Dicliptera chinensis
Dicliptera chinensis
1. The products in our compound library are selected from thousands of unique natural products; 2. It has the characteristics of diverse structure, diverse sources and wide coverage of activities; 3. Provide information on the activity of products from major journals, patents and research reports around the world, providing theoretical direction and research basis for further research and screening; 4. Free combination according to the type, source, target and disease of natural product; 5. The compound powder is placed in a covered tube and then discharged into a 10 x 10 cryostat; 6. Transport in ice pack or dry ice pack. Please store it at -20 °C as soon as possible after receiving the product, and use it as soon as possible after opening.
Natural products/compounds from Dicliptera chinensis
- Cat.No. Product Name CAS Number COA
-
BCN5948
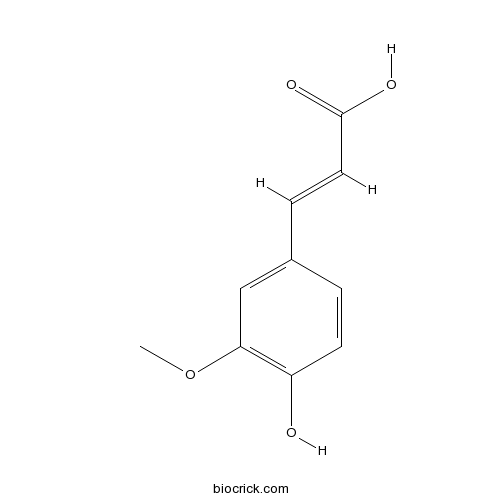
Ferulic acid1135-24-6
Instructions
-
BCN1717
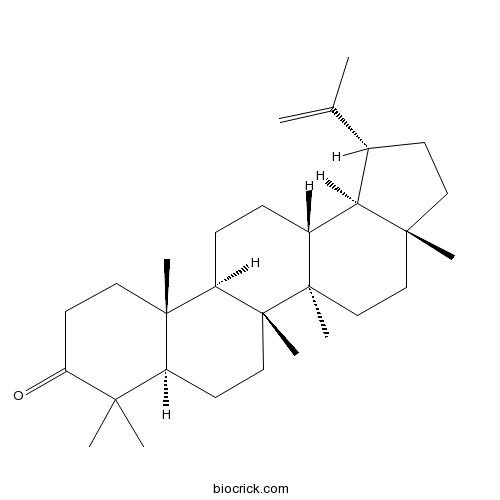
Lupenone1617-70-5
Instructions
-
BCN4865
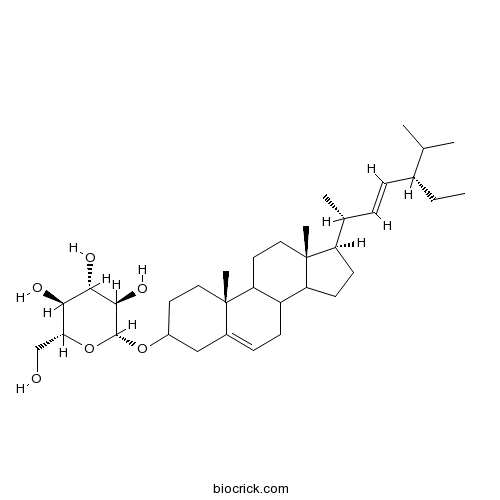
Stigmasterol glucoside19716-26-8
Instructions
-
BCN4955
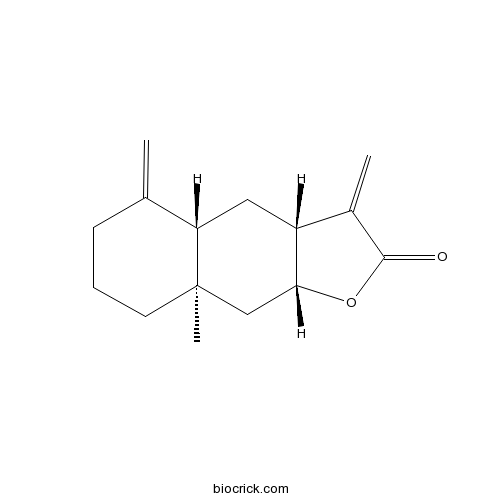
Isoalantolactone470-17-7
Instructions
-
BCN5572
Kaempferitrin482-38-2
Instructions

-
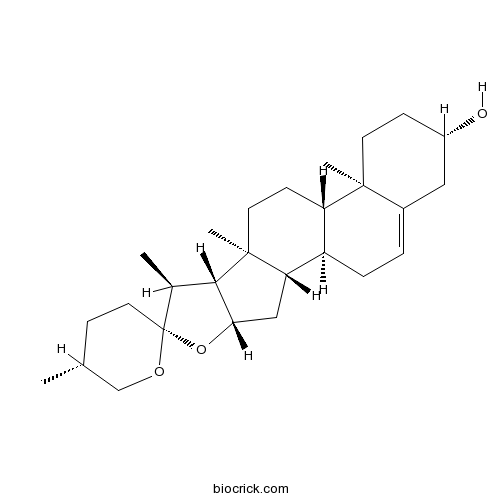
BCN6272
Diosgenin512-04-9
Instructions
-
BCN1033
Alantolactone546-43-0
Instructions
Screening for cytotoxic chemical constituents from Justicia procumbens by HPLC-DAD-ESI-MS and NMR.[Pubmed: 29372338]
The Acanthaceae family is an important source of therapeutic drugs and ethno medicines. There are many famous medicinal plants from this family, such as Andrographis paniculata, Baphicacanthus cusia, and Dicliptera chinensis. Justicia procumbens (J. procumbens) is widely distributed in tropical and sub-tropical of the world. It has long been used in traditional Chinese medicine for cancer. The 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide assay showed the ethyl acetate extract of J. procumbens had a cytotoxic activity. Therefore, qualitative and quantitative analysis of the chemical constituents in the ethyl acetate extract was important for understanding its pharmacological mechanism.
Isolation, characterization and bioactivities of the polysaccharides from Dicliptera chinensis (L.) Juss.[Pubmed: 28344090]
The polysaccharides of Dicliptera chinensis (L.) Juss. (DCP-1 and DCP-2) were extracted and isolated using the methods of water extract-ethanol precipitate and sephadex column chromatography and characterized by gel permeation chromatography (GPC), Fourier transform infrared spectrometry (FT-IR) and gas chromatography (GC), respectively. The antioxidant activity of DCPs was evaluated by scavenging activity of DPPH, hydroxyl, superoxide anion and ABTS radical. Moreover, the anti-aging activity of DCP-2 was investigated using an aging model-induced by D-galactose (D-gal) in mice. The results show that the weight average molecular weight (Mw) of DCP-2 was 2 273Da with a narrow polydispersity index of 1.01, and it was a heteropolysaccharide and consisted of glucose, galactose, arabinose, rhamnose and mannose with a molar ratio of 3.20:2.54:1.69:1.58:1.00. DCP-2 had stronger antioxidant activity against DPPH, hydroxyl, superoxide anion and ABTS radical, while DCP-1 had hardly any antioxidant activity and DCP had weaker antioxidant activity. Furthermore, DCP-2 can enhance antioxidant capacity and had anti-aging activity against D-gal induced aging mice. These results proposed that DCP-2 might be developed as a potential functional food with the activity of anti-aging.
Dicliptera Chinensis polysaccharides target TGF-β/Smad pathway and inhibit stellate cells activation in rats with dimethylnitrosamine-induced hepatic fibrosis.[Pubmed: 26828995]
This study aims to study impact of Dicliptera chinensis polysaccharide (DCP) on hepatic fibrosis (HF) and activation of hepatic stellate cells (HSCs). Liver fibrosis model was induced by intraperitoneal injection of dimethyl nitrosamines (DMN) in rat. Rats in treatment group were administrated with different concentrations of DCP (0, 100, 300 mg/kg) by intraperitoneal injection. Hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) and Masson's trichrome staining were used to assess histo-pathological change. α-SMA, TGF-β1 and pSmad 2/3 were assayed by immuno-histochemistry. HSC-T6 cells were stimulated by recombined rat TGF-β1 (1 ng/mL) to simulate an activating model in vitro and then interfered with DCP (concentration of 0, 25, 50, 100, 200, 400 µg/ml). MTT assay was used to determine cell proliferation and western blotting was used to detect α-SMA and pSmad 2/3 expression. Results demonstrated that DCP alleviated DMN-induced liver fibrosis in rat and significantly down-regulated TGF-β1 expression, pSmad2/3 and α-SMA in liver tissue in a dose-dependent way. DCP inhibited proliferation and activation of TGF-β1-stimulated HSC-T6 in vitro and significantly down-regulated α-SMA and pSmad2/3 expression. In conclusion, this study revealed that DCP attenuates progression of liver fibrosis through suppressing TGF-β/Smad pathway. DCP is a potential botanical polysaccharide to management liver fibrosis.
Hepatoprotective effects of Dicliptera chinensis polysaccharides on dimethylnitrosamine-induced hepatic fibrosis rats and its underlying mechanism.[Pubmed: 26727645]
Dicliptera chinensis is a traditional herbal medicine used anciently in China for hepatopathy treatment, especially in south areas. Our several studies have demonstrated that dicliptera chinensis polysaccharides (DCP), which has a markedly protective effects on chemistry-induced models of acute liver injury in rats. In this study, we further investigated the potentially hepatoprotective effect of dicliptera chinensis polysaccharides (DCP) on hepatic fibrosis (HF) rats induced by dimethylnitrosamine (DMN).
[Studies on structure characteristic of polysaccharide P1A from Dicliptera chinensis].[Pubmed: 26281585]
The chemical structures of P1 A was identified by complete acid hydrolysis, partial acid hydrolysis, periodate oxidation-Smith degradation, methylation analysis, IR and NMR. The results showed that P1 A had a backbone consisting rhamnose, mannose, glucose and galactose. The side chain possessed arabinose and xylose. 1-->, 1-->6 and non-reducing terminal linkages existed in polysaccharide P1A, but there are doubling amount of 1-->2 and 1-->4 linkages. Oxidable linkage of P1 A accounted for 45%, and inoxidable linkage of P1A accounted for 55%. Mannose, glucose and galactose were mainly linked by 1-->2 linkage. Rhamnose, arabinose and xylose were mainly linked by 1-->2 and 1-->4 linkages. PlA contained beta-Glc(1,6)-,beta-Gal(1,3)-,beta-Man(1,4)-beta-Rha,-Glc(1,4)-, Glc(1)-,-Gal(1,4)- and Man(1)-.
[Research on active extracts of Dicliptera chinensis on liver protection].[Pubmed: 20450052]
To search pharmacody namic active extracts of Dicliptera chinensis for protecting liver.
[Studies on the chemical constituents in herbs of ethanolic extract from herbs of Dicliptera chinensis].[Pubmed: 17048644]
To study the chemical constituents of ethanolic extract from herbs of Dicliptera chinensis.


