Vulpic acidCAS# 521-52-8 |
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 521-52-8 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 54690323 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C19H14O5 | M.Wt | 322.32 |
| Type of Compound | Miscellaneous | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | Soluble in Chloroform,Dichloromethane,Ethyl Acetate,DMSO,Acetone,etc. | ||
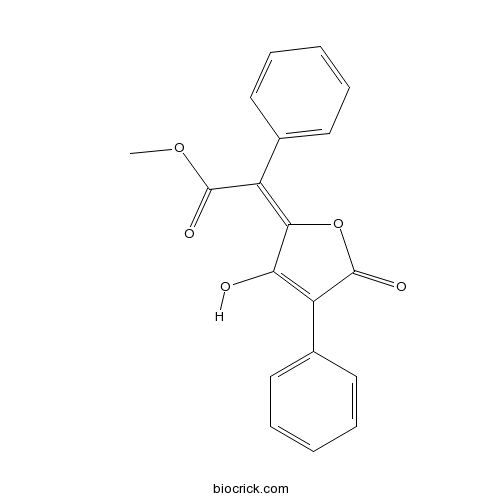
| Chemical Name | methyl (2E)-2-(3-hydroxy-5-oxo-4-phenylfuran-2-ylidene)-2-phenylacetate | ||
| SMILES | COC(=O)C(=C1C(=C(C(=O)O1)C2=CC=CC=C2)O)C3=CC=CC=C3 | ||
| Standard InChIKey | OMZRMXULWNMRAE-BMRADRMJSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C19H14O5/c1-23-18(21)15(13-10-6-3-7-11-13)17-16(20)14(19(22)24-17)12-8-4-2-5-9-12/h2-11,20H,1H3/b17-15+ | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | 1. Vulpic acid can inhibit one or more enzymes (PfFabI, PfFabG, and PfFabZ) from the plasmodial fatty acid biosynthesis (FAS-II) pathway, a potential drug target for liver stage activity. 2. Vulpic acid has therapeutic and prophylactic potential to be antibacterial and antiplasmodial agents. |
| Targets | Fatty Acid Synthase |

Vulpic acid Dilution Calculator

Vulpic acid Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 3.1025 mL | 15.5125 mL | 31.0251 mL | 62.0501 mL | 77.5627 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.6205 mL | 3.1025 mL | 6.205 mL | 12.41 mL | 15.5125 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.3103 mL | 1.5513 mL | 3.1025 mL | 6.205 mL | 7.7563 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0621 mL | 0.3103 mL | 0.6205 mL | 1.241 mL | 1.5513 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.031 mL | 0.1551 mL | 0.3103 mL | 0.6205 mL | 0.7756 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- Pedicin
Catalog No.:BCN4845
CAS No.:521-51-7
- Cannabinol
Catalog No.:BCN7968
CAS No.:521-35-7
- Sciadopitysin
Catalog No.:BCN5662
CAS No.:521-34-6
- Bilobetin
Catalog No.:BCN5661
CAS No.:521-32-4
- Stanolone
Catalog No.:BCC9153
CAS No.:521-18-6
- Androstenediol
Catalog No.:BCC8828
CAS No.:521-17-5
- Dromostanolone propionate
Catalog No.:BCC8954
CAS No.:521-12-0
- Mestanolone
Catalog No.:BCC9022
CAS No.:521-11-9
- 2-Hydroxy-7-O-methylscillascillin
Catalog No.:BCN5659
CAS No.:52096-50-1
- H-Val-pNA
Catalog No.:BCC3139
CAS No.:52084-13-6
- NCS-382
Catalog No.:BCC6794
CAS No.:520505-01-5
- Isoschaftoside
Catalog No.:BCN3011
CAS No.:52012-29-0
- Physcion
Catalog No.:BCN5663
CAS No.:521-61-9
- Frangulin A
Catalog No.:BCC8174
CAS No.:521-62-0
- Cinnamoylcocaine
Catalog No.:BCN1429
CAS No.:521-67-5
- Broxyquinoline
Catalog No.:BCC4642
CAS No.:521-74-4
- Karanjin
Catalog No.:BCN8370
CAS No.:521-88-0
- 2,4-Dihydroxy-6-methoxy-3-formylacetophenone
Catalog No.:BCN1430
CAS No.:52117-67-6
- 3-O-Acetylpinobanksin
Catalog No.:BCN5660
CAS No.:52117-69-8
- H-Tyr(Bzl)-OBzl.HCl
Catalog No.:BCC3131
CAS No.:52142-01-5
- Piperitol
Catalog No.:BCN3968
CAS No.:52151-92-5
- 7-Hydroxy-2,3,4,5-tetrahydro-1H-benzofuro[2,3-c]azepin-1-one
Catalog No.:BCC3960
CAS No.:521937-07-5
- N'-Methylammodendrine
Catalog No.:BCN2147
CAS No.:52196-10-8
- Evoxine
Catalog No.:BCN5664
CAS No.:522-11-2
Potential of lichen secondary metabolites against Plasmodium liver stage parasites with FAS-II as the potential target.[Pubmed:23806111]
J Nat Prod. 2013 Jun 28;76(6):1064-70.
Chemicals targeting the liver stage (LS) of the malaria parasite are useful for causal prophylaxis of malaria. In this study, four lichen metabolites, evernic acid (1), Vulpic acid (2), psoromic acid (3), and (+)-usnic acid (4), were evaluated against LS parasites of Plasmodium berghei. Inhibition of P. falciparum blood stage (BS) parasites was also assessed to determine stage specificity. Compound 4 displayed the highest LS activity and stage specificity (LS IC50 value 2.3 muM, BS IC50 value 47.3 muM). The compounds 1-3 inhibited one or more enzymes (PfFabI, PfFabG, and PfFabZ) from the plasmodial fatty acid biosynthesis (FAS-II) pathway, a potential drug target for LS activity. To determine species specificity and to clarify the mechanism of reported antibacterial effects, 1-4 were also evaluated against FabI homologues and whole cells of various pathogens (S. aureus, E. coli, M. tuberculosis). Molecular modeling studies suggest that lichen acids act indirectly via binding to allosteric sites on the protein surface of the FAS-II enzymes. Potential toxicity of compounds was assessed in human hepatocyte and cancer cells (in vitro) as well as in a zebrafish model (in vivo). This study indicates the therapeutic and prophylactic potential of lichen metabolites as antibacterial and antiplasmodial agents.


