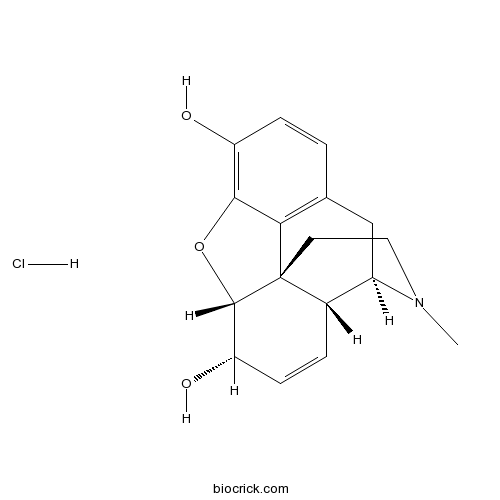
Morphine hydrochlorideNarcotic opioid analgesic CAS# 52-26-6 |
- Mc-MMAD
Catalog No.:BCC1735
CAS No.:1401963-15-2
- Docetaxel Trihydrate
Catalog No.:BCC1535
CAS No.:148408-66-6
- Colchicine
Catalog No.:BCN6271
CAS No.:64-86-8
- D-64131
Catalog No.:BCC1510
CAS No.:74588-78-6
- 7-Xylosyltaxol
Catalog No.:BCN5341
CAS No.:90332-66-4
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 52-26-6 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 5464110 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C17H20ClNO3 | M.Wt | 321.8 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | Soluble to 50 mM in water | ||
| Chemical Name | (4R,4aR,7S,7aR,12bS)-3-methyl-2,4,4a,7,7a,13-hexahydro-1H-4,12-methanobenzofuro[3,2-e]isoquinoline-7,9-diol;hydrochloride | ||
| SMILES | CN1CCC23C4C1CC5=C2C(=C(C=C5)O)OC3C(C=C4)O.Cl | ||
| Standard InChIKey | XCKKIKBIPZJUET-VYKNHSEDSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C17H19NO3.ClH/c1-18-7-6-17-10-3-5-13(20)16(17)21-15-12(19)4-2-9(14(15)17)8-11(10)18;/h2-5,10-11,13,16,19-20H,6-8H2,1H3;1H/t10-,11+,13-,16-,17-;/m0./s1 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Narcotic opioid analgesic. |

Morphine hydrochloride Dilution Calculator

Morphine hydrochloride Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 3.1075 mL | 15.5376 mL | 31.0752 mL | 62.1504 mL | 77.688 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.6215 mL | 3.1075 mL | 6.215 mL | 12.4301 mL | 15.5376 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.3108 mL | 1.5538 mL | 3.1075 mL | 6.215 mL | 7.7688 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0622 mL | 0.3108 mL | 0.6215 mL | 1.243 mL | 1.5538 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0311 mL | 0.1554 mL | 0.3108 mL | 0.6215 mL | 0.7769 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- Thio-TEPA
Catalog No.:BCC5354
CAS No.:52-24-4
- Prednisolone Acetate
Catalog No.:BCC4831
CAS No.:52-21-1
- Spironolactone
Catalog No.:BCC4366
CAS No.:52-01-7
- Dehydroespeletone
Catalog No.:BCN5652
CAS No.:51995-99-4
- Schaftoside
Catalog No.:BCN2343
CAS No.:51938-32-0
- 5-Aminoindole
Catalog No.:BCC8735
CAS No.:5192-03-0
- TNP
Catalog No.:BCC7822
CAS No.:519178-28-0
- CJ 033466
Catalog No.:BCC7562
CAS No.:519148-48-2
- Tasisulam
Catalog No.:BCC4407
CAS No.:519055-62-0
- Dehydrohautriwaic acid
Catalog No.:BCN7586
CAS No.:51905-84-1
- 4-(N-Methyl)-aminoantipyrine
Catalog No.:BCC8652
CAS No.:519-98-2
- Sulochrin
Catalog No.:BCN6959
CAS No.:519-57-3
- H-D-Pen-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3307
CAS No.:52-67-5
- Lynestrenol
Catalog No.:BCC9014
CAS No.:52-76-6
- Haloperidol
Catalog No.:BCC4909
CAS No.:52-86-8
- H-Cys-OH
Catalog No.:BCC2902
CAS No.:52-90-4
- 6-Methoxyluteolin
Catalog No.:BCN3613
CAS No.:520-11-6
- Pectolinarigenin
Catalog No.:BCN5813
CAS No.:520-12-7
- Kaempferol
Catalog No.:BCN5653
CAS No.:520-18-3
- Hesperidin
Catalog No.:BCN5654
CAS No.:520-26-3
- Diosimin
Catalog No.:BCN4993
CAS No.:520-27-4
- Tectochrysin
Catalog No.:BCN5655
CAS No.:520-28-5
- Tricin
Catalog No.:BCN5656
CAS No.:520-32-1
- Hesperetin
Catalog No.:BCN5657
CAS No.:520-33-2
Intraspinal administration of morphine hydrochloride combined with low doses of bupivacaine in hemorrhoidectomy: a clinical randomized trial.[Pubmed:28256813]
Minerva Anestesiol. 2017 Sep;83(9):930-938.
BACKGROUND: Intrathecal local anesthetics, associated or not to opioids, is commonplace in anorectal surgery, but it is unknown which is the option with the best risk-benefit ratio. The main aim was to assess whether the combination of morphine (50 mcg) with low-dose bupivacaine (3 mg) in an intradural solution has a better analgesic short-term effect than bupivacaine alone at standard doses (5 mg) in hemorrhoidectomy. METHODS: Sixty-six patients of any sex were randomly assigned to two alternative treatments and 63 patients were considered valid for analysis. Hyperbaric bupivacaine 3 mg combined with 50 mcg of intradural Morphine hydrochloride (BUP-MOR group) was compared with 5 mg hyperbaric bupivacaine (BUP group). The primary outcome was pain evaluated through a visual analog scale (from 0 to 100 mm) at 24 hours post-surgery. The proportion of patients requiring rescue analgesia, and those presenting with motor blockade and other adverse events was also compared between the two groups. RESULTS: BUP-MOR group showed a higher efficacy than BUP group in the visual analog scale at 24 hours postsurgery (15+/-12 vs. 33+/-22 mm; P<0.001). Also, BUP-MOR group presented a lower percentage of patients who needed rescue analgesia at resuscitation room (6.7% vs. 24.2%; P=0.08) and a lower proportion of patients who had motor blockade (23.3% vs. 51.5%; P=0.02), while they presented a non-significant increased incidence of urinary retention (23.3% vs. 9.0%; P=0.17). CONCLUSIONS: The addition of intradural morphine allows a reduction in the dosage of local anesthetic improves short-term postoperative analgesia and is associated with less motor blockade.
Safety profile of extended-release morphine sulfate with sequestered naltrexone hydrochloride in older patients: pooled analysis of three clinical trials.[Pubmed:26695349]
Curr Med Res Opin. 2016;32(3):563-72.
OBJECTIVE: Clinical trial safety data following chronic administration of extended-release opioids within an older population is limited. Embeda * is an extended-release formulation of morphine sulfate surrounding sequestered naltrexone hydrochloride (MSN) and is designed to deter opioid misuse and abuse. The present analysis compared pooled safety outcomes among patients aged >/=65 years and those aged <65 years from three phase 2/3 studies (ranging from 2 weeks to 12 months) in patients treated with MSN. RESEARCH DESIGN AND METHODS: Subgroup analysis of patients aged >/=65 years and <65 years was performed on pooled data for adverse events (AEs), potentially clinically significant laboratory values (hematology/chemistry), and signs/symptoms of opioid withdrawal using the Clinical Opiate Withdrawal Scale (COWS) (phase 3 trials only) for patients who received at least one dose (short-term studies, maximum dose was 160 mg/d or 320 mg/d depending on study; long-term study, no maximum dose) of study medication during titration and maintenance phases. CLINICAL TRIAL REGISTRATION: ClinicalTrials.gov: NCT00420992, NCT00415597. RESULTS: During titration, 173 (17.1%) of 1012 patients treated with MSN were aged >/=65 years, while during maintenance 76/564 (13.5%) patients were aged >/=65 years. Treatment-emergent AEs were similar in frequency and type between the two cohorts, with the most common being constipation, nausea, and somnolence; no consistent patterns relating to age and only one possibly treatment-related serious AE in patients >/=65 years was noted. No clinically significant differences in laboratory values or COWS scores (average maximum score /=65 years and <65 years. Key limitations include the variable study designs and length of treatment (2 weeks-12 months), small sample size, and the inclusion of only those patients who were otherwise in relatively good health with restrictions on concomitant medications.
Development of Poly(lactide-co-glicolide) Nanoparticles Incorporating Morphine Hydrochloride to Prolong its Circulation in Blood.[Pubmed:27908267]
Curr Pharm Des. 2017;23(13):2015-2025.
BACKGROUND: Formulations incorporating nanoparticles (NPs) are widely used to prolong drug release. In this regard, poly(lactide-co-glicolide) (PLGA) is often used in their preparation due to its high degree of biocompatibility and biodegradability. In the present study, morphine HCl is incorporated in PLGA-NPs and different preparation alternatives are evaluated for their effects on the properties, stability and capacity of encapsulation. METHODS: NPs were prepared by a double emulsion solvent diffusion-ammonium loading (DESD-AL) or double emulsion solvent diffusion-traditional (DESD-T) technique. NP morphology, size, zeta potential and encapsulation efficiency were investigated. In vitro studies were performed in phosphate buffer pH 7.4 at 37 masculineC and deionized water at 4 masculineC. Adult male Swiss mice were used to study the pharmacokinetic behavior in vivo. RESULTS: Our results show that DESD-AL provides a higher level of morphine entrapment and that increasing the sonication time reduces the size but does not appreciably reduce the entrapment percentage. It was also observed that NP stability was greater when Pluronic F68 was used rather than PVA, and that in vitro assays provided better results with low concentrations of both stabilizers. Lyophilized NPs, after rehydration showed properties that were only slightly different from those of the untreated ones, with no sign of precipitation or aggregation. Finally, the obtained NPs enhanced morphine bioavailability. CONCLUSIONS: In conclusion, a useful method for encapsulating morphine in order to obtain an extended delivery period is described and its effects are compared with those of the free drug.
A multicenter, primary-care-based, open-label study to assess the success of converting opioid-experienced patients with chronic moderate-to-severe pain to morphine sulfate and naltrexone hydrochloride extended-release capsules using a standardized conversion guide.[Pubmed:26185466]
J Pain Res. 2015 Jul 8;8:347-60.
OBJECTIVE: To evaluate the conversion of opioid-experienced patients with chronic moderate-to-severe pain to extended-release morphine sulfate with sequestered naltrexone hydrochloride (MSN) using a standardized conversion guide. METHODS: This open-label, single-arm study was conducted in 157 primary care centers in the United States. A total of 684 opioid-experienced adults with chronic moderate-to-severe pain were converted to oral administration of MSN from transdermal fentanyl and oral formulations of hydrocodone, hydromorphone, methadone, oxycodone, oxymorphone, and other morphine products using a standardized conversion guide. The primary endpoint was the percentage of patients achieving a stable MSN dose within a 6-week titration phase. Secondary endpoints included duration of time to stable dose, number of titration steps, safety and efficacy measures, and investigator assessment of conversion guide utility. RESULTS: Of the 684 patients, 51.3% were converted to a stable dose of MSN (95% confidence interval: 47.5%, 55.1%). The mean (standard deviation) number of days to stable dose was 20 (8.94), and number of titration steps to stable dose was 2.4 (1.37). The majority of adverse events were mild/moderate and consistent with opioid therapy. Mean pain scores at stable dose decreased from baseline. Investigators were generally satisfied with the conversion guide and, in 94% of cases, reported they would use it again. CONCLUSION: Conversion to MSN treatment using the standardized MSN conversion guide was an attainable goal in approximately half of the population of opioid-experienced patients with chronic moderate-to-severe pain. Investigators found the guide to be a useful tool to assist conversion of opioid-experienced patients to MSN.


