Potentilla discolor
Potentilla discolor
1. The products in our compound library are selected from thousands of unique natural products; 2. It has the characteristics of diverse structure, diverse sources and wide coverage of activities; 3. Provide information on the activity of products from major journals, patents and research reports around the world, providing theoretical direction and research basis for further research and screening; 4. Free combination according to the type, source, target and disease of natural product; 5. The compound powder is placed in a covered tube and then discharged into a 10 x 10 cryostat; 6. Transport in ice pack or dry ice pack. Please store it at -20 °C as soon as possible after receiving the product, and use it as soon as possible after opening.
Natural products/compounds from Potentilla discolor
- Cat.No. Product Name CAS Number COA
-
BCN2932
Mauritianin109008-28-8
Instructions

-
BCN1688
Catechin154-23-4
Instructions
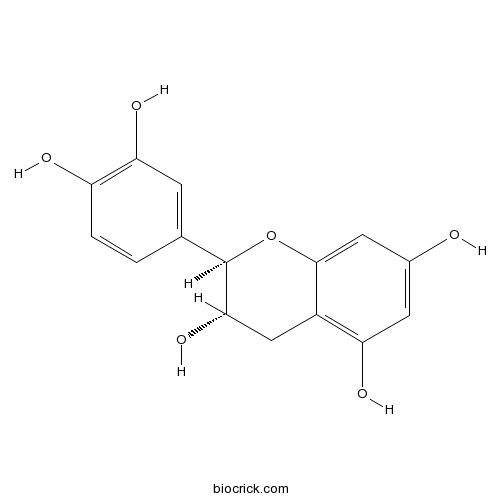
-
BCN5533
Ellagic acid476-66-4
Instructions
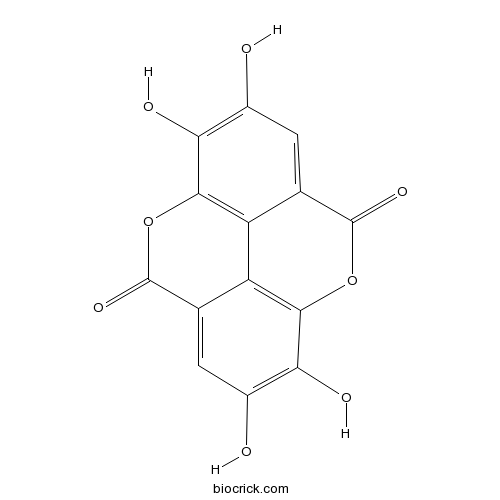
Three new C-27-carboxylated-lupane-triterpenoid derivatives from Potentilla discolor Bunge and their in vitro antitumor activities.[Pubmed: 28388692]
Three new lupane-triterpenoids (1-3) along with six known compounds (4-9) were isolated from the ethanolic extract of whole plant of Potentilla discolor Bunge. The structures of Compounds 1-3 were established by extensive 1D and 2D NMR together with other spectrum analysis, indicating that their C-27 positions were highly oxygenated, which were rarely found in nature. Their in vitro anti-proliferative activities against HepG-2, MCF-7 and T-84 cell lines were evaluated by Cell Counting Kit-8 (CCK-8) assay, and the results showed different activities for three cell lines with IC50 values ranging from 17.84 to 40.64 μM. In addition, the results from Hoechst 33258 and AO/EB staining as well as annexinV-FITC assays exhibited Compound 1 caused a markedly increased HepG-2 cellular apoptosis in a dose-dependent manner. The further mechanisms of Compound 1-induced cellular apoptosis were confirmed that 1 induced the production of ROS and the alteration of pro- and anti-apoptotic proteins, which led to the dysfunction of mitochondria and activation of caspase-9 and caspase-3 and finally caused cellular apoptosis. These results would be useful in search for new potential antitumor agents and for developing semisynthetic lupane-triterpenoid derivatives with high antitumor activity.
Metabonomic analysis of the therapeutic effect of Potentilla discolor in the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus.[Pubmed: 25118630]
Type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) is increased worldwide in parallel with the obesity epidemic. Potentilla discolor is one of the most important crude materials in Traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) for therapy of hyperglycemia and hyperlipidemia. In this work, a plasma metabonomic approach based on the combination of UPLC-Q-TOF with multivariate data analysis was applied to investigate the therapeutic effects of the extract of P. discolor (EPD) and corosolic acid (CA), the main bioactive compounds of P. discolor. Male C57BL/6 mice were fed with high-fat diet (HFD-fed group) for 8 weeks and then treated with EPD (EPD-treated group) or CA (CA-treated group) for another 8 weeks. After the experimental period, samples of plasma were collected and analyzed by ultra-performance liquid chromatography/quadrupole time of flight mass spectrometry (UPLC-Q-TOF). The principal component analysis (PCA) and partial least squares discriminant analysis (PLS-DA) models were built to find biomarkers of T2DM and investigate the therapeutic effects of EPD and CA. 26 metabolites, which are distributed in several metabolic pathways, were identified as potential biomarkers of T2DM. It was found that EPD and CA could reverse the pathological process of T2DM through regulating the disturbed pathway of metabolism. The metabonomic results are beneficial not only for the evaluation of the therapeutic effect of TCM but also for the elucidation of the underlying molecular mechanism.
[Study on chemical constituents of triterpenoids from Potentilla discolor].[Pubmed: 24417146]
To study the triterpenoids constituents in Potentilla discolor.
Simultaneous determination of corosolic acid and euscaphic acid in the plasma of normal and diabetic rat after oral administration of extract of Potentilla discolor Bunge by high-performance liquid chromatography/electrospray ionization mass spectrometry.[Pubmed: 24311372]
Potentilla discolor Bunge has been used for diabetes in China for a long time. Corosolic acid (CA) and euscaphic acid (EA), with significant anti-diabetic activity, are two major triterpenoids in P. discolor. In this study, a specific, sensitive and convenient LC-MS method has been developed for simultaneous determination of CA and EA in the plasma of normal and diabetic rats after oral administration of the extract of P. discolor. The chromatographic separation was achieved using an Alltima C18 column (53 × 7.0 mm, i.d., 3 µm) with a mobile phase composed of 0.1% formic acid water and 0.1% formic acid acetonitrile at a flow rate of 1.0 mL/min. The detection was performed by MS with electrospray ionization interface in negative selected ion monitoring mode. All the validation data, such as specificity, linearity (r(2) > 0.9991 within 0.025-10.0 µg/mL), lower limit of quantitation (2.5 ng/mL), precision (intra- and inter-day <14.7%), accuracy (<15.0%), recovery (85.7-110.8%) and stability were determined and all of them were within the required limits. This method was successfully applied for the evaluation of the pharmacokinetic behaviors of these two compounds in the plasma of normal and diabetic rats.
Anti-hyperglycemic effect of Potentilla discolor decoction on obese-diabetic (Ob-db) mice and its chemical composition.[Pubmed: 22960384]
Potentilla discolor is used as an ethnomedicine in treatments of diabetes mellitus in China for years. In the present study, the anti-hyperglycemic effects of a clinical active extract (decoction) from P. discolor were investigated in Ob-db mice. Four week's treatment of P. discolor decoction ameliorated the development of hyperlipidemia, lipid peroxidation and hyperglycemia associated with hyperphagia and polydypsia in Ob-db mice. P. discolor significantly attenuated the increase of blood glucose and cholesterol levels in Ob-db mice. These findings clearly provided evidences regarding the anti-hyperglycemic potentials of P. discolor decoction. High-resolution liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry/mass spectrometry (HR-LC-MS/MS) was used to analyze the phytochemicals in P. discolor decoction. In an comprehensive analysis of phytochemicals in P. discolor, thirty-five components were identified or characterized in P. discolor decoction and only sixteen of them have been reported in P. discolor previously. There are five major components identified in P. discolor decoction. One of the major components is a flavonoid sulfate, and this is the first evidence for the presences of sulfated flavonoid in P. discolor. Sulfated flavonoids have been reported to improve the complications of diabetes mellitus by inhibition of the aldose reductase in both experimental animals and clinical trials. Therefore, the sulfated flavonoid in P. discolor decoction may in part contribute to the anti-hyperglycemic effect of P. discolor.
[Effects of Astragalus membranaceus and Potentilla discolor mixture on insulin resistance and its related mRNA expressions in KKAy mice with type 2 diabetes].[Pubmed: 22805090]
To investigate the effects of Astragalus membranaceus and Potentilla discolor mixture (APM) on insulin resistance (IR) and mRNA expressions of IR-related genes, including phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3-K), phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase (PEPCK) and peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ coactivator 1 (PGC1) in KKAy mice with early type 2 diabetes and to explore the gene regulation mechanisms of AMP.
Quality evaluation of Potentilla discolor by high-performance liquid chromatography coupled with diode array detection and electrospray ionisation tandem mass spectrometry.[Pubmed: 21425380]
The whole herb of Potentilla discolor has long been used for treatment of diarrhoea, malaria, haemoptysis and haematemesis in clinical applications. However, until now, there has been no literature regarding to the quality control of it.
Antidiabetic and antioxidant effects of extracts from Potentilla discolor Bunge on diabetic rats induced by high fat diet and streptozotocin.[Pubmed: 20816941]
Potentilla discolor Bunge, commonly found at the north temperate and boreal zone, has been used for diabetes in China for a long time. Flavonoids and triterpenoids are two major types of compounds in P. discolor. This study was designed primarily to investigate the effects of total flavonoids extract (TFE) and total triterpenoids extract (TTE) of P. discolor Bunge on blood glucose, lipid profiles and antioxidant parameters on diabetic rats induced by high fat diet and streptozotocin.
Structural determination of two new triterpenoids from Potentilla discolor Bunge by NMR techniques.[Pubmed: 18509870]
Two new pentacyclic triterpenoids, 3alpha, 30-dihydroxylup-20(29)-en-27-oic acid (1) and (20S)-3alpha, 29-dihydroxylupan-27-oic acid (2) were isolated from the whole herbs of Potentilla discolor Bunge. The structures of these two new compounds were elucidated, and complete assignments of the (1)H and (13)C NMR spectroscopic data were achieved by 1D and 2D NMR experiments (HSQC, HMBC, (1)H-(1)HCOSY and ROESY).


