Usnic acidCAS# 125-46-2 |
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 125-46-2 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 5646 | Appearance | Powder |
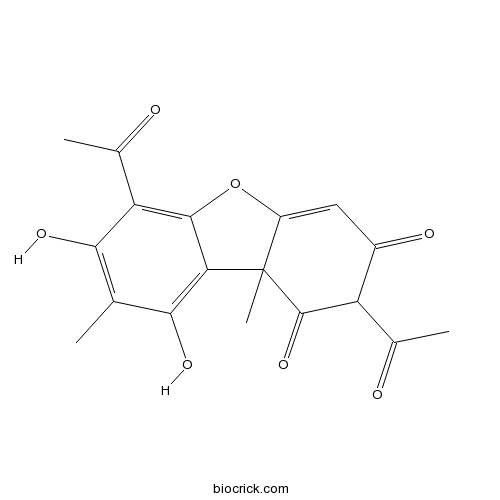
| Formula | C18H16O7 | M.Wt | 344.3 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | Soluble in Chloroform,Dichloromethane,Ethyl Acetate,DMSO,Acetone,etc. | ||
| Chemical Name | 2,6-diacetyl-7,9-dihydroxy-8,9b-dimethyldibenzofuran-1,3-dione | ||
| SMILES | CC1=C(C(=C2C(=C1O)C3(C(=CC(=O)C(C3=O)C(=O)C)O2)C)C(=O)C)O | ||
| Standard InChIKey | CUCUKLJLRRAKFN-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C18H16O7/c1-6-14(22)12(8(3)20)16-13(15(6)23)18(4)10(25-16)5-9(21)11(7(2)19)17(18)24/h5,11,22-23H,1-4H3 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||

Usnic acid Dilution Calculator

Usnic acid Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.9044 mL | 14.5222 mL | 29.0444 mL | 58.0889 mL | 72.6111 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.5809 mL | 2.9044 mL | 5.8089 mL | 11.6178 mL | 14.5222 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.2904 mL | 1.4522 mL | 2.9044 mL | 5.8089 mL | 7.2611 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0581 mL | 0.2904 mL | 0.5809 mL | 1.1618 mL | 1.4522 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.029 mL | 0.1452 mL | 0.2904 mL | 0.5809 mL | 0.7261 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- Primidone
Catalog No.:BCC4930
CAS No.:125-33-7
- Vomicine
Catalog No.:BCN6735
CAS No.:125-15-5
- Isobornyl acetate
Catalog No.:BCN8296
CAS No.:125-12-2
- Prednisone 21-acetate
Catalog No.:BCC9128
CAS No.:125-10-0
- Ajugamarin L2
Catalog No.:BCN3662
CAS No.:124961-67-7
- Ajugacumbin A
Catalog No.:BCN3657
CAS No.:124961-66-6
- Raddeanoside R8
Catalog No.:BCN6555
CAS No.:124961-61-1
- Tectoroside
Catalog No.:BCN6672
CAS No.:124960-89-0
- Tolterodine tartrate
Catalog No.:BCC4586
CAS No.:124937-52-6
- (R)-(+)-Tolterodine
Catalog No.:BCC4054
CAS No.:124937-51-5
- Benzoyl leuco methylene blue
Catalog No.:BCC8862
CAS No.:1249-97-4
- Isoaltholactone
Catalog No.:BCN4826
CAS No.:124868-11-7
- Aminoglutethimide
Catalog No.:BCC4368
CAS No.:125-84-8
- 8-Prenylluteone
Catalog No.:BCN4771
CAS No.:125002-91-7
- Fmoc-D-Ala-OPfp
Catalog No.:BCC3037
CAS No.:125043-04-1
- 8-(3-Ethoxy-2-hydroxy-3-methylbutyl)-7-methoxycoumarin
Catalog No.:BCN1594
CAS No.:125072-68-6
- Epinortrachelogenin
Catalog No.:BCN3719
CAS No.:125072-69-7
- XL388
Catalog No.:BCC2059
CAS No.:1251156-08-7
- 26-Nor-8-oxo-alpha-onocerin
Catalog No.:BCN6131
CAS No.:125124-68-7
- 1-(4-methoxyphenyl)-2-methylpropan-1-one
Catalog No.:BCN8163
CAS No.:2040-20-2
- Rosthornin A
Catalog No.:BCN6132
CAS No.:125164-55-8
- Vibralactone D
Catalog No.:BCN6747
CAS No.:1251748-32-9
- N-Methoxyanhydrovobasinediol
Catalog No.:BCN4856
CAS No.:125180-42-9
- Rosthornin B
Catalog No.:BCN6133
CAS No.:125181-21-7
Usnic acid, as a biotic factor, changes the ploidy level in mosses.[Pubmed:29531694]
Ecol Evol. 2018 Feb 8;8(5):2781-2787.
Lichens and mosses often share the same environmental conditions where they compete for substrate and other essential factors. Lichens use secondary metabolites as allelochemicals to repel surrounding plants and potential rivals. In mosses, endoreduplication leads to the occurrence of various ploidy levels in the same individual and has been suggested as an adaptation to abiotic stresses. Here, we show that also biotic factors such as Usnic acid, an allelochemical produced by lichens, directly influenced the level of ploidy in mosses. Application of Usnic acid changed the nuclei proportion and significantly enhanced the endoreduplication index in two moss species, Physcomitrella patens and Pohlia drummondii. These investigations add a new aspect on secondary metabolites of lichens which count as biotic factors and affect ploidy levels in mosses.
Usnic acid-loaded polyaniline/polyurethane foam wound dressing: preparation and bactericidal activity.[Pubmed:29752105]
Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2018 Aug 1;89:33-40.
The improved bactericidal activity of new composites for wound dressing prototypes represents an important strategy for development of more efficient devices that make use of synergistic interaction between components. The doping level of polyaniline represents a critical parameter for its corresponding biologic activity. In this work, it is explored the doping effect of Usnic acid on undoped polyaniline, that introduces important advantages namely, improved bactericidal activity of polyaniline and the anti-biofilm properties of lichen derivative. The deposition of the resulting material on polyurethane foam potentializes its applicability as wound dressing, characterizing a new platform for application against Escherichia coli and Staphylococcus aureus.
Usnic acid reactive metabolites formation in human, rat, and mice microsomes. Implication for hepatotoxicity.[Pubmed:29981369]
Food Chem Toxicol. 2018 Oct;120:112-118.
Usnic acid is a lichen compound which is extensively studied due to its cytotoxic, antiproliferative, antimicrobial, antiviral, antiprotozoal, and anti-inflammatory activities. Despite a broad spectrum of biological properties, Usnic acid is a hepatotoxic agent, thus its potential use as a drug is limited. Certain hepatotoxic drugs may act by generating reactive metabolites that damage the liver. The aim of the study was to predict the biotransformation of Usnic acid enantiomers to reactive products using a trapping assay with glutathione in human, rat, and mice liver microsomes. Our results indicate that each enantiomer forms two reactive metabolites; in turn, these metabolites form adducts with glutathione, which may partially explain the toxicity of Usnic acid. In silico analysis indicated structural alerts for the generation of reactive metabolites in Usnic acid formula. This study proposes a novel mode of the hepatic toxicity of Usnic acid enantiomers; it also provides some useful suggestions for designing safer Usnic acid derivatives.


