TriflorosideCAS# 53823-10-2 |
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 53823-10-2 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 101688128 | Appearance | Powder |
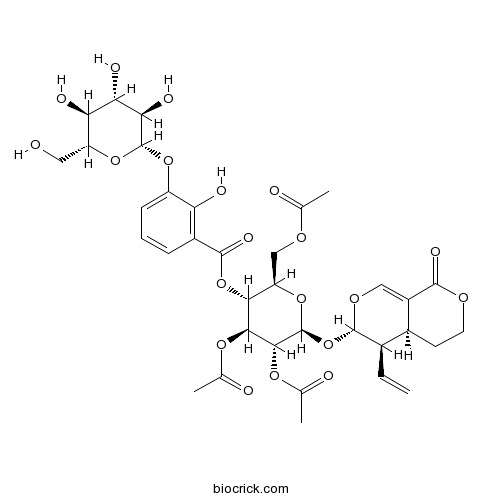
| Formula | C35H42O20 | M.Wt | 782.70 |
| Type of Compound | Iridoids | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | Soluble in Chloroform,Dichloromethane,Ethyl Acetate,DMSO,Acetone,etc. | ||
| Chemical Name | [(2R,3R,4S,5R,6S)-4,5-diacetyloxy-2-(acetyloxymethyl)-6-[[(3S,4R,4aS)-4-ethenyl-8-oxo-4,4a,5,6-tetrahydro-3H-pyrano[3,4-c]pyran-3-yl]oxy]oxan-3-yl] 2-hydroxy-3-[(2S,3R,4S,5S,6R)-3,4,5-trihydroxy-6-(hydroxymethyl)oxan-2-yl]oxybenzoate | ||
| SMILES | CC(=O)OCC1C(C(C(C(O1)OC2C(C3CCOC(=O)C3=CO2)C=C)OC(=O)C)OC(=O)C)OC(=O)C4=C(C(=CC=C4)OC5C(C(C(C(O5)CO)O)O)O)O | ||
| Standard InChIKey | RMBMLYUFYBZPCX-XQARLGSBSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C35H42O20/c1-5-17-18-9-10-46-31(44)20(18)12-48-33(17)55-35-30(50-16(4)39)29(49-15(3)38)28(23(53-35)13-47-14(2)37)54-32(45)19-7-6-8-21(24(19)40)51-34-27(43)26(42)25(41)22(11-36)52-34/h5-8,12,17-18,22-23,25-30,33-36,40-43H,1,9-11,13H2,2-4H3/t17-,18+,22-,23-,25-,26+,27-,28-,29+,30-,33+,34-,35+/m1/s1 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | 1. Trifloroside is a bitter iridoid glycoside. |

Trifloroside Dilution Calculator

Trifloroside Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 1.2776 mL | 6.3881 mL | 12.7763 mL | 25.5526 mL | 31.9407 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.2555 mL | 1.2776 mL | 2.5553 mL | 5.1105 mL | 6.3881 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.1278 mL | 0.6388 mL | 1.2776 mL | 2.5553 mL | 3.1941 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0256 mL | 0.1278 mL | 0.2555 mL | 0.5111 mL | 0.6388 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0128 mL | 0.0639 mL | 0.1278 mL | 0.2555 mL | 0.3194 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- Onitisin
Catalog No.:BCN5713
CAS No.:53823-03-3
- Onitin
Catalog No.:BCN5712
CAS No.:53823-02-2
- 1-Benzothiophene-3-carbaldehyde
Catalog No.:BCC8454
CAS No.:5381-20-4
- DCC
Catalog No.:BCC2810
CAS No.:538-75-0
- Ribostamycin Sulfate
Catalog No.:BCC4710
CAS No.:53797-35-6
- CP-724714
Catalog No.:BCC1188
CAS No.:537705-08-1
- UF 010
Catalog No.:BCC6478
CAS No.:537672-41-6
- Lycernuic acid A
Catalog No.:BCN5711
CAS No.:53755-77-4
- Lyclaninol
Catalog No.:BCN5710
CAS No.:53755-76-3
- Neorauflavene
Catalog No.:BCN4848
CAS No.:53734-75-1
- Neorauflavane
Catalog No.:BCN4791
CAS No.:53734-74-0
- Luteolin-7-O-glucoside
Catalog No.:BCN5388
CAS No.:5373-11-5
- 3-(beta-D-Glucopyranosyloxy)-2-hydroxybenzoic acid methyl ester
Catalog No.:BCN7734
CAS No.:53827-68-2
- Flavaprin
Catalog No.:BCN5714
CAS No.:53846-49-4
- 8-Prenylnaringenin
Catalog No.:BCN2998
CAS No.:53846-50-7
- Caboxine A
Catalog No.:BCN5715
CAS No.:53851-13-1
- Desoxo-narchinol A
Catalog No.:BCN7636
CAS No.:53859-06-6
- Ticlopidine HCl
Catalog No.:BCC4973
CAS No.:53885-35-1
- Hordenine
Catalog No.:BCN1424
CAS No.:539-15-1
- Perillen
Catalog No.:BCN6527
CAS No.:539-52-6
- Allicin
Catalog No.:BCN2347
CAS No.:539-86-6
- Tranilast
Catalog No.:BCC2514
CAS No.:53902-12-8
- Nb-Feruloyltryptamine
Catalog No.:BCN3899
CAS No.:53905-13-8
- Pentostatin
Catalog No.:BCC1845
CAS No.:53910-25-1
Isolation and identification of constituents with activity of inhibiting nitric oxide production in RAW 264.7 macrophages from Gentiana triflora.[Pubmed:23599008]
Planta Med. 2013 May;79(8):680-6.
Gentiana triflora is widely used to treat inflammation, jaundice, hepatitis, and rheumatism. In this study, three new compounds, including a benzo seven-membered ring compound, gentioxepine (1), two secoiridoid glucosides, (1S,5R,9R)-deglucosylTrifloroside (2) and (1S,5R,9R)-scabraside (3), together with seven known ones, (+)-syringaresinol (4), deglucogelidoside (5), 3,4-dihydro-1H,6H,8H-naphtho[1,2-c:4,5-c',d']dipyrano-1,8-dione (6), deglucoscabraside (7), 2-hydroxy-3-O-beta-D-glucosyloxy benzoic acid methyl ester (8), gentiolactone (9), and Trifloroside (10), were isolated from the ethanol extract of Gentiana triflora. Their structures were mainly confirmed on the basis of NMR, MS, IR, CD, and UV spectral evidences. Inhibiting activities of nitric oxide production of eight of the compounds isolated, as well as gentiopicroside, were evaluated in the macrophage cell line RAW 264.7. The results show that the three new compounds and compound 7 could significantly suppress lipopolysaccharide-induced production of NO, with IC50s of 2.2 microM, 37.5 microM, 17.6 microM and 6.9 microM, respectively. Among them, compounds 1, 3, and 7 showed stronger inhibitory activity than that of the clinically used drug indometacin. Other tested compounds exerted moderate inhibiting activities.
Secoiridoid glycosides and an antifungal anthranilate derivative from Gentiana tibetica.[Pubmed:9611826]
Phytochemistry. 1998 Apr;47(7):1223-6.
Repetitive chromatography of the methanol extract of the roots of Gentiana tibetica afforded two new secoiridoid glycosides and a novel antifungal anthranilic acid derivative, together with beta-sitosterol, daucosterol, oleanolic acid, loganic acid, gentiopicroside, sweroside, 2'-(2,3-dihydroxybenzoyl)sweroside, Trifloroside, rindoside and macrophylloside A. The structures of the new products were determined mainly by spectroscopic methods as 8-hydroxy-10-hydrosweroside, isomacrophylloside and ethyl N-docosanoylanthranilate. Ethyl N-docosanoylanthranilate inhibited the growth of the human pathogenic fungi Candida albicans and Aspergillus flavus. The taxonomic significance of the constituent is discussed briefly.
The Glycosidase Treatment of Gentianae Scabrae Radix Converts Trifloroside into Deglucosyltrifloroside with an Enhancement of Antioxidative Effects.[Pubmed:28933978]
J Med Food. 2017 Oct;20(10):951-958.
Herbal medicines were subjected to enzyme reaction by using a commercial glycosidase AMG-300L, and were evaluated for enhancement of their antioxidative activities. The methanolic extract of Gentianae Scabrae Radix (GSR) showed the most dramatic changes after enzyme reaction, as seen in the high-performance liquid chromatography profiles and an increase in the 2,2-diphenyl-1-picrylhydrazyl (DPPH) radical scavenging effect. Trifloroside (1, TF) was identified as being significantly decreased by enzyme reaction, whereas deglucosylTrifloroside (2, DTF) increased. The optimal reaction time to induce DTF was 24 h at 30 degrees C. The content increased from 1.00 +/- 0.29 mg/g of extract (gex) to 2.80 +/- 0.85 mg/gex after 24 h of enzyme reaction. DTF showed better antioxidative effect than TF in the DPPH, Trolox equivalent antioxidant capacity, and reactive oxygen species (ROS) in HT22 cell assays. In addition, when HT22 cells were stressed by 5 mM glutamate, 50 muM of DTF significantly inhibited the glutamate-induced lactate dehydrogenase leakage, Ca(2+) influx, lipid peroxidation, and intracellular ROS production. These data demonstrated that the enzyme-treated GSR and its increased level of antioxidant DTF could be useful as a starting point in the discovery of functional foods to prevent various oxidative stresses, especially neurodegenerative disorders.
A bitter herbal medicine Gentiana scabra root extract stimulates glucagon-like peptide-1 secretion and regulates blood glucose in db/db mouse.[Pubmed:26129938]
J Ethnopharmacol. 2015 Aug 22;172:219-26.
ETHNOPHARMACOLOGICAL RELEVANCE: Gentiana scabra root extract (GS) is frequently prescribed as an internal remedy in traditional Korean medicine for treatment of diabetes mellitus. GS contains bitter iridoid glycosides including loganic acid, gentiopicrin, Trifloroside, and rindoside. We previously reported that the intestinal bitter taste sensation stimulates GLP-1 secretion, and thereupon hypothesized that the blood glucose regulatory effect of GS is due to its GLP-1 secreting effect in enteroendocrine L cells. MATERIALS AND METHOD: We studied GLP-1 secreting effect of GS treatment and its cellular downstream mechanism in human enteroendocrine NCI-H716 cells using the G protein-coupled receptor (GPCR) pathway inhibitors. Intracellular calcium assay also demonstrated the signal transduction pathway stimulated by the GS treatment. Using db/db mice, we performed oral glucose tolerance test (OGTT) to examine the blood glucose lowering effect of GS administration. We also collected the mouse plasma during the OGTT to measure the GLP-1 and insulin levels. RESULT: We demonstrated dose-dependent GLP-1 secreting effect of GS on the NCI-H716 cells. The GLP-1 secreting effect of GS is mediated by the G protein betagamma-subunit and inositol triphosphate. Using db/db mice, we found that the effect of GS on lowering blood glucose is due to its GLP-1 secretion, and consequential insulinotropic effect. The chemical fingerprint of GS was obtained through a direct analysis in realtime mass spectrometry (DART-MS) and high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC)/MS. Through the GLP-1 secretion study, we found that loganic acid, an iridoid glycoside, contributes to the GLP-1 secreting effect of GS. CONCLUSION: The findings of this study highlight the potential of exploiting the antidiabetic effect of GS on type 2 diabetes mellitus patients.
Acyl secoiridoids and antifungal constituents from Gentiana macrophylla.[Pubmed:9397205]
Phytochemistry. 1996 Jul;42(5):1305-13.
LC-UV-mass spectrometry and bioassay co-directed fractionation of an aqueous acetone extract of the roots of Gentiana macrophylla gave three new chromene derivatives and two novel and six known secoiridoids, along with kurarinone, kushenol I, beta-sitosterol, stigmasterol, daucosterol, beta-sitosterol-3-O-gentiobioside, alpha-amyrin, oleanolic acid, isovitexin, gentiobiose and methyl 2-hydroxy-3-(1-beta-D-glucopyranosyl)oxybenzoate. The structures of the new products were established from spectral and chemical evidence as 2-methoxyanofinic acid and macrophyllosides A-D. The six known secoiridoids were gentiopicroside, sweroside, 6'-O-beta-D-glucosylgentiopicroside, 6'-O-beta-D-glucosylsweroside, Trifloroside and rindoside. The new acid (2-methoxyanofinic acid), its methyl ester, kurarinone and kushenol I were shown to be active against the plant pathogenic fungus Cladosporium cucumerinum. The methyl ester and kurarinone inhibited also the growth of the human pathogenic yeast Candida albicans. Structure-activity relationships were studied. Thus, addition of a methoxyl group to the benzene nucleus of anofinic acid (2,2-dimethyl-2H-1-benzopyran-6-carboxylic acid) increased the antifungal activity remarkably whereas glycosylation at the carboxylic moiety was found to remove the activity. Esterification of the new acid induced its activity against C. albicans, but decreased its growth inhibition properties against C. cucumerinum. Hydroxylation of kurarinone at the 3 beta-position removed its activity against C. albicans and decreased the inhibition of C. cucumerinum. In addition, the chemotaxonomic significance of the identified constituents is discussed.
Preparative Separation and Purification of Four Glycosides from Gentianae radix by High-Speed Counter-Current Chromatography and Comparison of Their Anti-NO Production Effects.[Pubmed:29149084]
Molecules. 2017 Nov 17;22(11). pii: molecules22112002.
Secoiridoid and iridoid glycosides are the main active components of Gentianaeradix. In this work, one iridoid and three secoiridoid glycosides from Gentianaeradix have been purified by high-speed counter-current chromatography in two runs using different solvent systems. Ethyl acetate-n-butanol-water (2:1:3, v/v/v) was the optimum solvent system to purify ca. 4.36 mg of loganic acid, 3.05 mg of swertiamarin, and 35.66 mg of gentiopicroside with 98.1%, 97.2% and 98.6% purities, respectively, while 31.15 mg of Trifloroside with 98.9% purity was separated using hexane-ethyl acetate-methanol-water (1:3:1:3, v/v/v/v). The structures of the glycosides were identified by mass spectrometry and NMR. After separation, the anti-nitric oxide production effects of the compounds on lipopolysaccharide-induced BV-2 murine microglial cells were also evaluated. All of the compounds inhibited the production of nitric oxide in lipopolysaccharide-induced BV-2 cells with high cell viabilities in a concentration-dependent manner, which demonstrated that were able to be used as a nitric oxide inhibitor.
Iridoids from seeds of Gentiana lutea.[Pubmed:12822897]
Nat Prod Res. 2003 Aug;17(4):221-4.
In the seeds of Gentiana lutea L. there were also detected, in addition to the known sweroside and getiopicroside, loganic acid 3 and Trifloroside 4 that is present as main glycosidic component. The structures of 3 and 4 were established by spectroscopic studies.
Secoiridoids from Gentiana siphonantha.[Pubmed:9396170]
Phytochemistry. 1997 Nov;46(6):1035-8.
Repeated fractionations of the methanol extract of the subterranean parts (rhizomes and roots) of Gentiana siphonantha afforded two new and five known secoiridoids, in addition to the widespread plant constituents beta-sitiosterol, daucosterol and oleanolic acid. The structures of the new acyl secoiridoid glycosides were elucidated as 6'-gentisoyl 8-epikingiside and 2'-gentisoyl gelidoside mainly by a combination of high field NMR techniques. The known secoiridoids were identified as gentiolactone, gentiopicroside, sweroside, gelidoside and Trifloroside. None of these constituents was active against human pathogenic fungi (Candida albican, Aspergillus flavus and Trichoderma viride). The chemotaxonomic significance of the isolates is discussed briefly.


