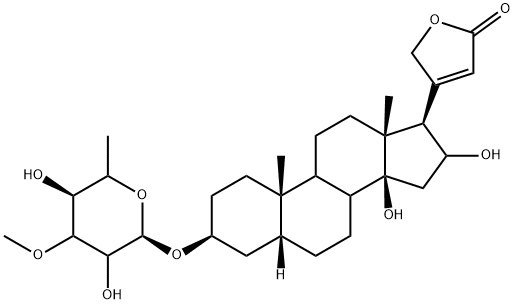
StrospesideCAS# 595-21-1 |
Quality Control & MSDS
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 595-21-1 | SDF | File under preparation. |
| PubChem ID | N/A | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C30H46O9 | M.Wt | 550.76 |
| Type of Compound | Cardenolides and its Sapogenins | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Synonyms | Gitoxigenin 3-O-monodigitaloside | ||
| Solubility | Soluble in Chloroform,Dichloromethane,Ethyl Acetate,DMSO,Acetone,etc. | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||

Strospeside Dilution Calculator

Strospeside Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 1.8157 mL | 9.0784 mL | 18.1567 mL | 36.3135 mL | 45.3918 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.3631 mL | 1.8157 mL | 3.6313 mL | 7.2627 mL | 9.0784 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.1816 mL | 0.9078 mL | 1.8157 mL | 3.6313 mL | 4.5392 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0363 mL | 0.1816 mL | 0.3631 mL | 0.7263 mL | 0.9078 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0182 mL | 0.0908 mL | 0.1816 mL | 0.3631 mL | 0.4539 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- Quercetin-3-O-α-(6'''-caffeoylglucosyl-β-1,2-rhamnoside)
Catalog No.:BCX1991
CAS No.:851222-75-8
- Digitoxigenin monodigitoxoside
Catalog No.:BCX1990
CAS No.:18404-43-8
- Isolithospermic acid
Catalog No.:BCX1899
CAS No.:1217879-76-9
- Ipalbinium
Catalog No.:BCX1898
CAS No.:110200-24-3
- Tenuifoliose D
Catalog No.:BCX1895
CAS No.:139682-04-5
- Licorisoflavan I
Catalog No.:BCX1894
CAS No.:2444736-45-0
- 3-epi-Tilifodiolide
Catalog No.:BCX1897
CAS No.:1983982-42-8
- Genistein 7-O-β-D-glucopyranoside-4’-O-[α-L-rhamnopyranosyl-(1→2)-β-D-glucopyranoside]
Catalog No.:BCX2014
CAS No.:361447-29-2
- 3,5,6,6-tetramethyl-4,5,5a,6,7,8-hexahydrocyclopenta[c]pentalen-2(1H)-one
Catalog No.:BCX1893
CAS No.:1689570-10-2
- 4-((2-ethylidene-4-hydroxy-6-methylhept-5-en-1-yl)oxy)-bergaptol
Catalog No.:BCX1892
CAS No.:2519548-06-0
- Abrine D
Catalog No.:BCX1896
CAS No.:862504-05-0
- Digitalin, 16-anhydro-
Catalog No.:BCX1891
CAS No.:7044-34-0
- Digitoxigenin glucomethyloside
Catalog No.:BCX1993
CAS No.:40950-57-0
- Anhydroperiplogenone
Catalog No.:BCX1994
CAS No.:1247-04-7
- 5,6,7,8-Tetrahydroxy-3',4'-dimethoxyflavone
Catalog No.:BCX1995
CAS No.:2930091-30-6
- (6S,9R)-2-Hydroxy-4-(2,6,6-trimethyl-4-oxo-cyclohex-2-enyl)-butyric acid
Catalog No.:BCX1996
CAS No.:2089289-59-6
- 5,6-Dihydroxy-8-methoxyflavone-7-O-glucuronide
Catalog No.:BCX1997
CAS No.:1169879-99-5
- 3-Hydroxy-1,2-dimethoxyxanthone
Catalog No.:BCX1998
CAS No.:20362-27-0
- 1,2,3-Trimethoxyxanthone
Catalog No.:BCX1999
CAS No.:27460-10-2
- 1-Methoxy-2,3-methylenedioxyxanthone
Catalog No.:BCX2000
CAS No.:63625-05-8
- 1,3-Dihydroxy-2-methoxyxanthone
Catalog No.:BCX2001
CAS No.:87339-74-0
- Digitalin
Catalog No.:BCX2002
CAS No.:752-61-4
- T-Muurolol
Catalog No.:BCX2003
CAS No.:19912-62-0
- T-Cadinol
Catalog No.:BCX2004
CAS No.:5937-11-1
Cytotoxicity and chromosomal aberrations induced by methanolic extract of Cuscuta reflexa and its pure compounds on meristematic cells of Allium species.[Pubmed:28649079]
Pak J Pharm Sci. 2017 Mar;30(2):521-529.
Cuscuta reflexa (Convolvulaceae), is commonly known as amarbel or akashbel. In Bangladesh and Nepal some of the tribes use C. reflexa against edema, body ache, cancer, skin infections and liver disorders. Despite its traditional uses there is no information regarding genotoxic effects of either the plant extract or its pure compounds. Methanolic extract of C. reflexa (MECR) and pure compounds derived from it namely, odoroside H, neritaloside, and Strospeside, were evaluated in Allium cepa L. and A. sativum L. for their effects on root growth, root apical meristem mitotic index (MI) , and chromosomal aberrations (CAs). In this study, we adopted a new method of calculating percent change in root length. MECR caused a concentration- and time- dependent inhibition in root length at 100 - 10000mug/ml in A. cepa root. It was accompanied by a subsequent decline in MI which is an indicative of its cytotoxic effect. On the contrary, at low concentrations a significant rise in root length was noticeable. In A. sativum, MECR also reduced the root length having IC(50) values ~8 x and 4.3 x lower than A. cepa. A variety of CAs were evident in both Allium systems after treatment with MECR, odoroside H and neritaloside. Thus in MECR, cardenolides glycosides, i.e. odoroside H and neritaloside could be accountable for its genotoxicity.
Cardiovascular activity of a methanolic extract of Digitalis purpurea spp. heywoodii.[Pubmed:10940580]
J Ethnopharmacol. 2000 Aug;71(3):437-42.
The paper deals with the effects of a glycosidal extract of Digitalis heywoodii, ssp. of Digitalis purpurea L., (Schrophulariaceae) grown in Badajoz (Spain), on isolated cardiac auricle of rabbits, urinary excretion of rats, as well as its emetic effect in pigeons. These effects using vehicle (propylene glycol-ethanol-water, 40:10:50) and digoxin as standards are presented. The extract at concentrations of 20 and 40 microg/ml produced an increase in the contraction force of auricles in a dose-dependent way. At doses of 15 and 30 mg/kg a slight diuretic and natriuretic effect was observed. The active dose range for emesis was 0.5-4 mg/kg and a decrease of the emesis time within 10 min of injection in dose-dependent manner was obtained. The pharmacological activity of the extract is related to gitoxin derivatives (digitalinum verum and Strospeside), the most abundant compounds obtained from the leaves of Digitalis purpurea spp. heywoodii.
Biotransformation of 5betaH-pregnan-3betaol-20-one and cardenolides in cell suspension cultures of Nerium oleander L.[Pubmed:24232778]
Plant Cell Rep. 1990 Apr;8(11):651-5.
In order to demonstrate enzyme activities playing a role in the biosynthesis of cardenolides and 2,6-dideoxysugars, 5betaH-pregnan-3betaol-20-one and cardenolides (digitoxigenin, oleandrigenin/L-oleandrose, oleandrin, neriifolin, digitoxigeninmonodigitoxoside and Strospeside) were fed to cell suspension cultures of Nerium oleander L.. It could be shown that cell suspension cultures of Nerium oleander L. are able to oxidize, isomerize and glucosylate 5betaH-steroidaglycones at C-3. The respective glucosides of the 5betaH-steroid-aglycones are the main biotransformation products. These cell cultures are an appropriate tool for the production of labelled 5betaH-steroidglucosides.
High-performance liquid chromatographic determination of secondary cardiac glycosides in Digitalis purpurea leaves.[Pubmed:2808604]
J Chromatogr. 1989 Oct 6;479(2):319-25.
An analytical method for the determination of secondary cardiac glycosides in Digitalis purpurea leaves by high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) is described. The procedure consisted of extraction of dry leaf powder with ethanol-chloroform (2:1) and clean-up by Sep-Pak cartridges prior to HPLC analysis. HPLC was performed on an octylsilyl bonded silica column, using acetonitrile-methanol-water (4:4:5) for trisdigitoxosides and acetonitrile-methanol-water (8:30:43) for Strospeside; the effluent was monitored by ultraviolet detection (at 220 nm). Quantitation of these cardiac glycosides was carried out by the internal standard method. The amounts of digitoxin, gitoxin, gitaloxin and Strospeside per 100 mg of dry leaf powder were estimated to be 22.6, 14.0, 54.7 and 1.9 micrograms, respectively. The method is sufficiently sensitive and reproducible to assay secondary glycosides in Digitalis purpurea leaves.
Bio-Transformation of (G-3H)-digitoxin and (G-3H)-digoxin by Digitalis purpurea.[Pubmed:17396954]
Planta Med. 1982 Oct;46(2):113-8.
The biotransformation of (G- (3)H) digitoxin and (G- (3)H) digoxin has been studied in a strain of Digitalis purpurea in which cardenolides of the B series were predominant. A direct method of introducing the tritiated glycosides into the plant is described and the conversions monitored at intervals during the subsequent 6 weeks. Conversion of labelled digitoxin to purpurea glycosides A and B, gitoxin and gitaloxin occurred. Of particular interest was the conversion of digitoxin to the digitalose - containing glycosides, Strospeside and verodoxin. Digoxin, an exogenous glycoside to D. purpurea, was glycosylated to desacetyl lanatoside C; there was some conversion to B and E series glycosides but only minimal formation of A series cardenolides.


