EvoxineCAS# 522-11-2 |
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 522-11-2 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 73416 | Appearance | Powder |
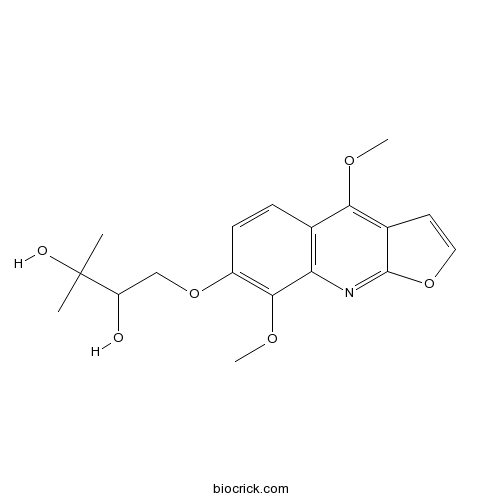
| Formula | C18H21NO6 | M.Wt | 347.4 |
| Type of Compound | Alkaloids | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | Soluble in Chloroform,Dichloromethane,Ethyl Acetate,DMSO,Acetone,etc. | ||
| Chemical Name | 1-(4,8-dimethoxyfuro[2,3-b]quinolin-7-yl)oxy-3-methylbutane-2,3-diol | ||
| SMILES | CC(C)(C(COC1=C(C2=C(C=C1)C(=C3C=COC3=N2)OC)OC)O)O | ||
| Standard InChIKey | FGANMDNHTVJAHL-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C18H21NO6/c1-18(2,21)13(20)9-25-12-6-5-10-14(16(12)23-4)19-17-11(7-8-24-17)15(10)22-3/h5-8,13,20-21H,9H2,1-4H3 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | 1. Evoxine is a small molecule that counteracts CO2-Induced immune suppression, it can counteract the CO2-induced transcriptional suppression of antimicrobial peptides in S2* cells. 2. Evoxine and arborinine display moderate antiplasmodial activity against the CQS D10 strain of Plasmodium falciparum, with IC(50) values of 24.5 and 12.3 microM, respectively. |
| Targets | AMPK |

Evoxine Dilution Calculator

Evoxine Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.8785 mL | 14.3926 mL | 28.7853 mL | 57.5705 mL | 71.9632 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.5757 mL | 2.8785 mL | 5.7571 mL | 11.5141 mL | 14.3926 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.2879 mL | 1.4393 mL | 2.8785 mL | 5.7571 mL | 7.1963 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0576 mL | 0.2879 mL | 0.5757 mL | 1.1514 mL | 1.4393 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0288 mL | 0.1439 mL | 0.2879 mL | 0.5757 mL | 0.7196 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- N'-Methylammodendrine
Catalog No.:BCN2147
CAS No.:52196-10-8
- 7-Hydroxy-2,3,4,5-tetrahydro-1H-benzofuro[2,3-c]azepin-1-one
Catalog No.:BCC3960
CAS No.:521937-07-5
- Piperitol
Catalog No.:BCN3968
CAS No.:52151-92-5
- H-Tyr(Bzl)-OBzl.HCl
Catalog No.:BCC3131
CAS No.:52142-01-5
- 3-O-Acetylpinobanksin
Catalog No.:BCN5660
CAS No.:52117-69-8
- 2,4-Dihydroxy-6-methoxy-3-formylacetophenone
Catalog No.:BCN1430
CAS No.:52117-67-6
- Karanjin
Catalog No.:BCN8370
CAS No.:521-88-0
- Broxyquinoline
Catalog No.:BCC4642
CAS No.:521-74-4
- Cinnamoylcocaine
Catalog No.:BCN1429
CAS No.:521-67-5
- Frangulin A
Catalog No.:BCC8174
CAS No.:521-62-0
- Physcion
Catalog No.:BCN5663
CAS No.:521-61-9
- Vulpic acid
Catalog No.:BCN6546
CAS No.:521-52-8
- Quercitrin
Catalog No.:BCN5665
CAS No.:522-12-3
- Deguelin
Catalog No.:BCN4804
CAS No.:522-17-8
- Norsanguinarine
Catalog No.:BCN3714
CAS No.:522-30-5
- Lochnerine
Catalog No.:BCN5667
CAS No.:522-47-4
- Tetrahydrozoline HCl
Catalog No.:BCC4339
CAS No.:522-48-5
- Dequalinium Chloride
Catalog No.:BCC4998
CAS No.:522-51-0
- Allo-Yohimbine
Catalog No.:BCN3487
CAS No.:522-94-1
- Tetrahydroberberine
Catalog No.:BCN2648
CAS No.:522-97-4
- Lamalbid
Catalog No.:BCN3750
CAS No.:52212-87-0
- 3-Epicorosolic acid
Catalog No.:BCN5666
CAS No.:52213-27-1
- Ciprofibrate
Catalog No.:BCC2266
CAS No.:52214-84-3
- Kaempferol-4'-O-beta-D-glucopyranoside
Catalog No.:BCN8130
CAS No.:52222-74-9
[New furoquinolins from Monnieria trifolia].[Pubmed:17401996]
Planta Med. 1981 Aug;42(8):400-2.
Four new furoquinoline alkaloids (evolatine, Evoxine, 6-methoxy-7-hydroxy-dictamnine, haplopine) are isolated from the leaves of Monnieria trifolia. The structures are elucidated by spectrometric methods and some chemical transformations.
Development of a whole-cell screening system for evaluation of the human CYP1A2-mediated metabolism.[Pubmed:21755496]
Biotechnol Bioeng. 2011 Dec;108(12):2932-40.
Cytochrome P450 1A2 (CYP1A2) is an important member of cytochrome P450 involved in drug metabolism. In this study, a cell line, Huh7-1A2-I-E, with high expression level of CYP1A2 is established based on Huh7 cells. To achieve this, we constructed a recombinant lentiviral vector, pLenti-1A2-I-E, containing a single promoter encoding CYP1A2 followed by an internal ribosome entry site (IRES) to permit the translation of enhanced green fluorescence protein (EGFP). Such a design has greatly facilitated the selection of stable cell lines because the translations of CYP1A2 and EGFP proteins would be based on a single bi-cistronic mRNA. The Huh7-1A2-I-E cells were evaluated as a cell-based model for identification of CYP1A2 inhibitors and for studies of cytotoxicity resulted from CYP-mediated drug metabolism. Treatment of Huh7-1A2-I-E cells and the Huh7-E control cells with aflatoxin B1 showed that cells with CYP1A2 expression are much more sensitive to aflatoxin B1 and the cellular toxicity of aflatoxin B1 in Huh7-1A2-I-E cells could be prevented by furafylline, a CYP1A2 inhibitor. A collection of approximately 200 drugs were screened using this system and results indicate that for most drugs the metabolism by CYP1A2 is unlikely to have made a major contribution to the in vitro cytotoxicity except for thimerosal and Evoxine. Several previously unidentified CYP1A2 inhibitors such as Evoxine and berberine were also identified in this study.
Biological activity of secondary metabolites from Peltostigma guatemalense.[Pubmed:19296377]
Nat Prod Res. 2009;23(4):370-4.
Leaves and wood of Peltostigma guatemalense, a novel species of the family Rutaceae, yielded a total of 14 secondary metabolites, i.e. methyl p-hydroxy benzoate, phenylacetic acid, beta-sitosterol, lupeol, syringaresinol, scopoletin, gardenin B (1), and seven alkaloids: gamma-fagarine (2), skimmianine (3), kokusaginine (4), 7-O-isopentenyl-gamma-fagarine (5), anhydro-Evoxine (6), Evoxine (7) and 4-methoxy-1-methyl-quinolin-2-one (8). The compounds have been identified by spectroscopic methods. Antibacterial and antimalarial in vitro activity of the isolated compounds were also determined. Methyl p-hydroxy benzoate and quinolone (8) were the most effective on Plasmodium falciparium strains.
Synthesis, structure and stereochemistry of quinoline alkaloids from Choisya ternata.[Pubmed:17728865]
Org Biomol Chem. 2007 Sep 21;5(18):2983-91.
A range of seventeen quinoline alkaloids, involving several types of oxidations during their biosynthetic pathways, have been isolated from leaves of Choisya ternata. In addition to the nine known quinoline alkaloids, eight new members of the furoquinoline family, derived mainly from prenylation at C-5 (including two novel hydroperoxides), have been identified. The absolute configurations and enantiopurity values of all chiral quinoline alkaloids have been determined. One of the isolated alkaloids, 7-isopentenyloxy-gamma-fagarine, has been used as a precursor for the chemical asymmetric synthesis of the enantiopure alkaloids: Evoxine, anhydroEvoxine and evodine. The possible roles of oxygenase and other oxygen-atom-transfer enzymes, in the biosynthetic pathways of the C. ternata alkaloids, have been discussed.
Antimicrobial Furoquinoline Alkaloids from Vepris lecomteana (Pierre) Cheek & T. Heller (Rutaceae).[Pubmed:29267257]
Molecules. 2017 Dec 21;23(1). pii: molecules23010013.
Three new prenylated furoquinoline alkaloids named lecomtequinoline A (1), B (2), and C (3), together with the known compounds anhydroEvoxine (4), Evoxine (5), dictamnine (6), N-methylflindersine (7), evoxanthine (8), hesperidin, lupeol, beta-sitosterol, stigmasterol, beta-sitosterol-3-O-beta-d-glucopyranoside, stearic acid, and myristyl alcohol, were isolated by bioassay-guided fractionation of the methanolic extracts of leaves and stem of Vepris lecomteana. The structures of compounds were determined by spectroscopic methods (NMR, MS, UV, and IR) and by comparison with previously reported data. Crude extracts of leaves and stem displayed high antimicrobial activity, with Minimum Inhibitory Concentration (MIC) (values of 10.1-16.5 and 10.2-20.5 microg/mL, respectively, against Escherichia coli, Bacillus subtilis, Pseudomonas agarici, Micrococcus luteus, and Staphylococcus warneri, while compounds 1-6 showed values ranging from 11.1 to 18.7 microg/mL or were inactive, suggesting synergistic effect. The extracts may find application in crude drug preparations in Western Africa where Vepris lecomteana is endemic, subject to negative toxicity results in vivo.
Acridone and furoquinoline alkaloids from Teclea gerrardii (Rutaceae: Toddalioideae) of southern Africa.[Pubmed:17174364]
Phytochemistry. 2007 Mar;68(5):663-7.
The combined hexane/CH(2)Cl(2) extract of the stem bark of Teclea gerrardii (Rutaceae: Toddalioideae) has yielded two acridone alkaloids, 3-hydroxy-1-methoxy-N-methylacridone (tegerrardin A) (1) and 3-hydroxy-N-methyl-1-(gamma,gamma-dimethylallyloxy)acridone (tegerrardin B) (2), three known acridones (3-5), two known furoquinolines (6,7), and the acridone precursor tecleanone (8). Arborinine (3) and Evoxine (6) displayed moderate antiplasmodial activity against the CQS D10 strain of Plasmodium falciparum, with IC(50) values of 12.3 and 24.5 microM, respectively.
A novel flavonoid and furoquinoline alkaloids from Vepris glomerata and their antioxidant activity.[Pubmed:22312722]
Nat Prod Commun. 2011 Dec;6(12):1847-50.
The dichloromethane extract of the aerial part of the plant Vepris glomerata (Rutaceae) yielded a new flavonoid, which was accorded the trivial name veprisinol (1), together with four known furoquinoline alkaloids: haplopine-3,3'-dimethylallyl ether (2), anhydroEvoxine (3), Evoxine (4) and skimmianine (5). The structures of the compounds were established by 1D and 2D NMR spectroscopy, as well as HREIMS. Compounds 1 and 2 have strong antioxidant potential, similar to and in some instances better than ascorbic acid and can be used as beneficial additives to antioxidant supplements.
Focused Screening Identifies Evoxine as a Small Molecule That Counteracts CO2-Induced Immune Suppression.[Pubmed:26701099]
J Biomol Screen. 2016 Apr;21(4):363-71.
Patients with severe lung disease may develop hypercapnia, elevation of the levels of CO2 in the lungs and blood, which is associated with increased risk of death, often from infection. To identify compounds that ameliorate the adverse effects of hypercapnia, we performed a focused screen of 8832 compounds using a CO2-responsive luciferase reporter in Drosophila S2* cells. We found that Evoxine, a plant alkaloid, counteracts the CO2-induced transcriptional suppression of antimicrobial peptides in S2* cells. Strikingly, Evoxine also inhibits hypercapnic suppression of interleukin-6 and the chemokine CCL2 expression in human THP-1 macrophages. Evoxine's effects are selective, since it does not prevent hypercapnic inhibition of phagocytosis by THP-1 cells or CO2-induced activation of AMPK in rat ATII pulmonary epithelial cells. The results suggest that hypercapnia suppresses innate immune gene expression by definable pathways that are evolutionarily conserved and demonstrate for the first time that specific CO2 effects can be targeted pharmacologically.


