DiosiminCAS# 520-27-4 |
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 520-27-4 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 5281613 | Appearance | Yellow powder |
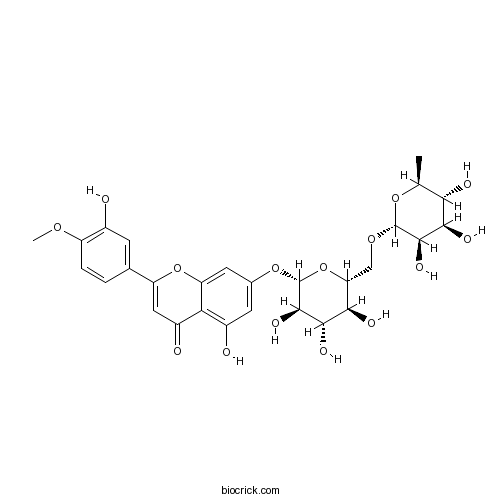
| Formula | C28H32O15 | M.Wt | 608.54 |
| Type of Compound | Flavonoids | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Synonyms | Barosmin; Buchu resin; Diosmetin 7-O-rhamnosylglucoside; Diosmetin 7-rutinoside; 3',5,7-Trihydroxy 4'-methoxyflavone 7-O-rutinoside | ||
| Solubility | DMSO : 100 mg/mL (164.33 mM; Need ultrasonic) | ||
| Chemical Name | 5-hydroxy-2-(3-hydroxy-4-methoxyphenyl)-7-[(2S,3R,4S,5S,6R)-3,4,5-trihydroxy-6-[[(2R,3R,4R,5R,6S)-3,4,5-trihydroxy-6-methyloxan-2-yl]oxymethyl]oxan-2-yl]oxychromen-4-one | ||
| SMILES | CC1C(C(C(C(O1)OCC2C(C(C(C(O2)OC3=CC(=C4C(=C3)OC(=CC4=O)C5=CC(=C(C=C5)OC)O)O)O)O)O)O)O)O | ||
| Standard InChIKey | GZSOSUNBTXMUFQ-YFAPSIMESA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C28H32O15/c1-10-21(32)23(34)25(36)27(40-10)39-9-19-22(33)24(35)26(37)28(43-19)41-12-6-14(30)20-15(31)8-17(42-18(20)7-12)11-3-4-16(38-2)13(29)5-11/h3-8,10,19,21-30,32-37H,9H2,1-2H3/t10-,19+,21-,22+,23+,24-,25+,26+,27+,28+/m0/s1 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Diosmin is a semisynthetic phlebotropic agent, and also an agonist of the aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AhR). Diosmin can prevent the progression of early diabetic neuropathy in rats, it has cardioprotective effect by the free radical scavenging and anti-hyperlipidaemic effects . |
| Targets | Bcl-2/Bax | HMG-CoA Reductase |
| In vitro | Electrospinning of diosmin from aqueous solutions for improved dissolution and oral absorption.[Pubmed: 25066074]Int J Pharm. 2014 Oct 1;473(1-2):407-13.A nanofibrous membrane carrier for nearly water insoluble drug Diosmin was formulated. The aim of this study was to evaluate the drug release and dissolution properties in an aqueous buffer of pH 7.8, and to compare the suitability of the drug carrier with the available drug forms and screen Diosmin absorption extent. |
| In vivo | Diosmin pretreatment improves cardiac function and suppresses oxidative stress in rat heart after ischemia/reperfusion.[Pubmed: 24769512]Eur J Pharmacol. 2014 Aug 5;736:131-7.Reperfusion of ischemic tissue leads to the generation of oxygen derived free radicals which plays an important role in cellular damage. Objective of the current study is to evaluate the cardio-protective and antioxidant effect of Diosmin on ischemia-reperfusion related cardiac dysfunction, oxidative stress and apoptosis.
Diosmin exhibits anti-hyperlipidemic effects in isoproterenol induced myocardial infarcted rats.[Pubmed: 24036254]Eur J Pharmacol. 2013 Oct 15;718(1-3):213-8.The aim of the present study was to evaluate the protective effects of Diosmin on experimentally induced myocardial infarcted rats. |
| Animal Research | Protective effect of diosmin against diabetic neuropathy in experimental rats.[Pubmed: 24461593]J Integr Med. 2014 Jan;12(1):35-41.The present study was undertaken to evaluate the effect of Diosmin in diabetic neuropathy in type 2 diabetic rats.
|
| Structure Identification | Biochimie. 2013 Nov;95(11):2042-9.Diosmin binding to human serum albumin and its preventive action against degradation due to oxidative injuries.[Pubmed: 23886889]Diosmin is a glycosylated polyphenolic compound, commonly found in fruits and vegetables, which is utilized for the pharmacological formulation of some drugs. |

Diosimin Dilution Calculator

Diosimin Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 1.6433 mL | 8.2164 mL | 16.4328 mL | 32.8655 mL | 41.0819 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.3287 mL | 1.6433 mL | 3.2866 mL | 6.5731 mL | 8.2164 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.1643 mL | 0.8216 mL | 1.6433 mL | 3.2866 mL | 4.1082 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0329 mL | 0.1643 mL | 0.3287 mL | 0.6573 mL | 0.8216 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0164 mL | 0.0822 mL | 0.1643 mL | 0.3287 mL | 0.4108 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- Hesperidin
Catalog No.:BCN5654
CAS No.:520-26-3
- Kaempferol
Catalog No.:BCN5653
CAS No.:520-18-3
- Pectolinarigenin
Catalog No.:BCN5813
CAS No.:520-12-7
- 6-Methoxyluteolin
Catalog No.:BCN3613
CAS No.:520-11-6
- H-Cys-OH
Catalog No.:BCC2902
CAS No.:52-90-4
- Haloperidol
Catalog No.:BCC4909
CAS No.:52-86-8
- Lynestrenol
Catalog No.:BCC9014
CAS No.:52-76-6
- H-D-Pen-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3307
CAS No.:52-67-5
- Morphine hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC6368
CAS No.:52-26-6
- Thio-TEPA
Catalog No.:BCC5354
CAS No.:52-24-4
- Prednisolone Acetate
Catalog No.:BCC4831
CAS No.:52-21-1
- Spironolactone
Catalog No.:BCC4366
CAS No.:52-01-7
- Tectochrysin
Catalog No.:BCN5655
CAS No.:520-28-5
- Tricin
Catalog No.:BCN5656
CAS No.:520-32-1
- Hesperetin
Catalog No.:BCN5657
CAS No.:520-33-2
- Diosmetin
Catalog No.:BCN2356
CAS No.:520-34-3
- Apigenin
Catalog No.:BCN5658
CAS No.:520-36-5
- Asebogenin
Catalog No.:BCN7232
CAS No.:520-42-3
- Psilocin
Catalog No.:BCC6168
CAS No.:520-53-6
- Spectabiline
Catalog No.:BCN2098
CAS No.:520-55-8
- Spartioidine
Catalog No.:BCN2134
CAS No.:520-59-2
- Rosmarinine
Catalog No.:BCN2124
CAS No.:520-65-0
- Echimidine
Catalog No.:BCN1967
CAS No.:520-68-3
- Medroxyprogesterone
Catalog No.:BCC5231
CAS No.:520-85-4
Electrospinning of diosmin from aqueous solutions for improved dissolution and oral absorption.[Pubmed:25066074]
Int J Pharm. 2014 Oct 1;473(1-2):407-13.
A nanofibrous membrane carrier for nearly water insoluble drug diosmin was formulated. The aim of this study was to evaluate the drug release and dissolution properties in an aqueous buffer of pH 7.8, and to compare the suitability of the drug carrier with the available drug forms and screen diosmin absorption extent. The membranes were produced from HPC/PVA/PEO-drug water solutions and then evaluated by SEM and DSC measurements. The results showed that diosmin was incorporated within the nanofibers in an amorphous state, and/or as a solid dispersion. The results of in vitro release experiments excerpt a very fast release of the drug, followed by the formation of an over saturated solution and partial precipitation of the drug (a "spring" effect). The enormous increases in dissolution of the drug from a nanofibrous carrier, compared to a micronized and crystalline form, was achieved. The in vivo bioavailability study carried out on rats showed higher initial drug plasma levels and higher AUC values after administration of the nanofibrous drug formulation, compared to the micronized form. The results of the study demonstrated that the improvement of the diosmin in vitro dissolution also brought the enhanced in vivo absorption extent of the drug.
Protective effect of diosmin against diabetic neuropathy in experimental rats.[Pubmed:24461593]
J Integr Med. 2014 Jan;12(1):35-41.
OBJECTIVE: The present study was undertaken to evaluate the effect of diosmin in diabetic neuropathy in type 2 diabetic rats. METHODS: Type 2 diabetes was induced in male Sprague-Dawley rats by single intraperitoneal injection of streptozotocin (35 mg/kg) and high-fat diet. Four weeks after the confirmation of diabetes, diabetic rats were treated with diosmin (50 and 100 mg/kg, p.o.) for next 4 weeks. Rats were evaluated for biochemical, behavioral and oxidative stress parameters. Eddy's hot plate and tail immersion test were performed on 6th, 7th, 8th, 9th and 10th weeks of experiment to assess thermal hyperalgesia and cold allodynia respectively. Further, the walking function test was performed for assessing the motor responses at the end of the treatment schedule. RESULTS: Rats were fed with high-fat diet throughout the experiment schedule and administration of low-dose streptozotocin induced significant elevation in blood glucose level and insulin resistance which was confirmed by oral glucose tolerance test. Treatment with diosmin at doses of 50 and 100 mg/kg significantly restored the reduced body weight, elevated blood sugar and lipid profiles. Further the dose-dependent improvement was observed in thermal hyperalgesia, cold allodynia and walking function in diabetic rats treated with diosmin. Elevated levels of malondialdehyde, and nitric oxide and decreased glutathione levels and superoxide dismutase activity in diabetic rats were restored significantly after the 4 weeks of diosmin treatment. CONCLUSION: Diosmin has shown beneficial effect in preventing the progression of early diabetic neuropathy in rats.
Diosmin exhibits anti-hyperlipidemic effects in isoproterenol induced myocardial infarcted rats.[Pubmed:24036254]
Eur J Pharmacol. 2013 Oct 15;718(1-3):213-8.
The aim of the present study was to evaluate the protective effects of diosmin on experimentally induced myocardial infarcted rats. Diosmin (5 and 10mg/kg body weight) was administered orally as pretreatment daily for a period of 10 days. Then isoproterenol (100mg/kg) was injected subcutaneously into rats at an interval of 24h for 2 days (on 11th and 12th day). Isoproterenol-induced myocardial infarcted rats showed significant changes in electrocardiogram and an increase in the levels of cardiac markers, compared with normal rats. Additionally, increased plasma lipid peroxidation products and altered lipid metabolism in the plasma were observed in the isoproterenol-induced myocardial infarcted rats. Pretreatment with diosmin (5 and 10mg/kg body weight) minimized the electrocardiographic changes, decreased the levels of serum cardiac marker enzymes reduced plasma lipid peroxidation and minimized the alterations in the lipid metabolism of isoproterenol-induced myocardial infarcted rats. Also, diosmin inhibited the enhanced activity of liver HMG CoA reductase. The in vitro study revealed the free radical scavenging activity of diosmin. The free radical scavenging and anti-hyperlipidaemic effects are the reasons for the cardioprotective effects of diosmin.
Diosmin pretreatment improves cardiac function and suppresses oxidative stress in rat heart after ischemia/reperfusion.[Pubmed:24769512]
Eur J Pharmacol. 2014 Aug 5;736:131-7.
Reperfusion of ischemic tissue leads to the generation of oxygen derived free radicals which plays an important role in cellular damage. Objective of the current study is to evaluate the cardio-protective and antioxidant effect of diosmin on ischemia-reperfusion related cardiac dysfunction, oxidative stress and apoptosis. Diosmin (50 and 100 mg/kg body weight (bw)) was given every day to the rats orally throughout the experimental period. Ischemia/reperfusion protocol was carried out ex vivo using langendorff perfusion method and the cardiac functional recovery was assessed in terms of percentage rate pressure product. Coronary effluents of LDH and CK-MB activities, antioxidant enzyme activities, lipid peroxidation products, activity of TCA cycle enzymes were evaluated. Moreover, in vitro superoxide anion and hydroxyl radical scavenging potential of diosmin was also quantified. Finally, quantitative real-time PCR was used for assessing Bcl-2 mRNA expression in heart. Cardiac functional recovery was impaired after reperfusion compared with continuously perfused heart. It was significantly prevented by diosmin treatment. Impaired antioxidant enzyme activities and elevated lipid peroxidation products level were also significantly suppressed. The activity of TCA cycle enzymes was protected against reperfusion stress. Down regulated Bcl-2 was also significantly increased. This study concluded that diosmin pretreatment prevents all the impaired patterns including cardiac function, oxidative stress and apoptosis associated with reperfusion in control heart by its antioxidant role.
Diosmin binding to human serum albumin and its preventive action against degradation due to oxidative injuries.[Pubmed:23886889]
Biochimie. 2013 Nov;95(11):2042-9.
Diosmin is a glycosylated polyphenolic compound, commonly found in fruits and vegetables, which is utilized for the pharmacological formulation of some drugs. The interactions of diosmin to human serum albumin have been investigated by fluorescence, UV-visible, FTIR spectroscopy, native electrophoresis and protein-ligand docking studies. The fluorescence studies indicate that the binding site of the additive involves modifications of environment around Trp214 at the level of subdomain IIA. Combining the curve-fitting results of infrared Amide I' band, the modifications of protein secondary structure have been estimated, indicating a decrease in alpha-helix structure following flavonoid binding. Data obtained by fluorescence and UV-visible spectroscopy, FTIR experiments and molecular modeling afforded a clear picture of the association mode of diosmin to HSA, suggesting that the primary binding site of diosmin is located in Sudlow's site I. Computational mapping confirms this observation suggesting that the possible binding site of diosmin is located in the hydrophobic cavity of subdomain IIA, whose microenvironment is able to help and stabilize the binding of the ligand in non-planar conformation. Moreover the binding of diosmin to HSA significantly contributes to protect the protein against degradation due to HCLO and Fenton reaction.


