EchimidineCAS# 520-68-3 |
- Heliosupine
Catalog No.:BCN1980
CAS No.:32728-78-2
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 520-68-3 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 5281729 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C20H31NO7 | M.Wt | 397.47 |
| Type of Compound | Alkaloids | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | Soluble in acetone, methanol and water | ||
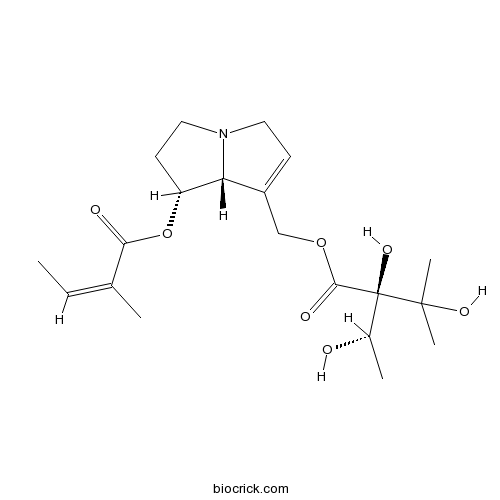
| Chemical Name | [(7R,8R)-7-[(Z)-2-methylbut-2-enoyl]oxy-5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-3H-pyrrolizin-1-yl]methyl (2R)-2,3-dihydroxy-2-[(1S)-1-hydroxyethyl]-3-methylbutanoate | ||
| SMILES | CC=C(C)C(=O)OC1CCN2C1C(=CC2)COC(=O)C(C(C)O)(C(C)(C)O)O | ||
| Standard InChIKey | HRSGCYGUWHGOPY-LYHHMGRNSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C20H31NO7/c1-6-12(2)17(23)28-15-8-10-21-9-7-14(16(15)21)11-27-18(24)20(26,13(3)22)19(4,5)25/h6-7,13,15-16,22,25-26H,8-11H2,1-5H3/b12-6-/t13-,15+,16+,20-/m0/s1 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | 1. Echimidine, a major hepatotoxic dehydropyrrolizidine alkaloid produced by E. plantagineum, in the honey (780 ng/g) and in the subsequent mead samples (236–540 ng/mL) . 2. Echimidine-N-Oxide has antifungal activity. |
| Targets | Antifection |

Echimidine Dilution Calculator

Echimidine Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.5159 mL | 12.5796 mL | 25.1591 mL | 50.3183 mL | 62.8978 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.5032 mL | 2.5159 mL | 5.0318 mL | 10.0637 mL | 12.5796 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.2516 mL | 1.258 mL | 2.5159 mL | 5.0318 mL | 6.2898 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0503 mL | 0.2516 mL | 0.5032 mL | 1.0064 mL | 1.258 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0252 mL | 0.1258 mL | 0.2516 mL | 0.5032 mL | 0.629 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- Rosmarinine
Catalog No.:BCN2124
CAS No.:520-65-0
- Spartioidine
Catalog No.:BCN2134
CAS No.:520-59-2
- Spectabiline
Catalog No.:BCN2098
CAS No.:520-55-8
- Psilocin
Catalog No.:BCC6168
CAS No.:520-53-6
- Asebogenin
Catalog No.:BCN7232
CAS No.:520-42-3
- Apigenin
Catalog No.:BCN5658
CAS No.:520-36-5
- Diosmetin
Catalog No.:BCN2356
CAS No.:520-34-3
- Hesperetin
Catalog No.:BCN5657
CAS No.:520-33-2
- Tricin
Catalog No.:BCN5656
CAS No.:520-32-1
- Tectochrysin
Catalog No.:BCN5655
CAS No.:520-28-5
- Diosimin
Catalog No.:BCN4993
CAS No.:520-27-4
- Hesperidin
Catalog No.:BCN5654
CAS No.:520-26-3
- Medroxyprogesterone
Catalog No.:BCC5231
CAS No.:520-85-4
- Isoschaftoside
Catalog No.:BCN3011
CAS No.:52012-29-0
- NCS-382
Catalog No.:BCC6794
CAS No.:520505-01-5
- H-Val-pNA
Catalog No.:BCC3139
CAS No.:52084-13-6
- 2-Hydroxy-7-O-methylscillascillin
Catalog No.:BCN5659
CAS No.:52096-50-1
- Mestanolone
Catalog No.:BCC9022
CAS No.:521-11-9
- Dromostanolone propionate
Catalog No.:BCC8954
CAS No.:521-12-0
- Androstenediol
Catalog No.:BCC8828
CAS No.:521-17-5
- Stanolone
Catalog No.:BCC9153
CAS No.:521-18-6
- Bilobetin
Catalog No.:BCN5661
CAS No.:521-32-4
- Sciadopitysin
Catalog No.:BCN5662
CAS No.:521-34-6
- Cannabinol
Catalog No.:BCN7968
CAS No.:521-35-7
Structure-activity relationship in the passage of different pyrrolizidine alkaloids through the gastrointestinal barrier: ABCB1 excretes heliotrine and echimidine.[Pubmed:24375927]
Mol Nutr Food Res. 2014 May;58(5):995-1004.
SCOPE: 1,2-Unsaturated pyrrolizidine alkaloids (PA) are found in plants such as Asteraceae and Boraginaceae families. Acute PA poisoning via contaminated food or feed causes severe damage to liver depending on species-specific oral bioavailability. For assessing PA bioavailability, their passage across the intestinal barrier was investigated using Caco-2 cells. METHODS: Differentiated Caco-2 cells were exposed in transport chambers to the PA heliotrine (Hn), Echimidine (Em), senecionine (Sc), and senkirkine (Sk). Cell supernatants were analyzed by LC-MS/MS. RESULTS: PA pass Caco-2 monolayer from the apical into basolateral compartment depending on their chemical structure. Compared to the cyclic diesters Sc and Sk with a passage rate of 47% +/- 4 and 40% +/- 3, respectively, the transferred amount of the monoester Hn (32% +/- 3) and open-chained diester Em (13% +/- 2) was substantially lower. This suggested an active transport of Hn and Em. Using Madin-Darby canine kidney II/P-glycoprotein (ABCB1)-overexpressing cells, the active excretion of Hn and Em by ABCB1 from the gastrointestinal epithelium into the gut lumen was shown. CONCLUSION: PA cross the intestinal barrier structure-dependently. The passage of the noncyclic PA Hn and Em is reduced by an ABCB1-driven efflux into the gastrointestinal lumen resulting in a decreased oral bioavailability.
Disturbance of gene expression in primary human hepatocytes by hepatotoxic pyrrolizidine alkaloids: A whole genome transcriptome analysis.[Pubmed:26100227]
Toxicol In Vitro. 2015 Oct;29(7):1669-82.
1,2-unsaturated pyrrolizidine alkaloids (PA) are plant metabolites predominantly occurring in the plant families Asteraceae and Boraginaceae. Acute and chronic PA poisoning causes severe hepatotoxicity. So far, the molecular mechanisms of PA toxicity are not well understood. To analyze its mode of action, primary human hepatocytes were exposed to a non-cytotoxic dose of 100 muM of four structurally different PA: Echimidine, heliotrine, senecionine, senkirkine. Changes in mRNA expression were analyzed by a whole genome microarray. Employing cut-off values with a |fold change| of 2 and a q-value of 0.01, data analysis revealed numerous changes in gene expression. In total, 4556, 1806, 3406 and 8623 genes were regulated by Echimidine, heliotrine, senecione and senkirkine, respectively. 1304 genes were identified as commonly regulated. PA affected pathways related to cell cycle regulation, cell death and cancer development. The transcription factors TP53, MYC, NFkappaB and NUPR1 were predicted to be activated upon PA treatment. Furthermore, gene expression data showed a considerable interference with lipid metabolism and bile acid flow. The associated transcription factors FXR, LXR, SREBF1/2, and PPARalpha/gamma/delta were predicted to be inhibited. In conclusion, though structurally different, all four PA significantly regulated a great number of genes in common. This proposes similar molecular mechanisms, although the extent seems to differ between the analyzed PA as reflected by the potential hepatotoxicity and individual PA structure.


