Hedysarum polybotrys
Hedysarum polybotrys
1. The products in our compound library are selected from thousands of unique natural products; 2. It has the characteristics of diverse structure, diverse sources and wide coverage of activities; 3. Provide information on the activity of products from major journals, patents and research reports around the world, providing theoretical direction and research basis for further research and screening; 4. Free combination according to the type, source, target and disease of natural product; 5. The compound powder is placed in a covered tube and then discharged into a 10 x 10 cryostat; 6. Transport in ice pack or dry ice pack. Please store it at -20 °C as soon as possible after receiving the product, and use it as soon as possible after opening.
Natural products/compounds from Hedysarum polybotrys
- Cat.No. Product Name CAS Number COA
-
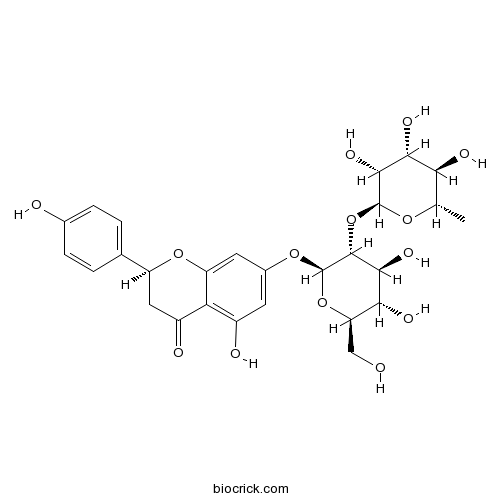
BCN6312
Naringin10236-47-2
Instructions
-
BCN5930
Calycosin20575-57-9
Instructions

-
BCN1061
Formononetin485-72-3
Instructions

-
BCN5926
Ononin486-62-4
Instructions

-
BCN2775
Hypaphorine487-58-1
Instructions

[Analysis Characteristics of Inorganic Elements in Different Organs of Hedysarum polybotrys in Different Growing Variation].[Pubmed: 30079704]
To study the characteristics of inorganic elements in different organs of Hedysarum polybotrys in different growing variation, including root, rhizome, leaf, flower and fruit.
[Comparison between Astragalus membranaceus var. mongholicus and Hedysarum polybotrys based on ITS sequences and metabolomics].[Pubmed: 27169287]
Astragalus membranaceus var. mongholicus and Hedysarum polybotrys belong to different genera, but have similar drug efficacy in traditional Chinese medicine theory, and H. polybotrys was used as the legal A. membranaceus var. mongholicus previously. In this study, similarities and differences between them were analyzed via their ITS/ITS2 fragments information. The ITS (internal transcribed spacer) regions were amplified using polymerase chain reaction and then sequenced in two-way. The alignment lengths of ITS regions were 616 bp, in which 508 loci were consistent, and 103 loci were different, accounting for 82.47% and 16.72% of the total ITS nucleotides in length, respectively. As genotype determines phenotype, 1HNMR-based metabolomic approach was further used to reveal the chemical similarities and differences between them. Thirty-four metabolites were identified in the 1H NMR spectra, and twenty-seven metabolites were the common components. Amino acids, carbohydrates and other primary metabolites were similar, while a large difference existed in the flavonoids and astragalosides. This study suggests that A. membranaceus var. mongholicus and H. polybotrys show similarities and differences from molecular and chemical perspectives, which has laid a foundation for elucidating the effective material basis of drug with similar efficacy and resources utilization.
Genetic diversity and distribution of rhizobia associated with the medicinal legumes Astragalus spp. and Hedysarum polybotrys in agricultural soils.[Pubmed: 26915496]
With the increasing cultivation of medicinal legumes in agricultural fields, the rhizobia associated with these plants are facing new stresses, mainly from fertilization and irrigation. In this study, investigations on the nodulation of three cultivated medicinal legumes, Astragalus mongholicus, Astragalus membranaceus and Hedysarum polybotrys were performed. Bacterial isolates from root nodules of these legumes were subjected to genetic diversity and multilocus sequence analyses. In addition, the distribution of nodule bacteria related to soil factors and host plants was studied. A total 367 bacterial isolates were obtained and 13 genospecies were identified. The predominant microsymbionts were identified as Mesorhizobium septentrionale, Mesorhizobium temperatum, Mesorhizobium tianshanense, Mesorhizobium ciceri and Mesorhizobium muleiense. M. septentrionale was found in most root nodules especially from legumes grown in the barren soils (with low available nitrogen and low organic carbon contents), while M. temperatum was predominant in nodules where the plants were grown in the nitrogen-rich fields. A. mongholicus tended to be associated with M. septentrionale, M. temperatum and M. ciceri in different soils, while A. membranaceus and H. polybotrys tended to be associated with M. tianshanense and M. septentrionale, respectively. This study showed that soil fertility may be the main determinant for the distribution of rhizobia associated with these cultured legume plants.
[Intervention of Qi-activating and Spleen-strengthening Herbs on Ca2+/CaMK II Signaling Pathways Key Factors in Skeletal Muscle Tissue of Rats with Spleen-qi Deficiency].[Pubmed: 26495660]
To observe changes of [Ca2+]i concentration and CaM, CaMK II and p-CaMK II of Ca2+/CaMK II signaling pathways in skeletal muscle tissue of rats with spleen-qi deficiency and intervention of Sijunzi decoction and extract of Hedysarum polybotrys.
Structural characterization and stimulating effect on osteoblast differentiation of a purified heteropolysaccharide isolated from Hedysarum polybotrys.[Pubmed: 25037407]
Radix Hedysari polysaccharides (HPS) is the principal active fraction of Radix Hedysari (RH). The information about HPS3d, the main fraction of HPS3, and its effect on bone is still unknown. In the present study, the purified HPS3d was obtained by anion-exchange column. It consisted of 94.38% polysaccharide, 3.40% protein and 13.30% uronic acid. The molecular weight was measured to be 84.6kDa. The backbone consisted of galactopyranose and galacturonopyranose, and the side chains were composed of glucopyranose, rhamnopyranose and arabinofuranose. The FT-IR and elemental analysis showed that HPS3d was the sulfated polysaccharide. HPS3d upregulated alkaline phosphatase (ALP) activity and the expression of other osteogenic marker genes in osteoblast. In addition, HPS3d increased the expression and transcriptional activity of Runt-related transcription factor 2 (Runx-2) and Osterix, the two master genes of osteoblast differentiation. These findings suggest that HPS3d stimulates osteoblast differentiation by activation of Runx-2 and Osterix.
Structural characterization and antioxidant activity of a heteropolysaccharide isolated from Hedysarum polybotrys.[Pubmed: 24625202]
A water-soluble polysaccharide (HPS3aS) with a molecular mass of 1.22 × 10(4) Da was isolated from Hedysarum polybotrys using anion-exchange and gel-permeation chromatography. HPS3aS exhibits a globular-shaped conformation in 0.1 M NaNO3 by size exclusion chromatography with multi-angle laser light scattering (SEC-MALLS). The investigation of the structural features of this heteropolysaccharide through a combination of chemical and instrumental analyses revealed that the backbone of HPS3aS is composed of α-D-(1 → 4)-linked glucopyranose residues, which occasionally branched at O-6. The branches are composed of (1 → 4)-linked galactopyranose residues and terminated with glucopyranose residues. HPS3aS possesses good in vitro antioxidant activity, as evaluated by scavenging assays with 1,1-diphenyl-2-picrylhydrazyl, hydroxyl, and superoxide radicals, which suggests that HPS3aS could be a potential antioxidant.
[Sulfated modification and anticoagulant activity in vitro of sulfated glucan isolated from the aqueous extract of Hedysarum polybotrys].[Pubmed: 24475703]
SHG was sulfated by chlorosulfonic acid-pyridine method, and six samples which we got were prepared in different reaction conditions. There is a characteristic absorption peak near 260 nm in UV spectra and there are two characteristic absorption peaks near 1240 cm(-1) and 810 cm(-1) in the FT-IR. Degree of sulfation (DS) was calculated by elemental analysis and turbidimetry. Under the same conditions the absorption peaks become strong with the DS increase. The anticoagulant activity of SHG and sulfated modification samples was evaluated by the classic coagulant assays of prothrombin time (PT), activated partial thrombin time (APTT) live enzymes, and plasma thrombin time (TT). Results show that sulfated SHG has a good anticoagulant activity in vitro, and DS increased activity within a certain range.
Immunomodulatory effects of Hedysarum polybotrys extract in mice macrophages, splenocytes and leucopenia.[Pubmed: 24300120]
Astragali Radix (Huang-Qi) is a popular herbal medicine commonly used as a constituent in tonic herbal preparations. Hedysarum polybotrys Handel-Mazzetti is one species used of Astragali Radix. In this study, the immunomodulatory properties of H. polybotrys were explored by LPS-activated and SNP-treated RAW 264.7 cells and splenocytes and, daunoblastina-induced leucopenia BALB/c mice. Formononetin was used as the bioactive marker to monitor the quality of the H. polybotrys extracts. H. polybotrys was extracted with hot-water and methanol, and MeOH extract partitioned with H2O (M-H) and ethyl acetate (M-EA) to yield four different fractions. M-EA had the highest formononetin and total proanthocyanidin content and showed stronger inhibitory effects on the production and expression of NO, PGE2, iNOS and COX-2 in LPS-activated RAW 264.7 cells and splenocytes than the other fractions. In addition, M-EA significantly stimulated the proliferation of LPS-activated RAW 264.7 cells and splenocytes, enhanced NO radicals scavenging and attenuated NO-induced cytotoxicity. Furthermore, M-EA also significantly increased the rate of recovery of white blood cells level in daunoblastina-induced leucopenia mice. These evidences suggest that this traditional Qi-tonifying herb has potential effects in clinical conditions when immune-enhancing and anti-inflammatory effect is desired.
[Ultrafiltration membrane extract mixture from Angelica sinensis and Hedysarum polybotrys induced transdifferentiation of BMSCs in mice: an experimental research].[Pubmed: 23905382]
To observe and evaluate the effect of transdifferentiation of bone marrow derived stroma cells (BMSCs) into nerve cells by ultrafiltration membrane extract mixture from Angelica sinensis and Hedysarum polybotrys.


