701
CAS No.:596-55-4
- AC 55649
Catalog No.:BCC7359
CAS No.:59662-49-6
- Calyciphylline A
Catalog No.:BCN4098
CAS No.:596799-30-3
- 3-O-Acetyl-beta-boswellic acid
Catalog No.:BCN2672
CAS No.:5968-70-7
- 6alpha-Hydroxyhispanone
Catalog No.:BCN7416
CAS No.:596814-48-1
Hepatoprotective constituents in plants. 14. Effects of soyasapogenol B, sophoradiol, and their glucuronides on the cytotoxicity of tert-butyl hydroperoxide to HepG2 cells.[Pubmed:12951488]
Biol Pharm Bull. 2003 Sep;26(9):1357-60.
The effects of Soyasapogenol B, sophoradiol, their glucuronides, and glycyrrhizin on the hepatotoxicity of tert-butyl hydroperoxide (t-BuOOH) in a human-liver-derived cell line (HepG2 cells) were investigated. Glycyrrhizin showed significant dose-dependent protective effects against the cytotoxicity of t-BuOOH. Among Soyasapogenol B and its glucuronides, the monoglucuronide showed the most potent hepatoprotective activity, followed by Soyasapogenol B itself. Soyasaponin III was weakly protective, while soyasaponin I increased the toxicity of t-BuOOH. Among sophoradiol and its glucuronides, sophoradiol itself showed the most potent hepatoprotective activity, which was equal to glycyrrhizin, while the monoglucuronide and kaikasaponin III showed an increase in cytotoxicity. These results were considerably different from those reported previously on the protective effects of these compounds using primary cultures of immunologically injured rat liver cells. Consequently, the hepatoprotective action of the triterpene derivatives investigated would be different in HepG2 cells and in rat primary hepatocyte cultures.
Soyasapogenol B and trans-22-dehydrocam- pesterol from common vetch (Vicia sativa L.) root exudates stimulate broomrape seed germination.[Pubmed:21480462]
Pest Manag Sci. 2011 Aug;67(8):1015-22.
BACKGROUND: Orobanche and Phelipanche species (the broomrapes) are root parasitic plants, some of which represent serious weed problems causing severe yield losses on important crops. Control strategies have largely focused on agronomic practices, resistant crop varieties and herbicides, albeit with marginal success. An alternative control method is the induction of suicidal seed germination with natural substances isolated from root exudates of host and non-host plants. RESULTS: Soyasapogenol B [olean-12-ene-3,22,24-triol(3beta,4beta,22beta)] and trans-22-dehydrocampesterol [(ergosta-5,22-dien-3-ol, (3beta,22E,24S)] were isolated from Vicia sativa root exudates. They were identified by comparing their spectroscopic and optical properties with those reported in the literature. Soyasapogenol B was very specific, stimulating the germination of O. minor seeds only, whereas trans-22-dehydrocampesterol stimulated P. aegyptiaca, O. crenata, O. foetida and O. minor. CONCLUSION: Soyasapogenol B and trans-22-deydrocampesterol were isolated for the first time from Vicia sativa root exudates, and their biological activity as stimulants of Orobanche or Phelipanche sp. seed germination was reported.
Effect of soyasapogenol A and soyasapogenol B concentrated extracts on HEP-G2 cell proliferation and apoptosis.[Pubmed:18361499]
J Agric Food Chem. 2008 Apr 23;56(8):2603-8.
The growth inhibition and the induction of apoptosis brought about by soyasaponins extracted from soy flour ( Glycine max (L.)) and concentrated for soyasapogenols A and B formed by hydrolysis were tested for cytoactivity in the human hepatocellular carcinoma cell line Hep-G2. Concentrated soyasapogenol A (SG-A) and Soyasapogenol B (SG-B) extracts contained approximately 69.3% and 46.2% of their respective aglycones (soyasapogenols) assessed by HPLC and ESI-MS, while the soyasaponin extract (TS), derived from crude methanol extraction, did not contain any detectable amounts of SG-A or SG-B. An MTT viability assay showed that all three extracts had an effect on Hep-G2 proliferation in a dose-response manner with 72 h LC50 values of 0.594+/-0.021 mg/mL for TS, 0.052+/-0.011 mg/mL for SG-A, and 0.128+/-0.005 mg/mL for SG-B. Apoptotic cells were determined by flow cytometry cell cycle analysis and confocal laser scanning microscopy (CLSM). Cell cycle analysis indicated a significant ( P< 0.05) greater sub-G1 buildup of apoptotic cells at 24 h (25.63+/-2.1%) and 72 h (47.1+/-3.5%) for the SG-A extract compared to SG-B, whereas the TS extract produced only a minor buildup of sub-G1 cells. CLSM confirmed a morphological change of all treatments after 24 h, at the respective LC50 concentrations. These results show that the samples that contained mainly soyasapogenols A and B showed a greater ability to inhibit proliferation of cultured Hep-G2 when compared to a total soyasaponin extract that did not contain any soyasapogenols.


