Lobelia chinensis
Lobelia chinensis
1. The products in our compound library are selected from thousands of unique natural products; 2. It has the characteristics of diverse structure, diverse sources and wide coverage of activities; 3. Provide information on the activity of products from major journals, patents and research reports around the world, providing theoretical direction and research basis for further research and screening; 4. Free combination according to the type, source, target and disease of natural product; 5. The compound powder is placed in a covered tube and then discharged into a 10 x 10 cryostat; 6. Transport in ice pack or dry ice pack. Please store it at -20 °C as soon as possible after receiving the product, and use it as soon as possible after opening.
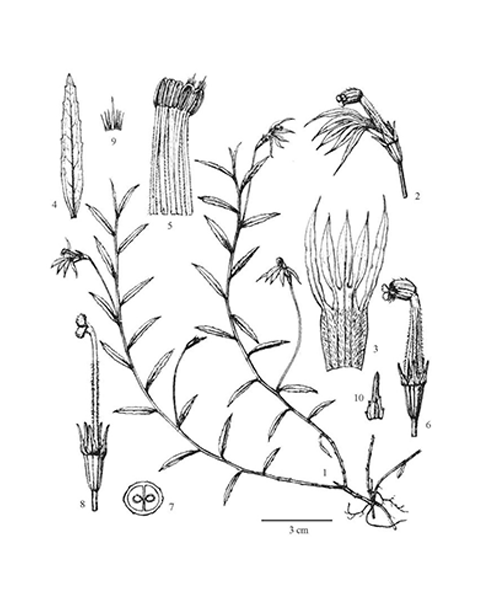
Natural products/compounds from Lobelia chinensis
- Cat.No. Product Name CAS Number COA
-
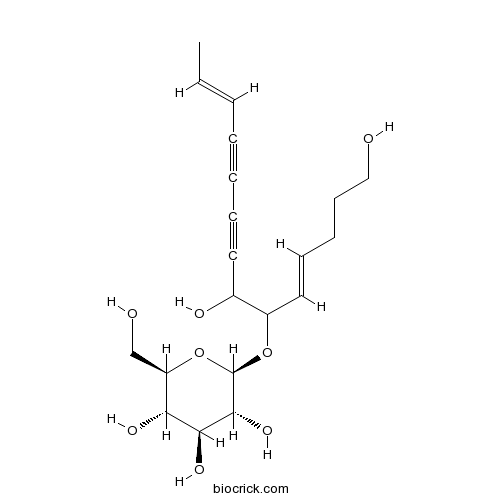
BCN5894
Lobetyolin136085-37-5
Instructions
-
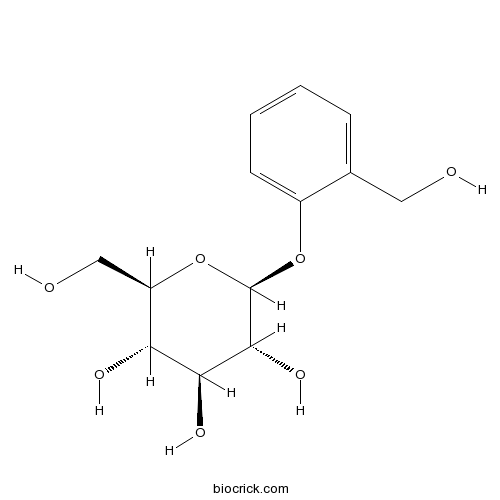
BCN6298
D-(-)-Salicin138-52-3
Instructions
-
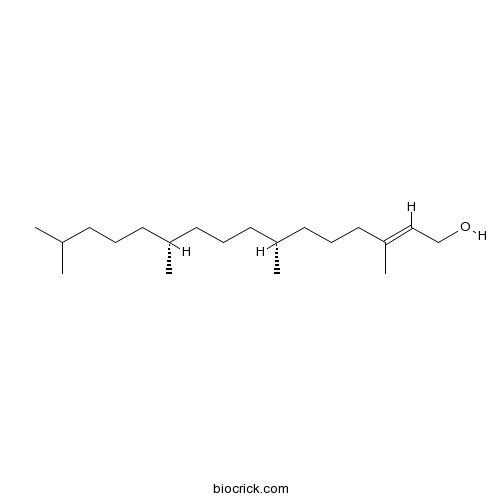
BCN1673
Phytol150-86-7
Instructions
-
BCN6283
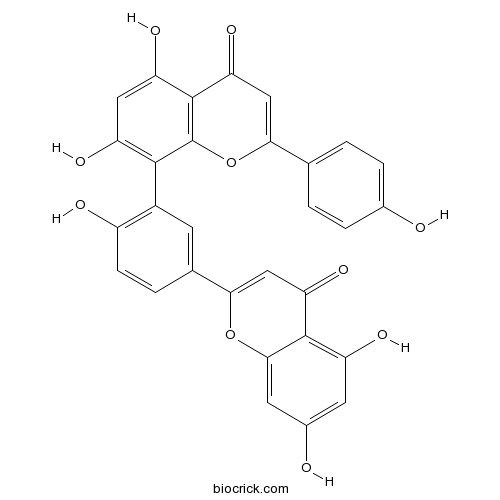
Amentoflavone1617-53-4
Instructions
-
BCN4885
Hydroxygenkwanin20243-59-8
Instructions

-
BCN5554
Linarin480-36-4
Instructions

-
BCN5600
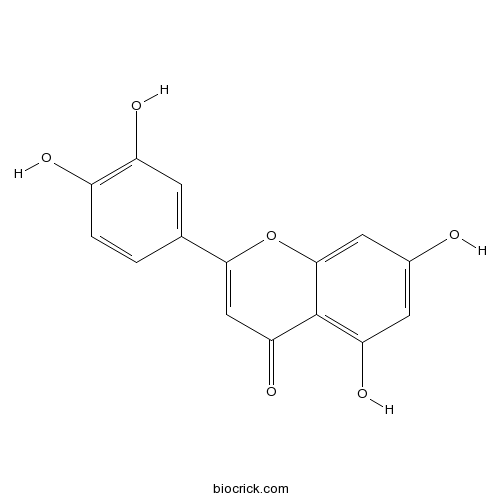
Luteolin491-70-3
Instructions
-
BCN3613
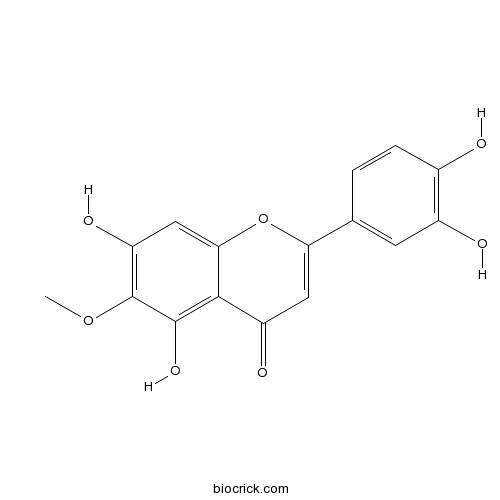
6-Methoxyluteolin520-11-6
Instructions
-
BCN5654
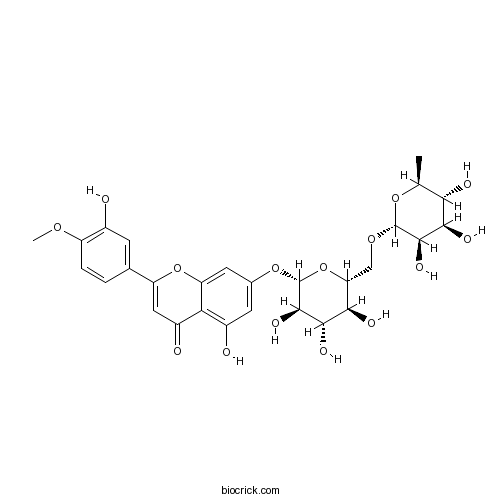
Hesperidin520-26-3
Instructions

-
BCN4993
Diosimin520-27-4
Instructions
-
BCN5657
Hesperetin520-33-2
Instructions
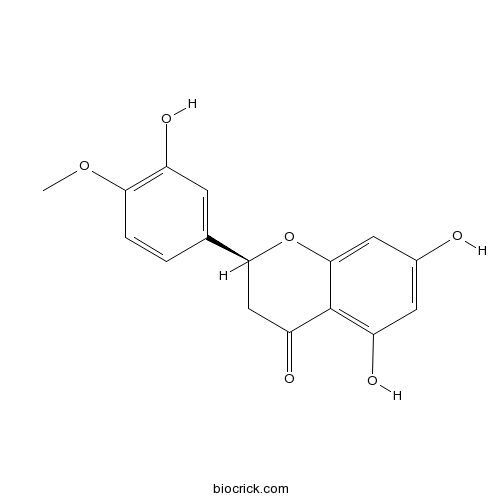
-
BCN2356
Diosmetin520-34-3
Instructions

-
BCX1035
Isoferulic Acid537-73-5
Instructions

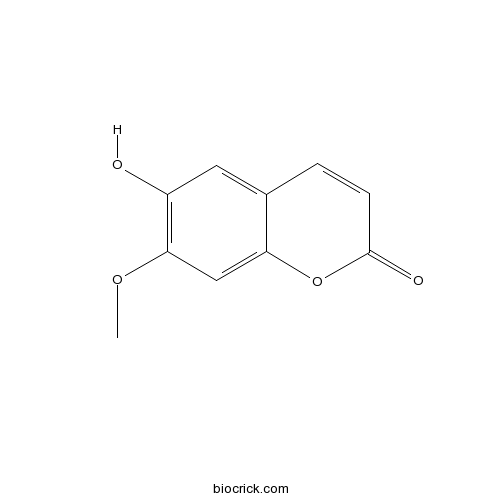
-
BCN4582
Isoscopoletin776-86-3
Instructions
Chemical Structure and Immunomodulating Activities of an α-Glucan Purified from Lobelia chinensis Lour.[Pubmed: 27314319]
A neutral α-glucan, named BP1, with a molecular mass of approximately 9.45 kDa, was isolated from Lobelia chinensis by hot-water extraction, a Q-Sepharose Fast Flow column and Superdex-75 column chromatography. Its chemical structure was characterized by monosaccharide analysis, methylation analysis and analysis of its FT-IR, high performance gel permeation chromatography (HPGPC) and 1D/2D-NMR spectra data. The backbone of BP1 consists of →₆α-d-Glcp¹→6,3α-d-Glcp¹→(₆α-d-Glcp¹)x-6,3α-d-Glcp¹-(₆α-d-Glcp¹)y→. The side chains were terminal α-d-Glcp¹→ and α-d-Glcp¹→ (₆α-d-Glcp¹)z→₄α-d-Glcp¹→₃α-d-Glcp¹→₄α-d-Glcp¹→ (x + y + z = 5), which are attached to the backbone at O-3 of 3,6α-d-Glcp¹. The results of the effect of BP1 on mouse macrophage cell line RAW 264.7 indicate that BP1 enhances the cell proliferation, phagocytosis, nitric oxide production and cytokine secretion in a dose-dependent manner. Because the inhibitor of Toll-like receptor 4 blocks the BP1-induced secretion of TNF-α and IL-6, we hypothesize that α-glucan BP1 activates TLR4, which mediates the above-mentioned immunomodulating effects.
Lobetyol activate MAPK pathways associated with G1/S cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in MKN45 cells in vitro and in vivo.[Pubmed: 27261585]
The agent lobetyol, which is isolated from Lobelia chinensis, was previously shown to be cytotoxicity againts several cancer cell lines in published report. Today, we perform a study in vitro and in vivo to analyze its anti-carcinoma effect in MKN45 cells and to explore the molecular mechanism.
Rapid Identification and Assignation of the Active Ingredients in Fufang Banbianlian Injection Using HPLC-DAD-ESI-IT-TOF-MS.[Pubmed: 27107094]
Fufang Banbianlian Injection (FBI) is a well-known traditional Chinese medicine formula composed of three herbal medicines. However, the systematic investigation on its chemical components has not been reported yet. In this study, a high-performance liquid chromatography combined with diode-array detector, and coupled to an electrospray ionization with ion-trap time-of-flight mass spectrometry (HPLC-DAD-ESI-IT-TOF-MS) method, was established for the identification of chemical profile in FBI. Sixty-six major constituents (14 phenolic acids, 14 iridoids, 20 flavonoids, 2 benzylideneacetone compounds, 3 phenylethanoid glycosides, 1 coumarin, 1 lignan, 3 nucleosides, 1 amino acids, 1 monosaccharides, 2 oligosaccharides, 3 alduronic acids and citric acid) were identified or tentatively characterized by comparing their retention times and MS spectra with those of standards or literature data. Finally, all constituents were further assigned in the individual herbs (InHs), although some of them were from multiple InHs. As a result, 11 compounds were from Lobelia chinensis Lour, 33 compounds were from Scutellaria barbata D. Don and 38 compounds were from Hedyotis diffusa Willd. In conclusion, the developed HPLC-DAD-ESI-IT-TOF-MS method is a rapid and efficient technique for analysis of FBI sample, and could be a valuable method for the further study on the quality control of the FBI.
An on-line high-performance liquid chromatography-diode-array detector-multi-stage mass spectrometry-deoxyribonucleic acid-4',6-diamidino-2-phenylindole-fluorescence detector system for screening the DNA-binding active compounds in Fufang Banbianlian Injection.[Pubmed: 26592560]
Fufang Banbianlian Injection (FBI), a well-known traditional Chinese medicine formula, has been recently approved and extensively used as a newly anti-inflammatory and anti-tumor drug. This prescription comprises an equal ratio of three traditional Chinese herbs, Lobelia chinensis Lour, Scutellaria barbata D. Don and Hedyotis diffusa Willd. The relationships between its chemical compositions and activities have not been understood well yet. To investigate the ingredients and their DNA-binding activities in FBI, an on-line high-performance liquid chromatography-diode-array detector-multi-stage mass spectrometry-deoxyribonucleic acid-4',6-diamidino-2-phenylindole-fluorescence detector (HPLC-DAD-MS(n)-DNA-DAPI-FLD) system was developed using a combination of chromatographic, mass spectrometric and fluorescent detection techniques. 4',6-Diamidino-2-phenylindole (DAPI) specifically binds to three ATT base pairs on the DNA minor groove, and thus can be used as a fluorescent probe for screening active compounds that compete ATT sequences with DAPI. Using this system, 21 of 58 identified or tentatively characterized compounds in FBI showed DNA-binding activities, with most of the active compounds being flavone glycosides. In addition, the structure-activity relationships of these active compounds suggested that conjugated planar structures are favorable for DNA-binding activities, and adjacent hydroxyl groups in flavonoids can significantly improve their activities. This is, to the best of our knowledge, the first application of DAPI as a fluorescent probe for the screening of DNA-binding active compounds in complex samples.


