Forsythia suspensa
Forsythia suspensa
1. The products in our compound library are selected from thousands of unique natural products; 2. It has the characteristics of diverse structure, diverse sources and wide coverage of activities; 3. Provide information on the activity of products from major journals, patents and research reports around the world, providing theoretical direction and research basis for further research and screening; 4. Free combination according to the type, source, target and disease of natural product; 5. The compound powder is placed in a covered tube and then discharged into a 10 x 10 cryostat; 6. Transport in ice pack or dry ice pack. Please store it at -20 °C as soon as possible after receiving the product, and use it as soon as possible after opening.
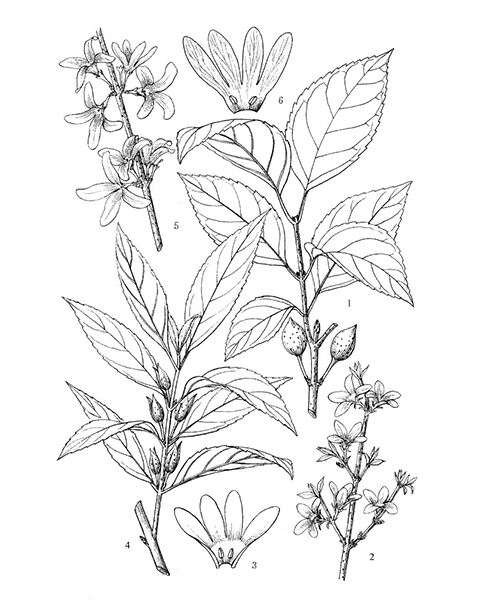

Natural products/compounds from Forsythia suspensa
- Cat.No. Product Name CAS Number COA
-
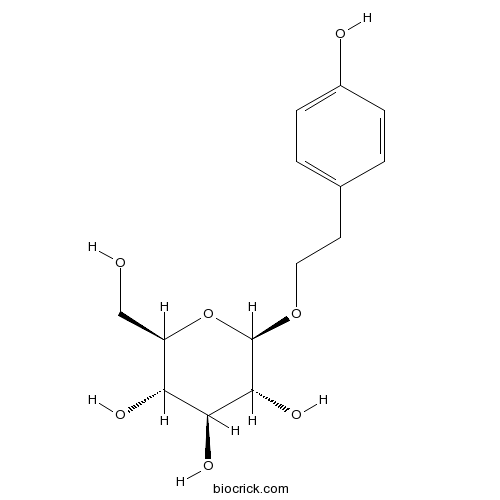
BCN5966
Salidroside10338-51-9
Instructions
-
BCN2787
Calceolarioside B105471-98-5
Instructions

-
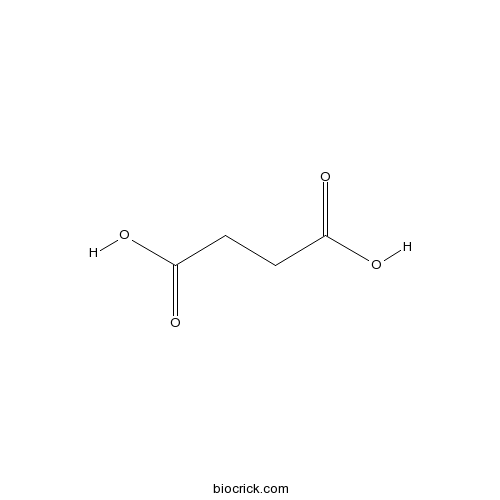
BCN5890
Succinic acid110-15-6
Instructions
-
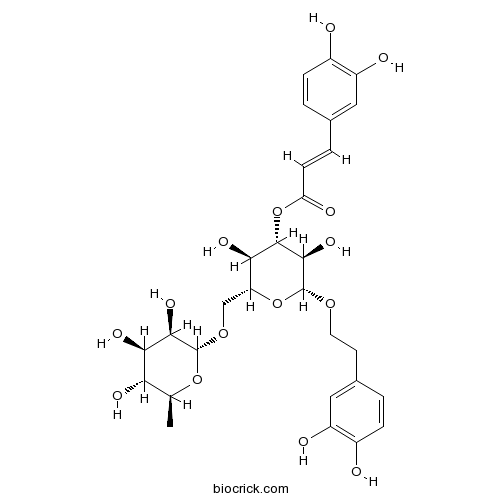
BCN6430
Forsythoside I1177581-50-8
Instructions
-
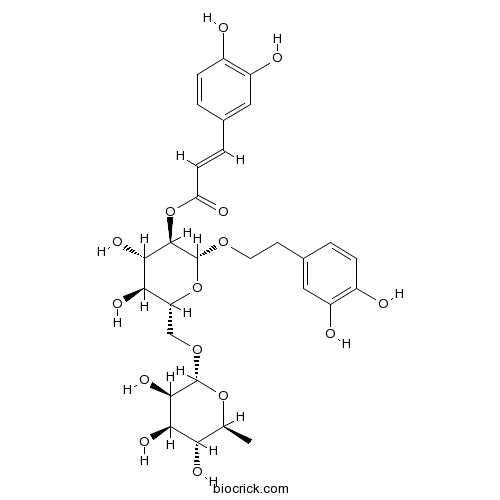
BCN6431
Forsythoside H1178974-85-0
Instructions
-
BCN6059
Syringin118-34-3
Instructions

-
BCN6105
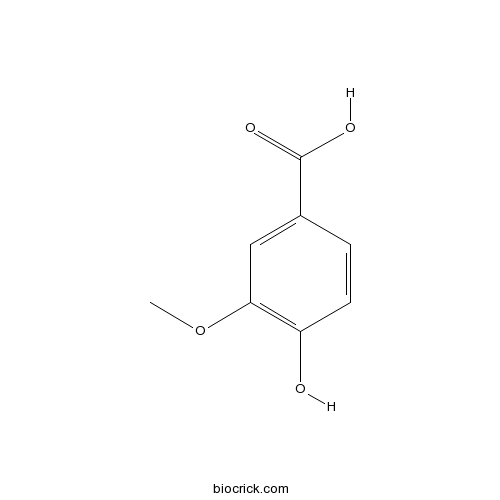
Vanillic acid121-34-6
Instructions
-
BCN1684
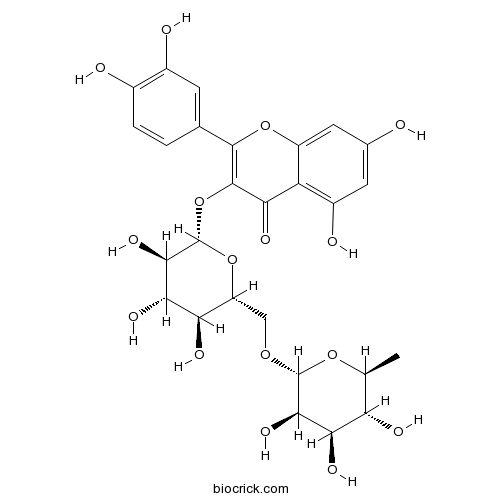
Rutin153-18-4
Instructions
-
BCN4081
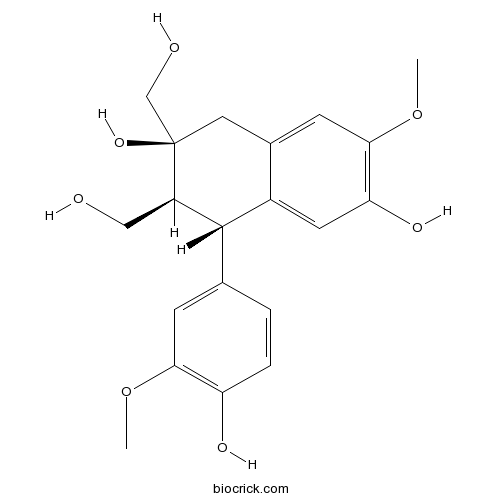
Cycloolivil3064-05-9
Instructions
-
BCN5979
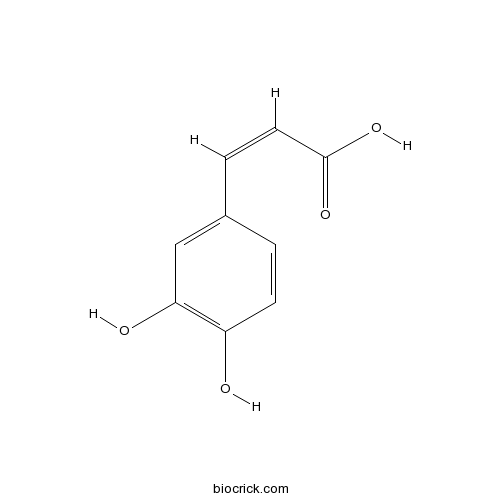
Caffeic acid331-39-5
Instructions
-
BCN5506
Asiatic acid464-92-6
Instructions

-
BCN5524
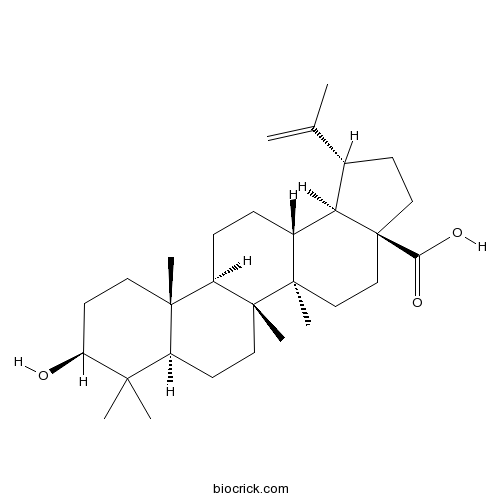
Betulinic acid472-15-1
Instructions
-
BCN5531
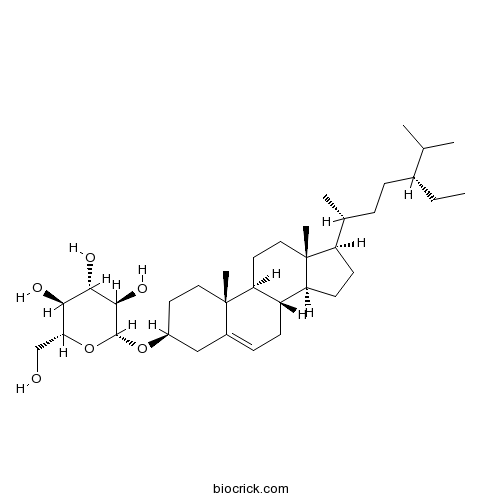
Daucosterol474-58-8
Instructions
-
BCN5549
Astragalin480-10-4
Instructions

-
BCN2653
Phillygenin487-39-8
Instructions

-
BCN1096
Phillyrin487-41-2
Instructions

-
BCN5616
Oleanolic acid508-02-1
Instructions

-
BCN5789
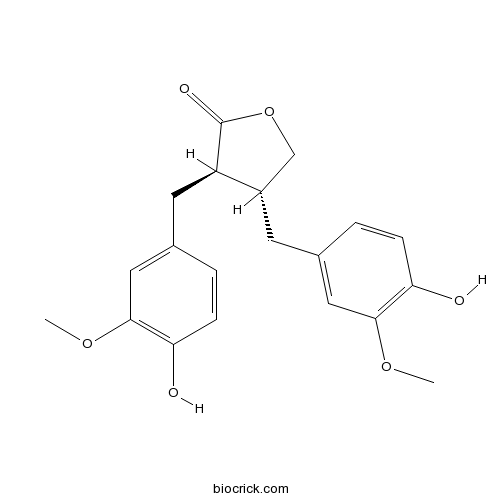
Matairesinol580-72-3
Instructions
-
BCN4136
Acteoside61276-17-3
Instructions

-
BCN1376
Pinoresinol 4-O-beta-D-glucopyranoside69251-96-3
Instructions

-
BCN4327
Ursolic acid77-52-1
Instructions

-
BCN1195
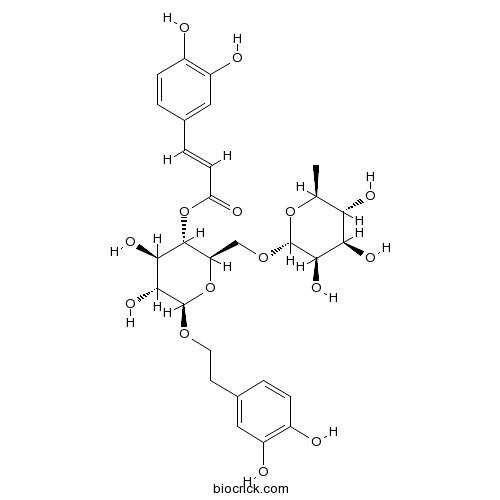
Forsythoside A79916-77-1
Instructions
-
BCN1015
Beta-Sitosterol83-46-5
Instructions
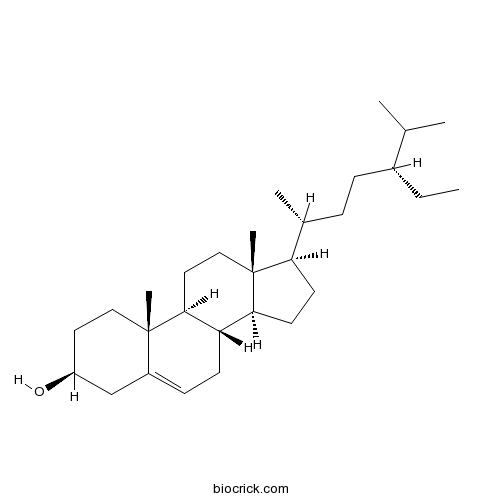
-
BCN2782
Forsythoside E93675-88-8
Instructions
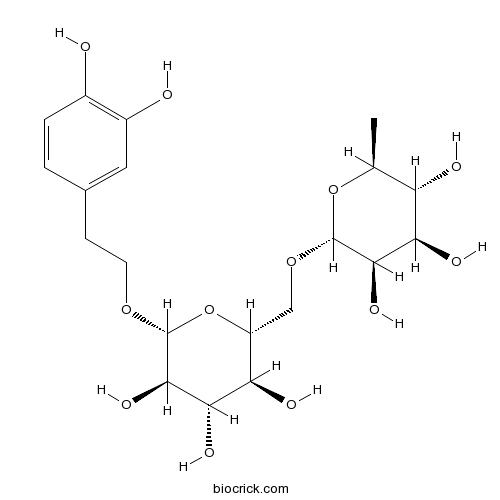
-
BCN1204
Poliumoside94079-81-9
Instructions

[Effects of Forsythia suspensa Volatile Oil Loaded Nanomicellar on Transdermal and Transmucosal Drug Delivery of Phillyrin in Vitro].[Pubmed: 30080015]
To prepare all components loaded liquid preparation of Forsythia suspensa( ACLL) by the technology of nanomicellar solubilization,and to investigate the effects of Forsythia suspensa volatile oil loaded nanomicellar on the transdermal and transmucosal drug delivery of phillyrin.
[Study on essential oil separation from Forsythia suspensa oil-bearing water body based on vapor permeation membrane separation technology].[Pubmed: 29751711]
To investigate the feasibility of vapor permeation membrane technology in separating essential oil from oil-water extract by taking the Forsythia suspensa as an example. The polydimethylsiloxane/polyvinylidene fluoride (PDMS/PVDF) composite flat membrane and a polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) flat membrane was collected as the membrane material respectively. Two kinds of membrane osmotic liquids were collected by self-made vapor permeation device. The yield of essential oil separated and enriched from two kinds of membrane materials was calculated, and the microscopic changes of membrane materials were analyzed and compared. Meanwhile, gas chromatography-mass spectrometry (GC-MS) was used to compare and analyze the differences in chemical compositions of essential oil between traditional steam distillation, PVDF membrane enriched method and PDMS/PVDF membrane enriched method. The results showed that the yield of essential oil enriched by PVDF membrane was significantly higher than that of PDMS/PVDF membrane, and the GC-MS spectrum showed that the content of main compositions was higher than that of PDMS/PVDF membrane; The GC-MS spectra showed that the components of essential oil enriched by PVDF membrane were basically the same as those obtained by traditional steam distillation. The above results showed that vapor permeation membrane separation technology shall be feasible for the separation of Forsythia essential oil-bearing water body, and PVDF membrane was more suitable for separation and enrichment of Forsythia essential oil than PDMS/PVDF membrane.
Forsythia suspensa extract attenuates breast muscle oxidative injury induced by transport stress in broilers.[Pubmed: 29528452]
This experiment was conducted with 144 male Arbor Acre broilers (one d old, weighing 45.6 ± 1.3 g) to determine protective effects of Forsythia suspensa extract (FSE) against breast muscle oxidative injury induced by transport stress (TS). The birds were randomly allotted to one of 4 treatments in a 2 × 2 factorial arrangement. The treatments consisted of broilers fed diets supplemented without or with FSE (100 mg/kg) and challenged without or with TS for 3 h before slaughter. Transport stress increased live BW loss of broilers (P < 0.05), and the adverse effect was attenuated by FSE (P < 0.05). Serum levels of corticoserone and lactate were increased for broilers after transportation (P < 0.05), whereas these parameters were not affected by FSE. After slaughter, neither breast muscle pH value at 45 min and 24 h postmortem nor 24 h drip loss value was influenced by TS or FSE, whereas TS increased the value of pH decline within 24 h postmortem (P < 0.05). Transportation decreased redness and increased yellowness value of breast muscle in broilers (P < 0.05), and FSE tended to have (P = 0.06) or had the converse changes (P < 0.05). Comparing with non-transported birds, the birds subjected to transportation had greater malondialdehyde (MDA) content and avUCP mRNA expression (P < 0.05) and lower 1,1-diphenyl-2-picryl-hydrazyl (DPPH) radical scavenging activity (P < 0.05) in breast muscle, whereas the birds supplemented with FSE had lower MDA content (P < 0.05) and greater DPPH radical scavenging activity (P < 0.05). Transport caused decreases (P < 0.05) in total antioxidant capacity and glutathione peroxidase activity, and the decreases were improved by FSE (P < 0.05). Collectively, live BW loss and breast muscle oxidative injury were increased by TS in broilers and could be attenuated by FSE via directly scavenging free radicals and increased antioxidant capacity. Therefore, FSE could protect broilers against breast muscle oxidative injury induced by TS.
Forsythia suspensa extract protects broilers against breast muscle oxidative injury induced by corticosterone mimicked pre-slaughter acute stress.[Pubmed: 29514276]
Broilers were used to determine the protective effects of Forsythia suspensa extract (FSE) against breast muscle oxidative injury induced by corticosterone (CS) mimicking pre-slaughter acute stress. A total of 144 male Arbor Acre broilers was randomly allotted to one of 4 treatments in a 2 × 2 factorial arrangement that included FSE supplementation (0 or 100 mg/kg) and subcutaneous injection of CS (0 or 4 mg/kg) at 3 h before slaughter. Corticosterone increased live BW loss, and the adverse effect was attenuated by FSE in broilers subjected to CS (P < 0.05). Serum levels of CS, uric acid, and glucose were increased, and postmortem breast muscle pH values at 45 min and 24 h were decreased for CS-challenged broilers (P < 0.05). Corticosterone increased lightness and yellowness values and decreased redness of breast muscle (P < 0.05), and FSE decreased yellowness and increased redness of breast muscle (P < 0.05). Drip loss was increased by CS for birds supplemented without FSE (P < 0.05) and decreased by FSE for birds under CS challenge (P < 0.05). Corticosterone increased monounsaturated fatty acid (FA) and decreased polyunsaturated FA in breast muscle (P < 0.05), and saturated FA was decreased and polyunsaturated FA was increased by FSE (P < 0.05). Malondialdehyde and carbonyl contents in breast muscle were increased by CS and decreased by FSE (P < 0.05). Inhibition of 1,1-diphenyl-2-picryl-hydrazyl was decreased by CS and increased by FSE (P < 0.05). The activities of total-antioxidant capacity, glutathione peroxidase, and superoxide dismutase in breast muscle were lower in birds subjected to CS (P < 0.05) and were greater in birds supplemented with FSE (P < 0.05). Collectively, live BW loss and breast muscle oxidative injury were increased by CS in broilers, and these stress-related adverse effects could be attenuated by FSE supplementation via enhanced scavenging ability of free radicals and antioxidant capacity. Therefore, FSE could protect broilers against breast muscle oxidative injury when acute stress happens.
Simultaneous Separation of Eight Lignans in Forsythia suspensa by β-Cyclodextrin-Modified Capillary Zone Electrophoresis.[Pubmed: 29495375]
None
Hepatoprotective effect of Forsythiae Fructus water extract against carbon tetrachloride-induced liver fibrosis in mice.[Pubmed: 29474900]
The fruit of Forsythia suspensa (Thunb.) Vahl, named Forsythiae Fructus (Lian-Qiao), is a well-known traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) used for clearing away heat and toxic material, eliminating the mass and relieving swelling.


