Ilex cornuta
Ilex cornuta
1. The products in our compound library are selected from thousands of unique natural products; 2. It has the characteristics of diverse structure, diverse sources and wide coverage of activities; 3. Provide information on the activity of products from major journals, patents and research reports around the world, providing theoretical direction and research basis for further research and screening; 4. Free combination according to the type, source, target and disease of natural product; 5. The compound powder is placed in a covered tube and then discharged into a 10 x 10 cryostat; 6. Transport in ice pack or dry ice pack. Please store it at -20 °C as soon as possible after receiving the product, and use it as soon as possible after opening.
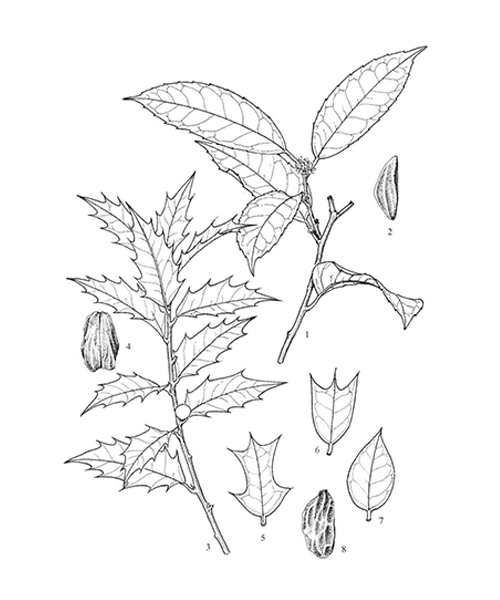
Natural products/compounds from Ilex cornuta
- Cat.No. Product Name CAS Number COA
-
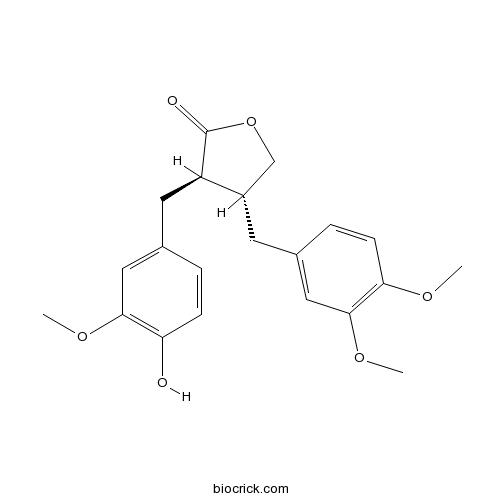
BCN1717
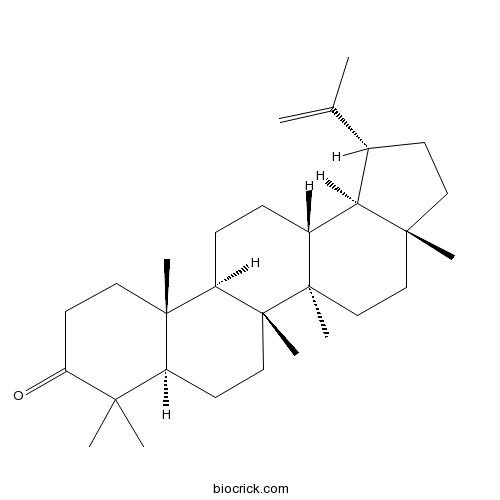
Lupenone1617-70-5
Instructions
-
BCN5370
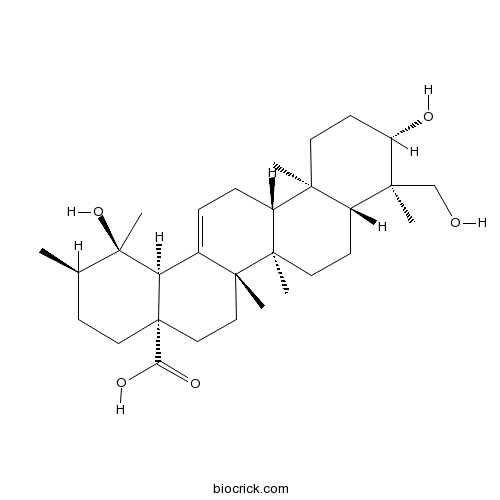
Rutundic acid20137-37-5
Instructions
-
BCN5291
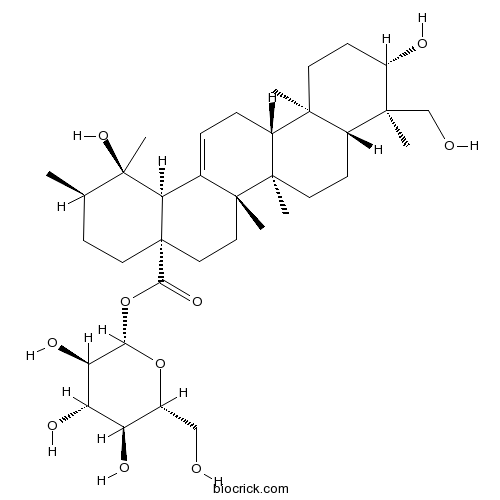
Ziyuglycoside II35286-59-0
Instructions

-
BCN1191
Pedunculoside42719-32-4
Instructions
-
BCN5506
Asiatic acid464-92-6
Instructions

-
BCN5551
Isorhamnetin480-19-3
Instructions

-
BCN5570
Hyperoside482-36-0
Instructions

-
BCN1061
Formononetin485-72-3
Instructions

-
BCN1247
Isorhamnetin-3-O-beta-D-Glucoside5041-82-7
Instructions

-
BCN2343
Schaftoside51938-32-0
Instructions

-
BCN5725
Lupeol545-47-1
Instructions

-
BCN6291
Arctigenin7770-78-7
Instructions
The sentinel tree nursery as an early warning system for pathway risk assessment: Fungal pathogens associated with Chinese woody plants commonly shipped to Europe.[Pubmed: 29186190]
Introduction of and invasion by alien plant pathogens represents the main cause of emerging infectious diseases affecting domesticated and wild plant species worldwide. The trade in living plants is the most common pathway of introduction. Many of the alien tree pathogens recently introduced into Europe were not previously included on any quarantine lists. To help determine the potential risk of pest introduction through trading of ornamental plants, a sentinel nursery was established in Beijing, China in 2008. The sentinel nursery planting included four of the most common ornamental woody species shipped to Europe including Ilex cornuta var. fortunae, Zelkova schneideriana, Fraxinus chinensis and Buxus microphylla. Symptoms developing on these species within the sentinel nursery were detected in 2013 and consisted of necrotic spots on leaves, canker and stem necrosis, shoot blight and shoot necrosis. Fungi associated with the trees and their symptoms included Alternaria alternata detected from all hosts; Diaporthe liquidambaris and Diaporthe capsici from bark and leaf necrosis of Zelkova schneideriana; Botryosphaeria dothidea and Nothophoma quercina from stem cankers on Fraxinus chinensis and leaf necrosis on Ilex cornuta; and Pseudonectria foliicola from leaf necrosis on Buxus microphylla. Next generation sequencing analysis from asymptomatic tissues detected eighteen OTU's at species level among which some taxa had not been previously recorded in Europe. These results clearly demonstrate that looking at trees of internationally traded species in the region of origin can reveal the presence of potentially harmful organisms of major forestry, landscape or crop trees. Results of this study also provide an indication as to how some disease agents can be introduced using pathways other than the co-generic hosts. Hence, sentinel nurseries represent one potential mechanism to address the current lack of knowledge about pests in the countries from where live plants are shipped and the threats they represent to native flora and crops in importing countries.
In Vitro Anti-Inflammatory Activity of Ilex cornuta Extract Mediated by Inhibition of Extracellular Signal-Regulated Kinase Phosphorylation.[Pubmed: 28854336]
None
Antioxidant and cardioprotective effects of Ilex cornuta on myocardial ischemia injury.[Pubmed: 28284430]
None
[Screening probiotic endophytic bacteria from medicinal plant flex cornuta and the phytopathogen-inhibiting effect].[Pubmed: 26571677]
Culturable endophytic bacteria were isolated from medicinal plant Ilex cornuta by plate-spreading method, strains with strong inhibitory effect on phytopathogen were screened by confrontation culture and fermentation filtrate culture methods, and the morphological changes of phytopathogen hyphae treated with endophytic bacteria were examined by microscopy and micrograph. Their phylogenetic relationships were determined by homology analysis of the 16S rDNA sequences of PCR products and the taxonomic status of the selected strains was determined based on their morphology, physiology, biochemical test results and 16S rDNA sequence analysis. A total of 85 endophytic bacteria were isolated from the healthy roots, stems, leaves and fruits of I. cornuta, and 10 strains of them showed strong inhibitory effect on Alternaria alternata, Magnaporthe grisea, Fusarium oxysporum, and were preliminarily identified belonging to four genera and seven species. Three strains with the strongest inhibitory effect, GG78 (60.3%), GG31 (48.1%) and GG13 (61.0%) belonged to Enterobacter cloacae, Enterobacter ludwigii and Bacillus cereus, respectively. Microscopic analyses showed that the inhibited phytopathogen hyphae became deformed, distorted, and partially expanded forming plasma concentration and hair-like branch on the hyphae base. These morphological changes could be caused by the extracellular metabolic substances secreted by the endophytic bacteria, such as antibiotics, hydrolytic enzymes, alkaloids and so on.
Two new triterpenoid saponins from Ilex cornuta.[Pubmed: 25978098]
Two new triterpenoid saponins (1 and 2) were isolated from the stems of Ilex cornuta, along with two known triterpenoids (3 and 4). The structures of compounds 1 and 2 were determined as ursane-12,19-diene-28-oic acid 3β-O-β-D-glucuronopyranoside-6-O-methyl ester (1), 3α,23α-dihydroxy-olean-9(11),12-diene-28-oic acid 28-O-β-D-glucopyranosyl ester (2), on the basis of hydrolysis and spectral evidence, including 1D and 2D NMR and high resolution electrospray ionization mass spectrometry (HR-ESI-MS) analyses. Protective effects of compounds 1-4 were tested against H(2)O(2)-induced H9c2 cardiomyocyte injury, and the data showed that all these compounds had no cell-protective effect.
Meroterpenes with toll-like receptor 3 regulating activity from the endophytic fungus Guignardia mangiferae.[Pubmed: 25519918]
The endophytic fungus Guignardia mangiferae isolated from Ilex cornuta leaves was shown to produce a family of meroterpenes with toll-like receptor 3 regulating activity (1-9), of which 1-3 possessed new structures. The absolute stereochemistry of 1-3 was assigned through a combination of nuclear magnetic resonance experiments, chemical derivation, CD spectra, and single-crystal X-ray diffraction analyses (CuK α ). The precursor labeled cultivation suggests that these meroterpenes are most likely assembled through terpenoid-shikimate pathways. Moreover, meroterpenes 1-3, 5-7, and 9 selectively upregulate, but 4 and 8 downregulate the toll-like receptor 3 expression in mouse dendritic cells at 10.0 µM.
Five new triterpenoidal saponins from the roots of Ilex cornuta and their protective effects against H₂O₂-induced cardiomyocytes injury.[Pubmed: 25172104]
Five new ursane-type triterpenoidal saponins (1-5), together with five known ones (6-10), were isolated from the EtOH extract of the roots of Ilex cornuta. The structures of saponins 1-5 were elucidated as 19α-hydroxyurs-12-en-28-oic acid 3β-O-β-D-glucuronopyranoside (1), 19α-hydroxyurs-12-en-28-oic acid 3β-O-β-D-glucuronopyranoside-6-O-ethyl ester (2), 19α-hydroxyurs-12-en-28-oic acid 3β-O-α-L-arabinopyranosyl-(1→2)-β-D-glucuronopyranoside (3), 3β-O-[α-L-arabinopyranosyl-(1→2)-β-D-glucuronopyranosyl]-19α-hydroxyurs-12-en-28-oic acid 28-O-β-D-glucopyranosyl ester (4) and 3β-O-[α-L-arabinopyranosyl-(1→2)-β-D-glucuronopyranoside-6-O-methyl ester]-19α-hydroxyurs-12-en-28-oic acid 28-O-β-D-glucopyranosyl ester (5), on the basis of spectroscopic analyses (IR, ESI-MS, HR-ESI-MS, 1D and 2D NMR) and chemical reactions. Protective effects of compounds 1-10 against H₂O₂-induced H9c2 cardiomyocyte injury were tested. Compounds 1-5, 7, and 10 showed cell-protective effects. Among them compound 5 exhibited the highest activity. No significant DPPH radical scavenging activity was observed for compounds 1-10.
New triterpenoid saponins from Ilex cornuta and their protective effects against H2O2-induced myocardial cell injury.[Pubmed: 24372391]
Five new triterpenoid saponins, 1-5, together with 10 known ones, 6-15 were isolated from the aerial parts of Ilex cornuta. The structures of compounds 1-5 were determined as 3β-O-α-L-arabinopyranosyl-19α,23-dihydroxy-20α-urs-12-en-28-oic acid 28-O-β-D-glucopyranosyl ester, 1; 3β-O-β-D-glucopyranosyl-(1→2)-α-L-arabinopyranosyl-19-hydroxy-20α-urs-12-en-28-oic acid 28-O-β-D-glucopyranosyl ester, 2; 19α,23-dihydroxyurs-12-en-28-oic acid 3β-O-β-D-glucuronopyranoside-6-O-methyl ester, 3; 19α,23-dihydroxyurs-12-en-28-oic acid 3β-O-[β-D-glucuronopyranoside-6-O-methyl ester]-28-O-β-D-glucopyranosyl ester, 4; and 3β-O-[α-L-arabinopyranosyl-(1→2)-β-D-glucuronic acid]-oleanolic acid 28-O-β-D-glucopyranosyl ester, 5, on the basis of spectroscopic analyses (IR, ESI-MS, HR-ESI-MS, 1D and 2D NMR) and chemical reactions. Protective effects of compounds 1-15 were tested against H2O2-induced H9c2 cardiomyocyte injury, and the data showed that compounds 1, 4, 6, and 13 had significant cell-protective effects. No significant DPPH radical scavenging activity was observed for compounds 1-15.


