Plantago asiatica
Plantago asiatica
1. The products in our compound library are selected from thousands of unique natural products; 2. It has the characteristics of diverse structure, diverse sources and wide coverage of activities; 3. Provide information on the activity of products from major journals, patents and research reports around the world, providing theoretical direction and research basis for further research and screening; 4. Free combination according to the type, source, target and disease of natural product; 5. The compound powder is placed in a covered tube and then discharged into a 10 x 10 cryostat; 6. Transport in ice pack or dry ice pack. Please store it at -20 °C as soon as possible after receiving the product, and use it as soon as possible after opening.
Natural products/compounds from Plantago asiatica
- Cat.No. Product Name CAS Number COA
-
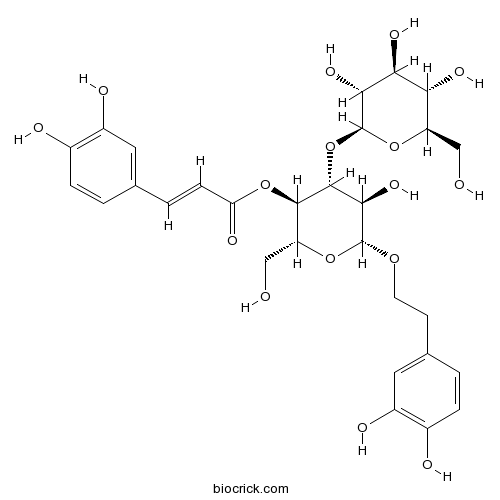
BCN6279
Plantamajoside104777-68-6
Instructions
-
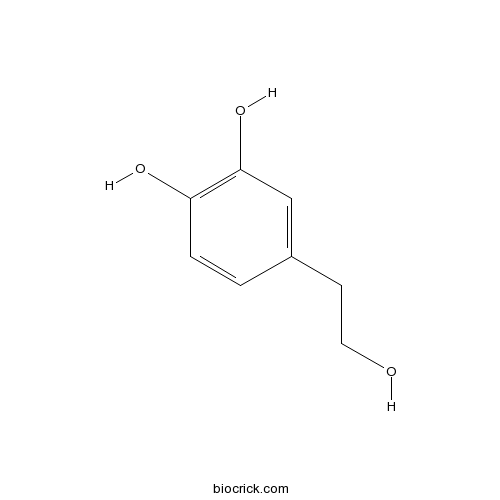
BCN5871
2-(3,4-Dihydroxyphenyl)ethanol10597-60-1
Instructions
-
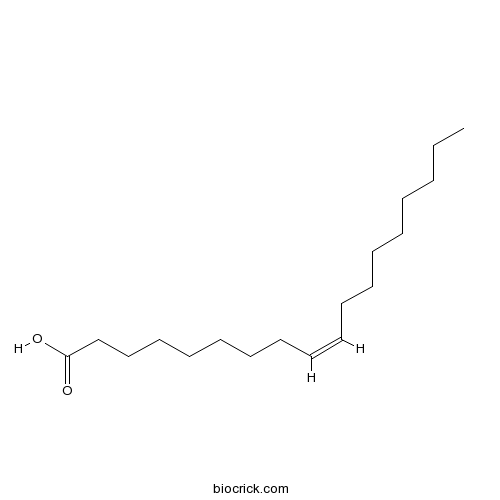
BCN7159
Oleic acid112-80-1
Instructions
-
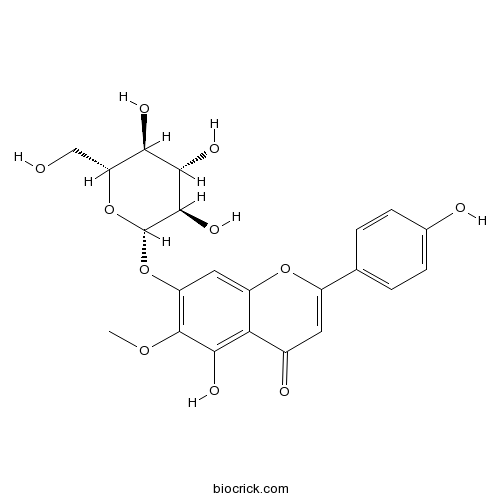
BCN2488
Homoplantaginin17680-84-1
Instructions
-
BCN5171
Geniposidic acid27741-01-1
Instructions

-
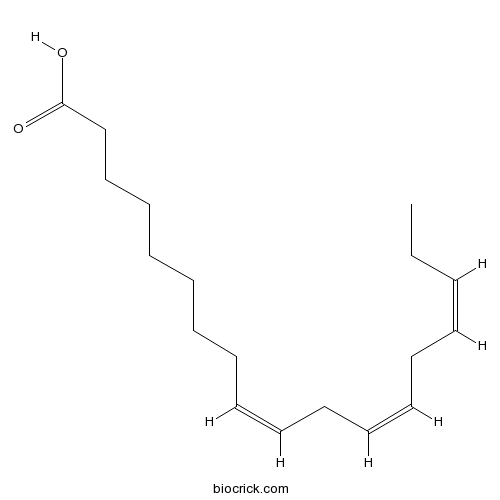
BCN8319
alpha-Linolenic acid463-40-1
Instructions
-
BCN5355
Aucubin479-98-1
Instructions

-
BCN5388
Luteolin-7-O-glucoside5373-11-5
Instructions

-
BCN1209
Eriodictyol552-58-9
Instructions

-
BCN3821
Linoleic acid60-33-3
Instructions

-
BCN4136
Acteoside61276-17-3
Instructions

Plantamajoside inhibits lipopolysaccharide-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition through suppressing the NF-κB/IL-6 signaling in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma cells.[Pubmed: 29710521]
Plantamajoside (PMS) is a major compound of Plantago asiatica and possesses anti-tumor activity. However, the effect of PMS on esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC) and the underlying mechanism of action are unclear. The present study aimed to evaluate the effect of PMS on lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) in ESCC. The results showed that PMS inhibited viability of ESCC cell lines (Eca-109 and TE-1) in a concentration-dependent manner. PMS also inhibited LPS-induced EMT in ESCC cells. PMS inhibited LPS-induced activation of the NF-κB pathway and IL-6 expression. PMS also suppressed IL-6-induced EMT in ESCC cells. Treatment of BAY11-7082 (an inhibitor of NF-κB) or antibody against IL-6 alleviated the effect of LPS-induced EMT in ESCC cells. Besides, inhibition of NF-κB decreased IL-6 expression. In conclusion, the results indicated that PMS inhibited LPS-induced EMT through suppressing the NF-κB/IL-6 signaling in ESCC cell lines, suggesting that PMS might be a useful agent for the treatment of ESCC.
Molecular properties and immunomodulatory activities of a water-soluble heteropolysaccharide isolated from Plantago asiatica L. leaves.[Pubmed: 29385853]
None
Plantamajoside Inhibits Lipopolysaccharide-Induced MUC5AC Expression and Inflammation through Suppressing the PI3K/Akt and NF-κB Signaling Pathways in Human Airway Epithelial Cells.[Pubmed: 29349683]
It has been reported that plantamajoside (PMS), a major natural compound isolated from Plantago asiatica, has anti-inflammatory activities. However, the effect of PMS on respiratory inflammatory diseases has not yet been studied. The present study aimed to evaluate the effect of PMS on lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced airway inflammation and the underlying mechanism. The results showed that PMS did not affect the cell viability of 16-HBE cells. PMS (20 and 40 μg/ml) decreased the expression levels of MUC5AC, IL-6, and IL-1β, which were induced by LPS treatment. PMS inhibited the LPS-induced phosphorylation of Akt and p65. In addition, inhibitors of the PI3K/Akt and NF-κB pathways attenuated the effect of LPS on 16-HBE cells. In conclusion, PMS inhibits LPS-induced MUC5AC expression and inflammation through suppressing the PI3K/Akt and NF-κB signaling pathways, indicating that PMS may be a potential therapy for the treatment of respiratory inflammatory diseases.
A new heteropolysaccharide from the seed husks of Plantago asiatica L. with its thermal and antioxidant properties.[Pubmed: 29138791]
None
Plantago asiatica L. Seed Extract Improves Lipid Accumulation and Hyperglycemia in High-Fat Diet-Induced Obese Mice.[Pubmed: 28665305]
None
Plantago asiatica L. Ameliorates Puromycin Aminonucleoside-Induced Nephrotic Syndrome by Suppressing Inflammation and Apoptosis.[Pubmed: 28420111]
None


