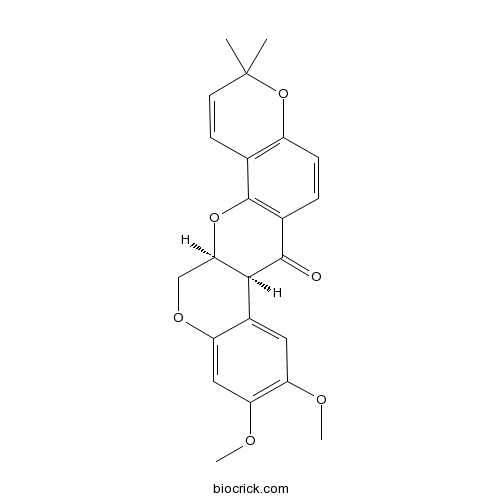
DeguelinAnticancer and antiviral agent CAS# 522-17-8 |
- 3,3'-Diindolylmethane
Catalog No.:BCC1306
CAS No.:1968-05-4
- BAM7
Catalog No.:BCC1397
CAS No.:331244-89-4
- Bendamustine HCl
Catalog No.:BCC1153
CAS No.:3543-75-7
- Betulinic acid
Catalog No.:BCN5524
CAS No.:472-15-1
- Brassinolide
Catalog No.:BCC1438
CAS No.:72962-43-7
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 522-17-8 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 107935 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C23H22O6 | M.Wt | 394.4 |
| Type of Compound | Flavonoids | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Synonyms | (-)-Deguelin; (-)-cis-Deguelin | ||
| Solubility | DMSO : 50 mg/mL (126.77 mM; Need ultrasonic) H2O : < 0.1 mg/mL (insoluble) | ||
| SMILES | CC1(C=CC2=C(O1)C=CC3=C2OC4COC5=CC(=C(C=C5C4C3=O)OC)OC)C | ||
| Standard InChIKey | ORDAZKGHSNRHTD-UXHICEINSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C23H22O6/c1-23(2)8-7-12-15(29-23)6-5-13-21(24)20-14-9-17(25-3)18(26-4)10-16(14)27-11-19(20)28-22(12)13/h5-10,19-20H,11H2,1-4H3/t19-,20+/m1/s1 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | 1. Deguelin has anti-cancer activity, such as anti osteosarcoma, lung cancer; via inducing the apoptosis of cancer cells through a ROS driven Akt pathway, EPC suppression by FAK-integrin-ILK-dependent actin remodeling . 2. Deguelin possesses antitumor effect by targeting Akt in dual axis such as EGFR and IGF1R signaling pathways and suggests that it provides an applicable therapeutic strategy for HNSCC patients. 3. Deguelin is a potent in vitro inhibitor of the mutant form of NPM1, which provides the molecular basis for its anti-leukemia activities in NPM1 mutant acute myeloid leukemia cells. |
| Targets | FAK | ROS | Caspase | Akt | ERK | PARP | EGFR | p53 | p21 | MMP(e.g.TIMP) | PKC | PI3K | MEK | NOS | COX | JNK | p38MAPK | ROCK | NF-kB | p65 | VEGFR |

Deguelin Dilution Calculator

Deguelin Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.5355 mL | 12.6775 mL | 25.355 mL | 50.7099 mL | 63.3874 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.5071 mL | 2.5355 mL | 5.071 mL | 10.142 mL | 12.6775 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.2535 mL | 1.2677 mL | 2.5355 mL | 5.071 mL | 6.3387 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0507 mL | 0.2535 mL | 0.5071 mL | 1.0142 mL | 1.2677 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0254 mL | 0.1268 mL | 0.2535 mL | 0.5071 mL | 0.6339 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
Anticancer and antiviral agent; chemopreventive and pro-apoptotic. Inhibits phorbol ester-induced ornithine decarboxylase and NADH:ubiquinone oxidoreductase activities (IC50 values are 11 and 6.9 nM respectively). Inhibits PI 3-kinase and reduces pAkt levels in pre-malignant and malignant human bronchial epithelial cells. Active in vivo.
- Quercitrin
Catalog No.:BCN5665
CAS No.:522-12-3
- Evoxine
Catalog No.:BCN5664
CAS No.:522-11-2
- N'-Methylammodendrine
Catalog No.:BCN2147
CAS No.:52196-10-8
- 7-Hydroxy-2,3,4,5-tetrahydro-1H-benzofuro[2,3-c]azepin-1-one
Catalog No.:BCC3960
CAS No.:521937-07-5
- Piperitol
Catalog No.:BCN3968
CAS No.:52151-92-5
- H-Tyr(Bzl)-OBzl.HCl
Catalog No.:BCC3131
CAS No.:52142-01-5
- 3-O-Acetylpinobanksin
Catalog No.:BCN5660
CAS No.:52117-69-8
- 2,4-Dihydroxy-6-methoxy-3-formylacetophenone
Catalog No.:BCN1430
CAS No.:52117-67-6
- Karanjin
Catalog No.:BCN8370
CAS No.:521-88-0
- Broxyquinoline
Catalog No.:BCC4642
CAS No.:521-74-4
- Cinnamoylcocaine
Catalog No.:BCN1429
CAS No.:521-67-5
- Frangulin A
Catalog No.:BCC8174
CAS No.:521-62-0
- Norsanguinarine
Catalog No.:BCN3714
CAS No.:522-30-5
- Lochnerine
Catalog No.:BCN5667
CAS No.:522-47-4
- Tetrahydrozoline HCl
Catalog No.:BCC4339
CAS No.:522-48-5
- Dequalinium Chloride
Catalog No.:BCC4998
CAS No.:522-51-0
- Allo-Yohimbine
Catalog No.:BCN3487
CAS No.:522-94-1
- Tetrahydroberberine
Catalog No.:BCN2648
CAS No.:522-97-4
- Lamalbid
Catalog No.:BCN3750
CAS No.:52212-87-0
- 3-Epicorosolic acid
Catalog No.:BCN5666
CAS No.:52213-27-1
- Ciprofibrate
Catalog No.:BCC2266
CAS No.:52214-84-3
- Kaempferol-4'-O-beta-D-glucopyranoside
Catalog No.:BCN8130
CAS No.:52222-74-9
- Parathyroid hormone (1-34) (human)
Catalog No.:BCC1046
CAS No.:52232-67-4
- Isomucronulatol
Catalog No.:BCN1428
CAS No.:52250-35-8
Deguelin, a selective silencer of the NPM1 mutant, potentiates apoptosis and induces differentiation in AML cells carrying the NPM1 mutation.[Pubmed:25242579]
Ann Hematol. 2015 Feb;94(2):201-10.
Nucleophosmin (NPM1) is a multifunctional protein that functions as a molecular chaperone, shuttling between the nucleolus and the cytoplasm. In up to one third of patients with acute myeloid leukemia, mutation of NPM1 results in the aberrant cytoplasmic accumulation of mutant protein and is thought to be responsible for leukemogenesis. Deguelin, a rotenoid isolated from several plant species, has been shown to be a strong anti-tumor agent. Human leukemia cell lines were used for in vitro studies. Drug efficacy was evaluated by apoptosis and differentiation assays, and associated molecular events were assessed by Western blot. Gene silencing was performed using small interfering RNA (siRNA). Deguelin exhibited strong cytotoxic activity in the cell line of OCI-AML3 and selectively down-regulated the NPM1 mutant protein, which was accompanied by up-regulation of the activity of caspase-6 and caspase-8 in high concentrations. Deguelin induced differentiation of OCI-AML3 cells at a nontoxic concentration which was associated with a decrease in expression of activated caspase-8, p53, p21, and the 30-kD form of CCAAT/enhancer binding protein alpha (C/EBPalpha), whereas no effects were found in OCIM2 cells expressing NPM-wt. Moreover, treatment with siRNA in the NPM mutant cell line OCI-AML3 decreased expression of p53, p21, pro-caspase-8, and the 30-kD form of C/EBPalpha, and it inhibited proliferation and induced differentiation of the OCI-AML3 cells. In conclusion, Deguelin is a potent in vitro inhibitor of the mutant form of NPM1, which provides the molecular basis for its anti-leukemia activities in NPM1 mutant acute myeloid leukemia cells.
Deguelin inhibits vasculogenic function of endothelial progenitor cells in tumor progression and metastasis via suppression of focal adhesion.[Pubmed:26078334]
Oncotarget. 2015 Jun 30;6(18):16588-600.
Deguelin is a nature-derived chemopreventive drug. Endothelial progenitor cells (EPCs) are bone-marrow (BM)-derived key components to induce new blood vessels in early tumorigenesis and metastasis. Here we determined whether Deguelin inhibits EPC function in vitro and in vivo at doses not affecting cancer cell apoptosis. Deguelin significantly reduced the number of EPC colony forming units of BM-derived c-kit+/sca-1+ mononuclear cells (MNCs), proliferation, migration, and adhesion to endothelial cell monolayers, and suppressed incorporation of EPC into tube-like vessel networks when co-cultured with endothelial cells. Deguelin caused cell cycle arrest at G1 without induction of apoptosis in EPC. In a mouse tumor xenograft model, tumor growth, lung metastasis and tumor-induced circulating EPCs were supressed by Deguelin treatment (2 mg/kg). In mice tranplanted with GFP-expressing BM-MNCs, Deguelin reduced the co-localization of CD31 and GFP, suggesting suppression of BM-derived EPC incoporation into tumor vessels. Interestingly, focal adhesion kinase (FAK)-integrin-linked kinase (ILK) activation and actin polymerization were repressed by Deguelin. Decreased number of focal adhesions and a depolarized morphology was found in Deguelin-treated EPCs. Taken together, our results suggest that the Deguelin inhibits tumorigenesis and metastasis via EPC suppression and that suppression of focal adhesion by FAK-integrin-ILK-dependent actin remodeling is a key underlying molecular mechanism.
Deguelin induces apoptosis by targeting both EGFR-Akt and IGF1R-Akt pathways in head and neck squamous cell cancer cell lines.[Pubmed:26075254]
Biomed Res Int. 2015;2015:657179.
Deguelin, a rotenoid compound from the African plant Mundulea sericea (Leguminosae), has been shown to possess antitumor activities but the exact role for the growth factor receptor mediated signaling pathway in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC) is currently still unclear. In the present study, we investigated the effect of Deguelin on epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) and insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor (IGF1R) pathways in HNSCC cell lines. Flowcytometric analysis revealed accumulation of annexin V positivity in Deguelin-treated cells, showing that Deguelin induced apoptosis. The Deguelin-induced apoptosis was accompanied by the reduction of constitutive phosphorylated levels of IGF1R, Akt, and extracellular signal-regulated kinase1/2 (ERK1/2). LY294002-mediated inhibition of phosphatidylinositol-3 kinase, which is an upstream effector for Akt activation, increased cleavage of poly(ADP-ribosyl) polymerase (PARP) but ERK inhibition by U0126 did not. Deguelin inhibited both IGF-1- and EGF-induced Akt activation. These results showed that Deguelin possessed antitumor effect by targeting Akt in dual axis such as EGFR and IGF1R signaling pathways and suggested that it provides an applicable therapeutic strategy for HNSCC patients.
Deguelin induces the apoptosis of lung cancer cells through regulating a ROS driven Akt pathway.[Pubmed:25741219]
Cancer Cell Int. 2015 Feb 25;15:25.
BACKGROUND: Duguelin is a rotenoid extracted from plants and has potent antitumor effects in vitro and in vivo. However, the mechanism underlying the antitumor effect remains unclear. Our preliminary study showed that Deguelin is effective to stimulate the generation of Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS). In the current study, we evaluated the in vitro cytotoxicity of Deguelin against lung cancer cells and studied whether a ROS scavenger, N-acetyl-cysteine (NAC), can reverse the inhibitory effect of Deguelin. RESULTS: We showed that the dose-dependent apoptotic inducing effect of Deguelin could be partially reversed by the co-administration of NAC. Moreover, Deguelin reduced the phosphorylation of Akt protein and induced the apoptotic protein Caspase-3 in a dose-dependent manner. Co-treatment with NAC partially attenuated this effect and rescued some cells from apoptosis. CONCLUSION: Deguelin induces the apoptosis of cancer cells through a ROS driven Akt pathway, which could translate into a promising therapeutic for lung cancer.
Deguelin inhibits the migration and invasion of U-2 OS human osteosarcoma cells via the inhibition of matrix metalloproteinase-2/-9 in vitro.[Pubmed:25322282]
Molecules. 2014 Oct 15;19(10):16588-608.
Osteosarcoma is the most common malignant primary bone tumor in children and young adults and lung metastasis is the main cause of death in those patients. Deguelin, a naturally occurring rotenoid, is known to be an Akt inhibitor and to exhibit cytotoxic effects, including antiproliferative and anticarcinogenic activities, in several cancers. In the present study, we determined if Deguelin would inhibit migration and invasion in U-2 OS human osteosarcoma cells. Deguelin significantly inhibited migration and invasion of U-2 OS human osteosarcoma cells which was associated with a reduction of activities of matrix metalloproteinases-2 (MMP-2) and matrix metalloproteinases-9 (MMP-9). Furthermore, results from western blotting indicated that Deguelin decreased the cell proliferation and cell growth-associated protein levels, such as SOS1, PKC, Ras, PI3K, p-AKT(Ser473), IRE-1alpha, MEKK3, iNOS, COX2, p-ERK1/2, p-JNK1/2, p-p38; the cell motility and focal adhesion-associated protein levels, such as Rho A, FAK, ROCK-1; the invasion-associated protein levels, such as TIMP1, uPA, MMP-2. MMP-9, MMP-13, MMP-1 and VEGF in U-2 OS cells. Confocal microscopy revealed that Deguelin reduced NF-kappaB p65, Rho A and ROCK-1 protein levels in cytosol. MMP-7, MMP-9 and Rho A mRNA levels were suppressed by Deguelin. These in vitro results provide evidence that Deguelin may have potential as a novel anti-cancer agent for the treatment of osteosarcoma and provides the rationale for in vivo studies in animal models.
Effects of deguelin on the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt pathway and apoptosis in premalignant human bronchial epithelial cells.[Pubmed:12591985]
J Natl Cancer Inst. 2003 Feb 19;95(4):291-302.
BACKGROUND: Because lung cancer is the leading cause of cancer-related death, new approaches for preventing and controlling the disease are needed. Chemoprevention approaches are both feasible and effective. We evaluated the potential of Deguelin, a natural plant product, as a lung cancer chemopreventive agent and investigated its mechanism of action. METHODS: The effects of Deguelin on proliferation and apoptosis of normal, premalignant, and malignant human bronchial epithelial (HBE) cells were assessed by using the MTT assay, a flow cytometry-based TUNEL assay, and western blot analyses. The effects of Deguelin on the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K)/Akt and mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) pathways were assessed by western blot analyses and with adenoviral vectors that expressed constitutively active Akt. RESULTS: Deguelin treatment in vitro at doses attainable in vivo inhibited the growth of and induced apoptosis of premalignant and malignant HBE cells but had minimal effects on normal HBE cells. Levels of phosphorylated Akt (pAkt) were higher in premalignant HBE cells than in normal HBE cells. In premalignant HBE cells, Deguelin inhibited PI3K activity and reduced pAkt levels and activity but had mimimal effects on the MAPK pathway. Although overexpression of a constitutively active Akt in premalignant and malignant HBE cells had no effect on growth inhibition mediated by N-(4-hydroxyphenyl)retinamide (4-HPR), a novel chemopreventive retinoid, it blocked Deguelin-induced growth arrest and apoptosis. CONCLUSIONS: The ability of Deguelin to inhibit PI3K/Akt-mediated signaling pathways may contribute to the potency and specificity of this pro-apoptotic drug. Because both premalignant and malignant HBE cells are more sensitive to Deguelin than normal HBE cells, Deguelin may have potential as both a chemopreventive agent for early stages of lung carcinogenesis and a therapeutic agent against lung cancer.
Anticancer action of cube insecticide: correlation for rotenoid constituents between inhibition of NADH:ubiquinone oxidoreductase and induced ornithine decarboxylase activities.[Pubmed:9520374]
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1998 Mar 31;95(7):3380-4.
Rotenone and rotenoid-containing botanicals, important insecticides and fish poisons, are reported to have anticancer activity in rats and mice. The toxic action of rotenone is attributed to inhibition of NADH:ubiquinone oxidoreductase activity and the purported cancer chemopreventive effect of Deguelin analogs has been associated with inhibition of phorbol ester-induced ornithine decarboxylase (ODC) activity. This study defines a possible relationship between these two types of activity important in evaluating the toxicology of rotenoid pesticides and the suitability of the anticancer model. Fractionation of cube resin (the commercial rotenoid pesticide) establishes that the activity in both assays is due primarily to rotenone (IC50 = 0.8-4 nM), secondarily to Deguelin, and in small part to rotenolone and tephrosin. In addition, the potency of 29 rotenoids from cube insecticide for inhibiting NADH:ubiquinone oxidoreductase in vitro assayed with bovine heart electron transport particles satisfactorily predicts their potency in vivo in the induced ODC assay using noncytotoxic rotenoid concentrations with cultured MCF-7 human breast cancer cells (r = 0.86). Clearly the molecular features of rotenoids essential for inhibiting NADH:ubiquinone oxidoreductase are similar to those for blocking ODC induction. This apparent correlation extends to 11 flavonoids and stilbenoids from cube resin (r = 0.98) and genistein and resveratrol except for lower potency and less selectivity than the rotenoids relative to cytotoxicity. These findings on cube insecticide constituents and our earlier study comparing rotenone and pyridaben miticide indicate that inhibition of NADH:ubiquinone oxidoreductase activity lowers the level of induced ODC activity leading to the antiproliferative effect and anticancer action.
Cancer chemopreventive activity mediated by deguelin, a naturally occurring rotenoid.[Pubmed:9270008]
Cancer Res. 1997 Aug 15;57(16):3424-8.
Deguelin, a natural product isolated from Mundulea sericea (Leguminosae), was shown previously to mediate strong inhibition of 12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol-13-acetate (TPA)-induced ornithine decarboxylase (ODC) activity in cell culture and to reduce the formation of preneoplastic lesions when mouse mammary glands were exposed to 7,12-dimethylbenz(a)anthracene. As reported currently, Deguelin was synthesized and evaluated for chemopreventive activity in the two-stage 7,12-dimethylbenz(a)anthracene/TPA skin carcinogenesis model with CD-1 mice and in the N-methylnitrosourea mammary carcinogenesis model with Sprague Dawley rats. In the mouse skin study, Deguelin reduced tumor incidence from 60% in the control group to 10% in the group treated with a dose of 33 microg, and multiplicity was reduced from 4.2 in the control group to 0.1 in the treatment group. When the dose was increased 10-fold to 330 microg, no tumors were observed in the treatment group. These results correlated with the potential of Deguelin to inhibit TPA-induced mouse epidermal ODC activity. When applied topically as a single dose in a time range of 2 h before to 2 h after TPA treatment, Deguelin (384 microg) reduced ODC induction by TPA (6.17 microg) by more than 85%. Time course studies indicated that Deguelin (33 microg) inhibited TPA (1.17 microg)-induced ODC activity by 70% without affecting the kinetics of induction over a period of 10 h. Complete inhibition of ODC induction was observed at a dose of 330 microg of Deguelin. In the rat mammary tumorigenesis study, intragastric administration of 2 or 4 mg of Deguelin/kg of body weight daily, 5 days/week, reduced tumor multiplicity from 6.8 tumors/rat in the control group to 5.1 or 3.2 tumors/animal, respectively. At the 4 mg of Deguelin/kg of body weight dose level, the tumor latency period was significantly increased. Tumor incidence, however, was unaffected. These data indicate that Deguelin exhibits cancer chemopreventive effects in skin and mammary tumorigenesis models and that additional studies are warranted to characterize the cancer chemopreventive or chemotherapeutic potential of this substance more fully.
Antiviral and antitumor antibiotics. XX. Effects of rotenone, deguelin, and related compounds on animal and plant viruses.[Pubmed:4312925]
Appl Microbiol. 1969 Oct;18(4):660-7.
Rotenoids and related compounds were investigated for their effects on animal and plant viruses. Of 35 compounds examined, rotenone, rotenone norketone, acetylrotenone, acetylrotenone norketone, Deguelin, deguelic acid, dehydroDeguelin, and isotubanol norketone, all used at low concentrations, suppressed the growth of Newcastle disease and herpes simplex viruses as determined by the agar diffusion, plaque inhibition method. Most of the compounds likewise decreased the number of necrotic spots on tobacco mosaic virus-infected leaf discs. Only derrisic acid completely inhibited the local lesion formation at subphytotoxic concentrations. Correlation of antiviral activity with respiratory inhibition of these compounds is discussed.


