Paeonia lactiflora
Paeonia lactiflora
1. The products in our compound library are selected from thousands of unique natural products; 2. It has the characteristics of diverse structure, diverse sources and wide coverage of activities; 3. Provide information on the activity of products from major journals, patents and research reports around the world, providing theoretical direction and research basis for further research and screening; 4. Free combination according to the type, source, target and disease of natural product; 5. The compound powder is placed in a covered tube and then discharged into a 10 x 10 cryostat; 6. Transport in ice pack or dry ice pack. Please store it at -20 °C as soon as possible after receiving the product, and use it as soon as possible after opening.
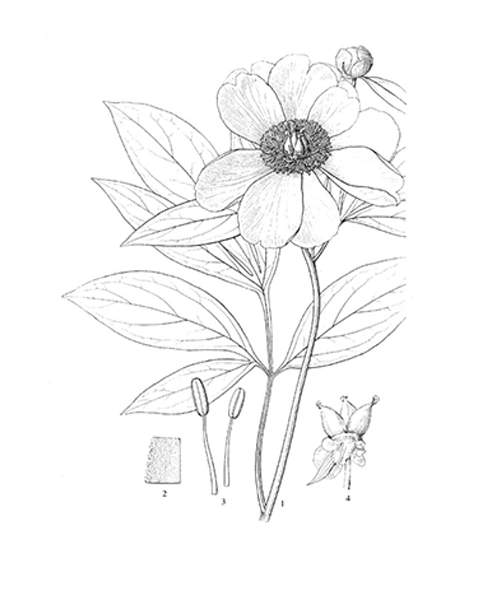
Natural products/compounds from Paeonia lactiflora
- Cat.No. Product Name CAS Number COA
-
BCN2941
6'-O-Galloyl paeoniflorin122965-41-7
Instructions

-
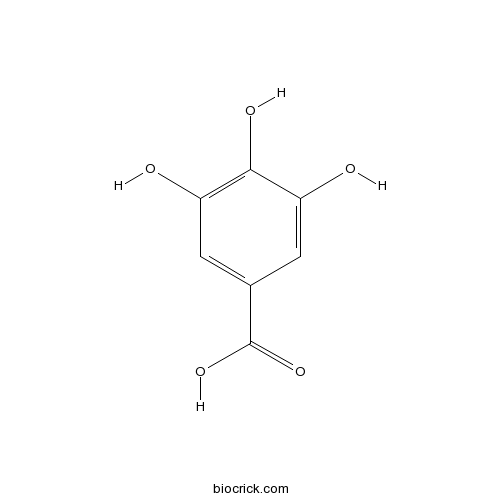
BCN1668
Gallic acid149-91-7
Instructions
-
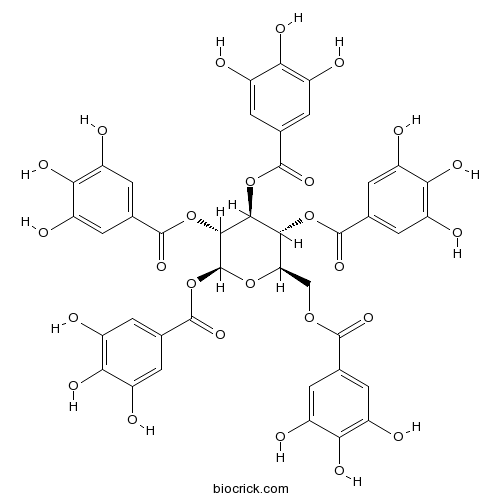
BCN2338
1,2,3,4,6-O-Pentagalloylglucose14937-32-7
Instructions
-
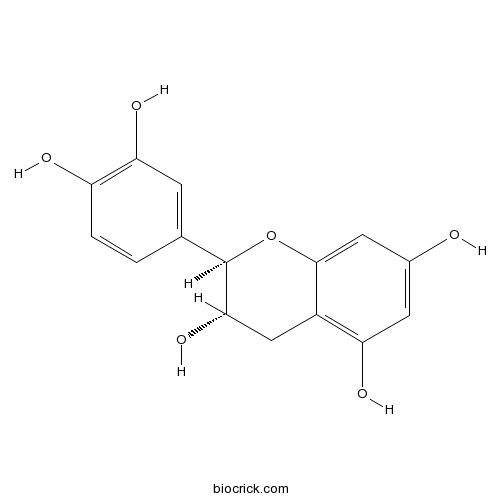
BCN1688
Catechin154-23-4
Instructions
-
BCN2798
Mudanpioside C172760-03-1
Instructions
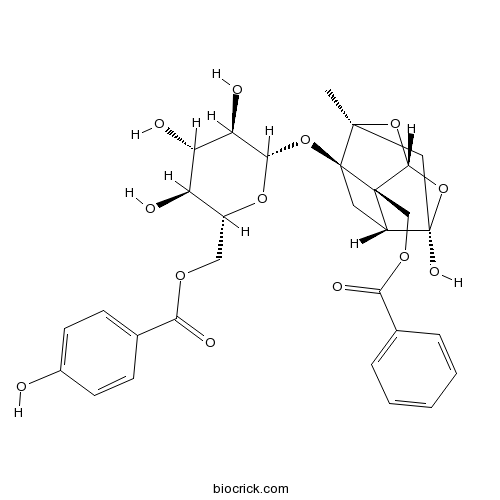
-
BCN6301
Paeoniflorin23180-57-6
Instructions

-
BCN6293
Benzoylpaeoniflorin38642-49-8
Instructions
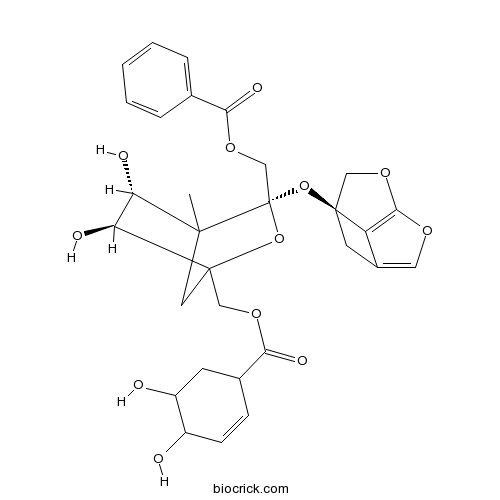
-
BCN1264
Albiflorin39011-90-0
Instructions

-
BCN6346
Oxypaeoniflorin39011-91-1
Instructions

-
BCN2799
Benzoyloxypeoniflorin72896-40-3
Instructions
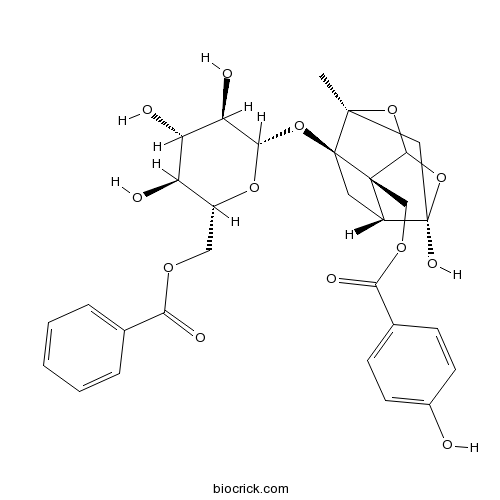
-
BCN4373
Ethyl gallate831-61-8
Instructions

-
BCN4424
Pyrogallol87-66-1
Instructions

-
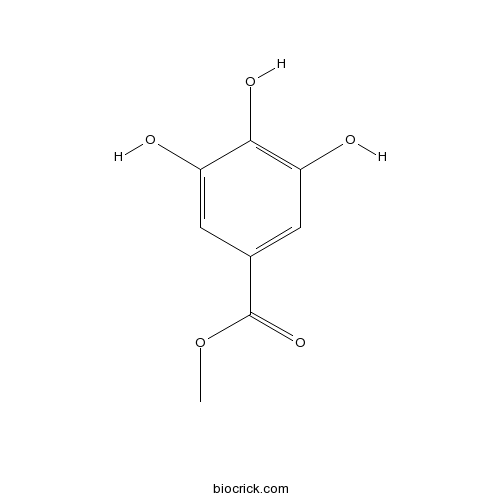
BCN3823
Methyl gallate99-24-1
Instructions
[Chemical constituents from water-soluble extract of dry roots of Paeonia lactiflora].[Pubmed: 30111055]
None
Characterization of the glycerol-3-phosphate acyltransferase gene and its real-time expression under cold stress in Paeonia lactiflora Pall.[Pubmed: 30096187]
Elucidating the cold tolerance mechanism of Paeonia lactiflora, which is one of the most valuable ornamental and medicinal plants in Asia, fundamentally impacts its breeding and production. The glycerol-3-phosphate acyltransferase (GPAT) gene plays a pivotal role in cold resistance in a variety of plant species. Here, we cloned the P. lactiflora GPAT gene, determined its expression pattern, and tested its role in cold resistance. We obtained the full-length P. lactiflora GPAT gene using tissue-cultured seedlings and real-time polymerase chain reaction and rapid amplification of cDNA ends analyses. We named this gene PlGPAT in P. lactiflora. Phylogenetic analysis indicates that the PlGPAT gene is closely related with the GPAT genes in core eudicots. The phylogenetic tree containing 31 angiosperm species based on GPAT protein sequences is largely consistent with the known phylogeny in flowering plants. We conducted a time-course PlGPAT expression analysis and demonstrated that PlGPAT expression is correlated with low-temperature stress. Our results suggest that the PlGPAT gene plays an important role in regulating cold resistance in P. lactiflora.
Paeoniflorin inhibits mast cell-mediated allergic inflammation in allergic rhinitis.[Pubmed: 30076630]
Paeoniflorin (PF), one of the main effective ingredients from the root of Paeonia lactiflora Pall., was reported to possess antitumor, anti-inflammatory, and antiallergic properties. However, the roles of PF in activated human mast cell line, HMC-1 cells, have not yet been elucidated. Thus, the aim of this study was to examine the antiallergic and anti-inflammatory effects of PF on phorbol-12-myristate 13-acetate plus calcium ionophore (PMACI)-induced human mast cells and to identify the mechanism responsible for these effects. Our results demonstrated that pretreatment with PF effectively attenuated PMACI-induced production of tumor necrosis factor-α and interleukin 1β in HMC-1 cells. In addition, PF significantly suppressed PMACI-induced histamine release and caspase-1 activation in HMC-1 cells. Furthermore, PF prevented the activation of nuclear factor κB (NF-κB) and mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) signaling pathways in activated HMC-1 cells. In conclusion, we showed for the first time that PF attenuated the mast cell-mediated allergic inflammatory response through suppressing the NF-κB and MAPK signaling pathways.
Efficacy and safety of Xuebijing injection (a Chinese patent) for sepsis: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials.[Pubmed: 29860133]
Xuebijing injection (XBJ), a Chinese patent medicine that was approved for treating sepsis in China in 2004, consists of Carthamus tinctorius L. (Carthami Flos, hong hua), Paeonia lactiflora Pall. (Paeoniae Radix Rubra, chi shao), Ligusticum chuanxiong Hort. (Chuanxiong Rhizoma, chuan xiong), Salvia miltiorrhiza Bge. (Salviae Miltiorrhizae Radix Et Rhizoma, dan shen) and Angelica sinensis (Oliv.) Diels (Angelicae Sinensis Radix, dang gui).
[Characterization of sediment of water extract of Guizhi decoction and its effect on relevant compound (fractions) in decoction].[Pubmed: 29751710]
In order to study the effect of sediment of water extract of Guizhi decoction on the stability, clarity and peaks area, and characterize the chemical composition of the sediments, HPLC and MS methods were established. Through comparison of the common peak areas and the turbidity value of water extract and filtrate, the sediments could greatly change the common peak areas of the decoction (for more than 5 times of the study standard); at the same time, the turbidity value of the decoction could increase by (38.66±1.57)% in 48 h [particularly by (24.54±1.68)% in 6 h]. The test indicated that the sediments had an effect on the stability and clarity under the test conditions in Guizhi decoction. The study confirmed that the sediments were mainly derived from Cassia twig, Paeonia lactiflora and Glycyrrhiza uralensis. On the basis of the reference information, the accurate molecular weight and fragment ion information provided by LC-MS were analyzed, the molecular formula of sediments components A-F were determined, and the possible structural information of components B, C, D and F were deduced. It was suggested that the multi-index, multi-target and multi-angle analysis could ensure the quality of traditional Chinese medicine and the effect of clinical medication. The study also suggested the effect of the sediments on clinical application and the preparation of traditional Chinese medicine.


