ZeatinCAS# 13114-27-7 |
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

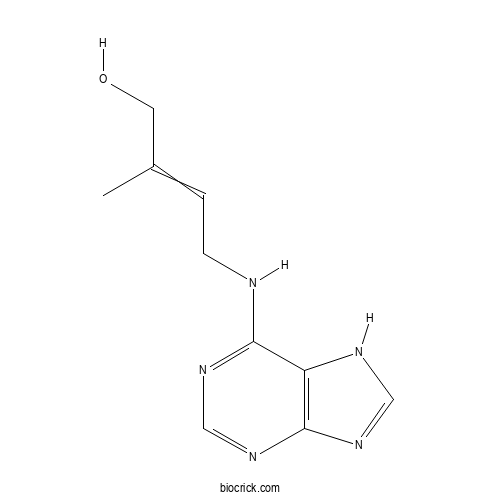
| Cas No. | 13114-27-7 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 15419.0 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C10H13N5O | M.Wt | 219.25 |
| Type of Compound | Alkaloids | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | Soluble in Chloroform,Dichloromethane,Ethyl Acetate,DMSO,Acetone,etc. | ||
| Chemical Name | 2-methyl-4-(7H-purin-6-ylamino)but-2-en-1-ol | ||
| SMILES | CC(=CCNC1=NC=NC2=C1NC=N2)CO | ||
| Standard InChIKey | UZKQTCBAMSWPJD-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C10H13N5O/c1-7(4-16)2-3-11-9-8-10(13-5-12-8)15-6-14-9/h2,5-6,16H,3-4H2,1H3,(H2,11,12,13,14,15) | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||

Zeatin Dilution Calculator

Zeatin Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 4.561 mL | 22.805 mL | 45.61 mL | 91.2201 mL | 114.0251 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.9122 mL | 4.561 mL | 9.122 mL | 18.244 mL | 22.805 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.4561 mL | 2.2805 mL | 4.561 mL | 9.122 mL | 11.4025 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0912 mL | 0.4561 mL | 0.9122 mL | 1.8244 mL | 2.2805 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0456 mL | 0.2281 mL | 0.4561 mL | 0.9122 mL | 1.1403 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- 6,8-Dihydroxy-1,2,7-trimethoxy-3-methylanthraquinone
Catalog No.:BCX1015
CAS No.:1622982-59-5
- Cycloastragenol-6-O-β-D-glucoside
Catalog No.:BCX1014
CAS No.:86764-12-7
- 6'-Hydroxy-3,4,2',3',4'-pentamethoxychalcone
Catalog No.:BCX1013
CAS No.:114021-62-4
- Isomaltotetraose
Catalog No.:BCX1012
CAS No.:35997-20-7
- Isomaltopentaose
Catalog No.:BCX1011
CAS No.:6082-32-2
- Isomaltohexaose
Catalog No.:BCX1010
CAS No.:6175-02-6
- Isomaltoheptaose
Catalog No.:BCX1009
CAS No.:6513-12-8
- Isomaltooctaose
Catalog No.:BCX1008
CAS No.:35867-37-9
- Alitame hydrate
Catalog No.:BCX1007
CAS No.:99016-42-9
- Euphorbetin
Catalog No.:BCX1006
CAS No.:35897-99-5
- Hericene A
Catalog No.:BCX1005
CAS No.:157207-54-0
- Hericene B
Catalog No.:BCX1004
CAS No.:157207-55-1
- Neopuerarin A
Catalog No.:BCX1017
CAS No.:1150314-34-3
- Docosyl ferulate
Catalog No.:BCX1018
CAS No.:101927-24-6
- Furopelargone B
Catalog No.:BCX1019
CAS No.:1143-46-0
- Pseudostellarin A
Catalog No.:BCX1020
CAS No.:156430-20-5
- Soyasaponin Be
Catalog No.:BCX1021
CAS No.:117210-14-7
- Diphylloside A
Catalog No.:BCX1022
CAS No.:113558-11-5
- Pseudoginsenoside
Catalog No.:BCX1023
CAS No.:96158-07-5
- Notoginsenoside D
Catalog No.:BCX1024
CAS No.:193895-50-0
- Flavanone hydrazone
Catalog No.:BCX1025
CAS No.:1692-46-2
- Gallic acid 4-O-β-D-glucopyranoside
Catalog No.:BCX1026
CAS No.:84274-52-2
- 18α,20β-Glycyrrhizic acid
Catalog No.:BCX1027
CAS No.:83896-44-0
- 6-Hydroxymusizin 8-glucoside
Catalog No.:BCX1028
CAS No.:23566-96-3
Analysis Transcriptome and Phytohormone Changes Associated with the Allelopathic Effects of Ginseng Hairy Roots Induced by Different-Polarity Ginsenoside Components.[Pubmed:38675697]
Molecules. 2024 Apr 19;29(8):1877.
The allelopathic autotoxicity of ginsenosides is an important cause of continuous cropping obstacles in ginseng planting. There is no report on the potential molecular mechanism of the correlation between polarity of ginsenoside components and their allelopathic autotoxicity. This study applied a combination of metabolomics and transcriptomics analysis techniques, combined with apparent morphology, physiological indexes, and cell vitality detection of the ginseng hairy roots, through which the molecular mechanism of correlation between polarity and allelopathic autotoxicity of ginsenosides were comprehensively studied. The hairy roots of ginseng presented more severe cell apoptosis under the stress of low-polarity ginsenoside components (ZG70). ZG70 exerted allelopathic autotoxicity by regulating the key enzyme genes of cis-Zeatin (cZ) synthesis pathway, indole-3-acetic acid (IAA) synthesis pathway, and jasmonates (JAs) signaling transduction pathway. The common pathway for high-polarity ginsenoside components (ZG50) and ZG70 to induce the development of allelopathic autotoxicity was through the expression of key enzymes in the gibberellin (GA) signal transduction pathway, thereby inhibiting the growth of ginseng hairy roots. cZ, indole-3-acetamid (IAM), gibberellin A1 (GA1), and jasmonoyl-L-isoleucine (JA-ILE) were the key response factors in this process. It could be concluded that the polarity of ginsenoside components were negatively correlated with their allelopathic autotoxicity.
Mitigating Effect of Trans-Zeatin on Cadmium Toxicity in Desmodesmus armatus.[Pubmed:38667301]
Cells. 2024 Apr 15;13(8):686.
Phytohormones, particularly cytokinin trans-Zeatin (tZ), were studied for their impact on the green alga Desmodesmus armatus under cadmium (Cd) stress, focusing on growth, metal accumulation, and stress response mechanisms. Using atomic absorption spectroscopy for the Cd level and high-performance liquid chromatography for photosynthetic pigments and phytochelatins, along with spectrophotometry for antioxidants and liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry for phytohormones, we found that tZ enhances Cd uptake in D. armatus, potentially improving phycoremediation of aquatic environments. Cytokinin mitigates Cd toxicity by regulating internal phytohormone levels and activating metal tolerance pathways, increasing phytochelatin synthase activity and phytochelatin accumulation essential for Cd sequestration. Treatment with tZ and Cd also resulted in increased cell proliferation, photosynthetic pigment and antioxidant levels, and antioxidant enzyme activities, reducing oxidative stress. This suggests that cytokinin-mediated mechanisms in D. armatus enhance its capacity for Cd uptake and tolerance, offering promising avenues for more effective aquatic phycoremediation techniques.
Effects of four bolete species on ectomycorrhizae formation and development in Pinus thunbergii and Quercus acutissima.[Pubmed:38664655]
BMC Ecol Evol. 2024 Apr 25;24(1):54.
BACKGROUND: Bolete cultivation is economically and ecologically valuable. Ectomycorrhizae are advantageous for plant development and productivity. This study investigated how boletes affect the formation of Pinus thunbergii and Quercus acutissima ectomycorrhizae using greenhouse-based mycorrhizal experiments, inoculating P. thunbergii and Q. acutissima with four species of boletes (Suillus bovinus, Suillus luteus, Suillus grevillei, and Retiboletus sinensis). RESULTS: Three months after inoculation, morphological and molecular analyses identified S. bovinus, S. luteus, S. grevillei and R. sinensis ectomycorrhizae formation on the roots of both tree species. The mycorrhizal infection rate ranged from 40 to 55%. The host plant species determined the mycorrhiza morphology, which was independent of the bolete species. Differences in plant growth, photosynthesis, and endogenous hormone secretion primarily correlated with the host plant species. Infection with all four bolete species significantly promoted the host plants' growth and photosynthesis rates; indole-3-acetic acid, Zeatin, and gibberellic acid secretion increased, and the abscisic acid level significantly decreased. Indole-3-acetic acid was also detected in the fermentation broths of all bolete species. CONCLUSIONS: Inoculation with bolete and subsequent mycorrhizae formation significantly altered the morphology and hormone content in the host seedlings, indicating growth promotion. These findings have practical implications for culturing pine and oak tree species.
Organic Supplementation of Vaccinium corymbosum Micropropagation Media.[Pubmed:38656515]
Methods Mol Biol. 2024;2788:197-207.
The best Vaccinium corymbosum plant growth under in vitro conditions can be achieved by using the right composition and pH of the medium. For the initial phase of in vitro culture, a combination of cytokinins-mostly Zeatin-can usually be used. Organic supplementation of the medium enables the use of a replacement for the expensive natural cytokinin used in micropropagation of highbush blueberry. This chapter describes the experiments with silicon Hydroplus Actisil (Si), coconut water (CW), and different pH (5.0; 5.5, and 6.0) as a stress factor. The addition of 200 mg dm(-3) silicon solution and 15% coconut water strongly stimulated highbush blueberry plant growth in vitro. Moreover, silicon solution benefits the negative effects of higher pH of the medium used for micropropagation of V. corymbosum. Maximum vegetative development of blueberry explants was obtained at pH 5.
Investigating the synergistic effects of biochar, trans-zeatin riboside, and Azospirillum brasilense on soil improvement and enzymatic activity in water-stressed wheat.[Pubmed:38654167]
BMC Plant Biol. 2024 Apr 23;24(1):314.
BACKGROUND: Water stress is a major danger to crop yield, hence new approaches to strengthen plant resilience must be developed. To lessen the negative effects of water stress on wheat plants, present study was arranged to investigate the role of synergistic effects of biochar, trans-Zeatin riboside (t-ZR), and Azospirillum brasilense on soil improvement and enzymatic activity in water-stressed wheat. RESULTS: In a three-replication experiment comprising of four treatments (T(0): Control, T(1): Drought stress (DS), T(2): DS + t-ZR with biochar, T(3): DS + A. brasilense with biochar), we observed notable improvements in soil quality and enzymatic activities in water-stressed wheat plants with the application of t-ZR and A. brasilense with biochar. In drought stress, Treatment having the application of A. brasilense with biochar performs best as compared to the other and significant increased the enzymatic activities such as peroxidase (7.36%), catalase (8.53%), superoxide dismutase (6.01%), polyphenol oxidase (14.14%), and amylase (16.36%) in wheat plants. Different enzymatic activities showed different trends of results. Soil organic C, dissolved organic C, dissolved organic N also enhanced 29.46%, 8.59%, 22.70% respectively with the application of A. brasilense with biochar under drought stress condition. CONCLUSIONS: The synergistic action of A. brasilense and biochar creates an effective microbiological environment that supports essential plant physiological processes during drought stress. This enhancement is attributed to improved soil fertility and increased organic matter content, highlighting the potential of these novel strategies in mitigating water stress effects and enhancing crop resilience.
Strigolactones affect the yield of Tartary buckwheat by regulating endogenous hormone levels.[Pubmed:38654155]
BMC Plant Biol. 2024 Apr 24;24(1):320.
BACKGROUND: As a newly class of endogenous phytohormones, strigolactones (SLs) regulate crop growth and yield formation by interacting with other hormones. However, the physiological mechanism of SLs affect the yield by regulating the balance of endogenous hormones of Tartary buckwheat is still unclear. RESULTS: In this study, a 2-year field experiment was conducted on Tartary buckwheat (Jinqiao 2) to study the effects of different concentrations (0, 10, and 20 micromol/L) of artificial synthetic analogs of SLs (rac-GR24) and inhibitor of SL synthesis (Tis-108) on the growth, endogenous-hormone content, and yield of Tartary buckwheat. The main-stem branch number, grain number per plant, grain weight per plant, and yield of Tartary buckwheat continuously decreased with increased rac-GR24 concentration, whereas the main-stem diameter and plant height initially increased and then decreased. Rac-GR24 treatment significantly increased the content of SLs and abscisic acid (ABA) in grains, and it decreased the content of Zeatin (Z) + Zeatin nucleoside (ZR). Conversely, Tis-108 treatment decreased the content of SLs and ABA but increased the content of Z + ZR. Results of correlation analysis showed that the content of ABA and SLs, the ratio of SLs/(Z + ZR), SLs/ABA, and ABA/(Z + ZR) were significantly negatively correlated with the yield of Tartary buckwheat, and that Z + ZR content was significantly positively correlated with the yield. Regression analysis further showed that ABA/ (Z + ZR) can explain 58.4% of the variation in yield. CONCLUSIONS: In summary, by adjusting the level of endogenous SLs in Tartary buckwheat, the balance of endogenous hormones in grains can be changed, thereby exerting the effect on yield. The results can provide a new agronomic method for the high-yield cultivation of Tartary buckwheat.
Longistylin A from Cajanus cajan (L.) Millsp. disturbs glycerophospholipid metabolism and cytokinin biosynthesis of Nocardia seriolae.[Pubmed:38631486]
J Ethnopharmacol. 2024 Apr 16;330:118199.
ETHNOPHARMACOLOGICAL RELEVANCE: Nocardiosis is an uncommon infectious disease that bears certain similarities to tuberculosis, with a continuous increase in its incidence and a poor prognosis. In traditional Chinese medicine, the leaves of Cajanus cajan (L.) Millsp. are employed to treat wounds, malaria, coughs, and abdominal pain. AIM OF THE STUDY: In this study, we investigated the effects and mechanisms of longistylin A (LGA), a natural stilbene isolated from C. cajan, as a potential antibiotic against nocardiosis. MATERIALS AND METHODS: LGA was isolated from the leaves of C. cajan and assessed using a minimum bactericidal concentration (MBC) determination against Nocardia seriolae. Multi-omics analysis encompassing genes, proteins, and metabolites was conducted to investigate the impact of LGA treatment on N. seriolae. Additionally, quantitative analysis of 40 cytokinins in N. seriolae mycelium was performed to assess the specific effects of LGA treatment on cytokinin levels. Cryo-scanning electron microscopy was utilized to examine morphological changes induced by LGA treatment, particularly in the presence of exogenous trans-Zeatin-O-glucoside (tZOG). The therapeutic effect of LGA was investigated by feeding N. seriolae-infected largemouth bass. RESULTS: LGA exhibited significant efficacy against N. seriolae, with MBC value of 2.56 mug/mL. Multi-omics analysis revealed that LGA disrupted glycerophospholipid metabolism and hormone biosynthesis by notably reducing the expression of glycerol-3-phosphate dehydrogenase and calmodulin-like protein. Treatment with LGA markedly disrupted 12 distinct cytokinins in N. seriolae mycelium. Additionally, the addition of exogenous tZOG counteracted the inhibitory effects of LGA on filamentous growth, resulting in mycelial elongation and branching. Furthermore, LGA treatment improved the survival rate of largemouth bass infected with N. seriolae. CONCLUSIONS: We found for the first time that LGA from C. cajan exhibited significant efficacy against N. seriolae by interfering with glycerophospholipid metabolism and cytokinin biosynthesis.
Physiological, Metabolic, and Transcriptomic Analyses Reveal Mechanisms of Proliferation and Somatic Embryogenesis of Litchi (Litchi chinensis Sonn.) Embryogenic Callus Promoted by D-Arginine Treatment.[Pubmed:38612774]
Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Apr 2;25(7):3965.
D-arginine (D-Arg) can promote embryogenic callus (EC) proliferation and increase the rate of somatic embryo induction of litchi (Litchi chinensis Sonn.), yet the mechanism underlying the processes is incompletely understood. To investigate the mechanism, physiological responses of polyamines (PAs) [putrescine (Put), spermidine (Spd), and spermine (Spm)] were investigated for D-Arg-treated litchi EC and enzyme activity related to polyamine metabolism, plant endogenous hormones, and polyamine- and embryogenic-related genes were explored. Results showed that the exogenous addition of D-Arg reduces the activity of diamine oxidase (DAO) and polyamine oxidase (PAO) in EC, reduces the production of H(2)O(2), promotes EC proliferation, and increases the (Spd + Spm)/Put ratio to promote somatic embryo induction. Exogenous D-Arg application promoted somatic embryogenesis (SE) by increasing indole-3-acetyl glycine (IAA-Gly), kinetin-9-glucoside (K9G), and dihydroZeatin-7-glucoside (DHZ7G) levels and decreasing trans-Zeatin riboside (tZR), N-[(-)-jasmonoyl]-(L)-valine (JA-Val), jasmonic acid (JA), and jasmonoyl-L-isoleucine (Ja-ILE) levels on 18 d, as well as promoting cell division and differentiation. The application of exogenous D-Arg regulated EC proliferation and somatic embryo induction by altering gene expression levels of the WRKY family, AP2/ERF family, C3H family, and C2H2 family. These results indicate that exogenous D-Arg could regulate the proliferation of EC and the SE induction of litchi by changing the biosynthesis of PAs through the alteration of gene expression pattern and endogenous hormone metabolism.
The PR-10 protein Pru p 1 is an endonuclease that preferentially cleaves single-stranded RNA.[Pubmed:38602716]
Chembiochem. 2024 Apr 11:e202400204.
Pathogenesis-related class 10 (PR-10) proteins play a crucial role in plant defense by acting as ribonucleases. The specific mechanism of action and substrate specificity of these proteins have remained largely unexplored so far. In this study, we elucidate the enzymatic activity of Pru p 1, a PR-10 protein from peach. We demonstrate that this protein catalyzes the endonucleolytic backbone cleavage of RNA substrates into short oligonucleotides. Initial cleavage products, identified through kinetic analysis, can bind again, priming them for further degradation. NMR binding site mapping reveals that the large internal cavity of Pru p 1, which is characteristic for PR-10 proteins, serves as an anchoring site for single-stranded ribonucleotide chains. We propose a structure-based mechanistic model that accounts for the observed cleavage patterns and the inhibitory effect of Zeatin, a nucleoside analog, on the ribonuclease activity of Pru p 1.
Insights into the Impact of Trans-Zeatin Overproduction-Engineered Sinorhizobium meliloti on Alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.) Tolerance to Drought Stress.[Pubmed:38564678]
J Agric Food Chem. 2024 Apr 17;72(15):8650-8663.
Plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria have been shown to enhance plant tolerance to drought stress through various mechanisms. However, there is limited research on improving drought resistance in alfalfa by genetically modifying PGPR to produce increased levels of cytokinins. Herein, we employed synthetic biology approaches to engineer two novel strains of Sinorhizobium meliloti capable of overproducing trans-Zeatin and investigated their potential in enhancing drought tolerance in alfalfa. Our results demonstrate that alfalfa plants inoculated with these engineered S. meliloti strains exhibited reduced wilting and yellowing while maintaining higher relative water content under drought conditions. The engineered S. meliloti-induced tZ activated the activity of antioxidant enzymes and the accumulation of osmolytes. Additionally, the increased endogenous tZ content in plants alleviated the impact of drought stress on the alfalfa photosynthetic rate. However, under nondrought conditions, inoculation with the engineered S. meliloti strains had no significant effect on alfalfa biomass and nodule formation.
Exploring the viability of Zeatin as a prospective therapeutic candidate for investigating the complex interplay between severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus (SARS-CoV) and Alzheimer's disease.[Pubmed:38559708]
In Silico Pharmacol. 2024 Mar 28;12(1):21.
The present research aims to explore the intricate link between SARS-CoV infection and susceptibility to Alzheimer's disease, focusing on the role of APOE4, a genetic factor associated with both conditions. Our research aims to uncover shared molecular pathways, considering APOE4's impact on lipid metabolism, immune responses, and neuroinflammation relevant to COVID-19 and AD. The Chyawanprash phytocompounds were subjected to in-silico ADMET profiling and Zeatin a neuroprotective cytokinin emerged as a promising regulator of the ACE2-SPIKE complex as it exhibits favourable pharmacological attributes, presenting as a non-substrate for Permeability glycoprotein, low Protein Binding Percentage, and distinctive toxicity endpoints. Therapeutic candidate. Zeatin's robust binding disrupts the intricate APOE4-ACE2-SPIKE interplay (AAS), offering a potential therapeutic avenue that is further corroborated by Molecular dynamic simulation as the system remained stable without any major fluctuation throughout the 100ns simulation. The AAS binding free energy, determined as -124.849 +/- 15.513 KJ/mol using MMPBSA assay, reveals significant contributions to complex stability from amino acids including, GLN41: 1.211 kcal/mol, GLU340: 1.188 kcal/mol, ALA344: 1.198 kcal/mol, while ARG38: 2.011 kcal/mol establishes pivotal strong bonds integral to the interaction between AAS and Zeatin. Rigorous cytotoxicity assessments reveal Zeatin's safety profile, highlighting its inhibitory effect on LN18 cell viability that sharply decreases to 32.47% at 200 microg/ml, underscoring its modulatory impact on cellular metabolism. These findings enhance our understanding of the convergent mechanisms linking SARS-CoV and AD, providing valuable insights for potential therapeutic interventions. Further research is warranted to elucidate the specific pathways and molecular mechanisms through which Zeatin exerts its protective effects.
Regulatory mechanism of GA(3) application on grape (Vitis vinifera L.) berry size.[Pubmed:38554534]
Plant Physiol Biochem. 2024 Mar 28;210:108543.
Gibberellin A(3) (GA(3)) is often used as a principal growth regulator to increase plant size. Here, we applied Tween-20 (2%)-formulated GA(3) (T1:40 mg/L; T2:70 mg/L) by dipping the clusters at the initial expansion phase of 'Red Globe' grape (Vitis vinifera L.) in 2018 and 2019. Tween-20 (2%) was used as a control. The results showed that GA(3) significantly increased fruit cell length, cell size, diameter, and volume. The hormone levels of auxin (IAA) and Zeatin (ZT) were significantly increased at 2 h (0 d) -1 d after application (DAA0-1) and remained significantly higher at DAA1 until maturity. Conversely, ABA exhibited an opposite trend. The mRNA and non-coding sequencing results yielded 436 differentially expressed mRNA (DE_mRNAs), 79 DE_lncRNAs and 17 DE_miRNAs. These genes are linked to hormone pathways like cysteine and methionine metabolism (ko00270), glutathione metabolism (ko00480) and plant hormone signal transduction (ko04075). GA(3) application reduced expression of insensitive dwarf 2 (GID2, VIT_07s0129g01000), small auxin-upregulated RNA (SAUR, VIT_08s0007g03120) and 1-aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylate synthase (ACS, VIT_18s0001g08520), but increased SAUR (VIT_04s0023g00560) expression. These four genes were predicted to be negatively regulated by vvi-miR156, vvi-miR172, vvi-miR396, and vvi-miR159, corresponding to specific lncRNAs. Therefore, miRNAs could affect grape size by regulating key genes GID2, ACS and SAUR. The R2R3 MYB family member VvRAX2 (VIT_08s0007g05030) was upregulated in response to GA(3) application. Overexpression of VvRAX2 in tomato transgenic lines increased fruit size in contrast to the wild type. This study provides a basis and genetic resources for elucidating the novel role of ncRNAs in fruit development.
Lipidomics, transcription analysis, and hormone profiling unveil the role of CsLOX6 in MeJA biosynthesis during black tea processing.[Pubmed:38544550]
Hortic Res. 2024 Jan 30;11(3):uhae032.
Jasmonates, such as jasmonic acid (JA) and methyl jasmonate (MeJA), are crucial aspect of black tea quality. However, lipids species, hormones, and genes regulated mechanism in the jasmonate biosynthesis during black tea processing are lacking. In this study, we employed lipidomics, hormone metabolism analysis, and transcriptome profiling of genes associated with the MeJA biosynthesis pathway to investigate these factors. The contents of lipids GLs, PLs, and TAG are decreased, accompanied by the main lipids species reduced during black tea processing. Galactolipids, primarily 34:3/36:6/36:3 DGDG and 36:6/36:5/36:4 MGDG, are transformed into massive MeJA and JA in black tea processing, accompanied by the decreased SA, MeSA, IAA, and BA and increased Zeatin. Additionally, the transcriptional activity of the primary genes in MeJA biosynthesis pathway exhibited downregulated trends except for AOS and OPR and non-primary genes tend to be a little high or have fluctuation of expression. Coordinated expression of main CsHPL (TEA008699), CsAOS (TEA001041), and CsJMT (TEA015791) control the flow of lipids degradation and MeJA production. A strong infected reduction of a key lipoxygenase gene, CsLOX6 (TEA009423), in tea buds significantly reduced the level of jasmonates and expression of downstream genes, accompanied by SA, MeSA level rising, and ABA declining. We have identified a key CsLOX6, as well as established galactolipids, mainly 34:3/36:6/36:3 DGDG and 36:6/36:5/36:4 MGDG, sources for MeJA biosynthesis regulated by dynamics hormone and controlled by coordinated expressed CsHPL (TEA008699), CsAOS (TEA001041), and CsJMT (TEA015791). Our findings provide a theoretical basis for breeding high-quality black tea and offer valuable insights for improving processing methods.
Insights into drought stress response mechanism of tobacco during seed germination by integrated analysis of transcriptome and metabolome.[Pubmed:38537383]
Plant Physiol Biochem. 2024 Apr;209:108526.
Drought stress inhibits seed germination, plant growth and development of tobacco, and seriously affects the yield and quality of tobacco leaves. However, the molecular mechanism underlying tobacco drought stress response remains largely unknown. In this study, integrated analysis of transcriptome and metabolome was performed on the germinated seeds of a cultivated variety K326 and its EMS mutagenic mutant M28 with great drought tolerance. The result showed that drought stress inhibited seed germination of the both varieties, while the germination rate of M28 was faster than that of K326 under drought stress. Besides, the levels of phytohormone ABA, GA19, and Zeatin were increased by drought stress in M28. Five vital pathways were identified through integrated transcriptomic and metabolomic analysis, including Zeatin biosynthesis, aspartate and glutamate synthesis, phenylamine metabolism, glutathione metabolism, and phenylpropanoid synthesis. Furthermore, 20 key metabolites in the above pathways were selected for further analysis of gene modular-trait relationship, and then four highly correlated modules were found. Then analysis of gene expression network was carried out of Top30 hub gene of these four modules, and 9 key candidate genes were identified, including HSP70s, XTH16s, APX, PHI-1, 14-3-3, SCP, PPO. In conclusion, our study uncovered some key drought-responsive pathways and genes of tobacco during seeds germination, providing new insights into the regulatory mechanisms of tobacco drought stress response.
Exploring the allelopathic autotoxicity mechanism of ginsenosides accumulation under ginseng decomposition based on integrated analysis of transcriptomics and metabolomics.[Pubmed:38515624]
Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2024 Mar 7;12:1365229.
Continuous cropping obstacles seriously constrained the sustainable development of the ginseng industry. The allelopathic autotoxicity of ginsenosides is the key "trigger" of continuous cropping obstacles in ginseng. During harvest, the ginseng plants could be broken and remain in the soil. The decomposition of ginseng residue in soil is one of the important release ways of ginsenosides. Therefore, the allelopathic mechanism of ginsenosides through the decomposed release pathway needs an in-depth study. To investigate this allelopathic regulation mechanism, the integrated analysis of transcriptomics and metabolomics was applied. The prototype ginsenosides in ginseng were detected converse to rare ginsenosides during decomposition. The rare ginsenosides caused more serious damage to ginseng hairy root cells and inhibited the growth of ginseng hairy roots more significantly. By high-throughput RNA sequencing gene transcriptomics study, the significantly differential expressed genes (DEGs) were obtained under prototype and rare ginsenoside interventions. These DEGs were mainly enriched in the biosynthesis of secondary metabolites and metabolic pathways, phytohormone signal transduction, and protein processing in endoplasmic reticulum pathways. Based on the functional enrichment of DEGs, the targeted metabolomics analysis based on UPLC-MS/MS determination was applied to screen endogenous differential metabolized phytohormones (DMPs). The influence of prototype and rare ginsenosides on the accumulation of endogenous phytohormones was studied. These were mainly involved in the biosynthesis of diterpenoid, Zeatin, and secondary metabolites, phytohormone signal transduction, and metabolic pathways. After integrating the transcriptomics and metabolomics analysis, ginsenosides could regulate the genes in phytohormone signaling pathways to influence the accumulation of JA, ABA, and SA. The conclusion was that the prototype ginsenosides were converted into rare ginsenosides by ginseng decomposition and released into the soil, which aggravated its allelopathic autotoxicity. The allelopathic mechanism was to intervene in the response regulation of genes related to the metabolic accumulation of endogenous phytohormones in ginseng. This result provides a reference for the in-depth study of continuous cropping obstacles of ginseng.


