Pteris multifida
Pteris multifida
1. The products in our compound library are selected from thousands of unique natural products; 2. It has the characteristics of diverse structure, diverse sources and wide coverage of activities; 3. Provide information on the activity of products from major journals, patents and research reports around the world, providing theoretical direction and research basis for further research and screening; 4. Free combination according to the type, source, target and disease of natural product; 5. The compound powder is placed in a covered tube and then discharged into a 10 x 10 cryostat; 6. Transport in ice pack or dry ice pack. Please store it at -20 °C as soon as possible after receiving the product, and use it as soon as possible after opening.
Natural products/compounds from Pteris multifida
- Cat.No. Product Name CAS Number COA
-
BCN5948
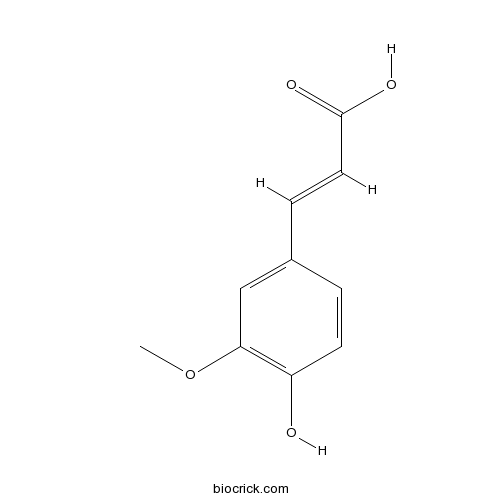
Ferulic acid1135-24-6
Instructions
-
BCN1112
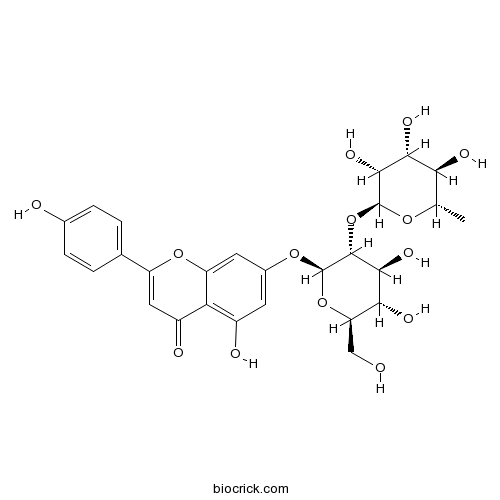
Rhoifolin17306-46-6
Instructions
-
BCN3013
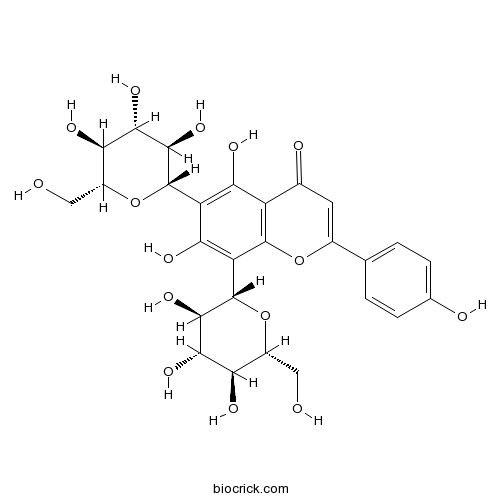
Vicenin -223666-13-9
Instructions
-
BCN5600
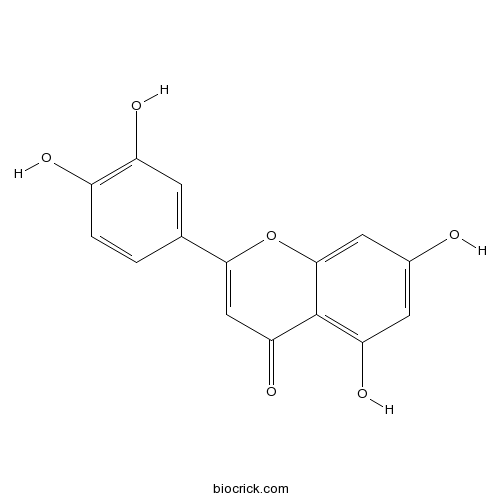
Luteolin491-70-3
Instructions
-
BCN5788
Cosmosiin578-74-5
Instructions

Pteris multifida, Cortex phellodendri, and probiotics attenuated inflammatory status and immunity in mice with a Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium infection.[Pubmed: 29517465]
Pteris multifida (PM) and Cortex phellodendri (CP) are medicinal foods used for gastrointestinal protection. Lactic-acid bacteria are probiotics. Salmonella Typhimurium strain ST21-infected mice were used to examine the alleviative effects of two lactic-acid bacteria (LAB) as well as aqueous extracts of PM and CP for a 4-day treatment. CP and LAB decreased fecal ST counts. CP and PM reduced the ST21 count in the blood, intestine, and liver. LAB lowered the ST21 count in the intestine and spleen. CP and LAB decreased the IFN-gamma level; PM lowered the TNF-alpha level; and both LAB and PM reduced the IL-1beta level in serum. PM and CP lowered the IgG level in serum. The data in a macrophage infection model indicate that TNF-alpha was partial involved in this alleviative effects, other mechanisms might be involved. In sum, these novel findings suggest that PM, CP, and LAB probiotics are potential anti-Salmonellae agents.
[Chemical constituents from Pteris multifida and cytotoxic activity].[Pubmed: 28936845]
The materials were extracted by 95% ethanol, and the extracting solution was isolated by kinds of chromatographic columns including polyamide, MCI, preparative MPLC, and preparative HPLC. Eight diterpenes and two sesquiterpenes were isolated from the plant. On analysis of ESI-MS and NMR spectroscopic data, the structures were established as ent-3β-hydroxy-kaur-16-en-19-al (1), 4-epi-kaurenic acid (2), mitrekaurenone (3), 7β,16α,17-trihydroxy-ent-kauran-19-oic acid (4), crotonkinin E (5), crotonkinin F (6), pterisolic acid A (7), pterisolic acid C (8), (2R)-pterosin P (9), and dehydropterosin B (10). Compounds 1-6 were obtained from Pteris for the first time, and compounds 7-10 were obtained from P. ensiformis for the first time. Compounds 5-8 showed moderate activity against HCT-116, HepG2 and BGC-823 cell lines, separately.
Cytotoxic pterosins from Pteris multifida roots against HCT116 human colon cancer cells.[Pubmed: 28532669]
None
Anti-Neuroinflammatory ent-Kaurane Diterpenoids from Pteris multifida Roots.[Pubmed: 28035965]
None
Chemical characterization, anti-benign prostatic hyperplasia effect and subchronic toxicity study of total flavonoid extract of Pteris multifida.[Pubmed: 27845168]
The decoction of Pteris multifida had been applied to attenuate symptoms of benign prostatic hyperplasia in Chinese folk medicine. In this study, the total flavonoid extract of Pteris multifida was processed at first. High performance liquor chromatography and tandem mass spectrometer assay revealed 10 flavonoids as key constituents of this extract. After 60-day administration, the total flavonoid extract (180 mg/kg, i. g.) decreased the prostate index in mice of benign prostatic hyperplasia apparently. Immunohistochemical assay revealed inhibition of vascular endothelial growth factor expression, together with activation of transforming growth factor-beta 1 expression in the prostatic samples after administration of the extract. A 90-day subchronic toxicity test was further undertaken in male Sprague-Dawley rats, and the no-observed-adverse-effect level for the extract was 200 mg/kg body weight/day. These results revealed that the total flavonoid extract of Pteris multifida exhibited positive effect with safety, which might be applied in treatment of benign prostatic hyperplasia.
Arsenic Induced Phytate Exudation, and Promoted FeAsO4 Dissolution and Plant Growth in As-Hyperaccumulator Pteris vittata.[Pubmed: 27483027]
Arsenic hyperaccumulator Pteris vittata (PV) is efficient in taking up As and nutrients from As-contaminated soils. We evaluated the mechanisms used by PV to mobilize As and Fe by examining the impacts of As and root exudates on FeAsO4 solubilization, and As and Fe uptake in four plants: As-hyperaccumulators PV and Pteris multifida (PM), nonhyperaccumulator Pteris ensiformis (PE), and angiosperm plant tomato (Solanum lycopersicum). Phytate and oxalate were dominant in fern plants (>93%), which were 50-83, 15-42, and 0-32 mg kg(-1) phytate and 10-15, 7-26, and 4-12 mg kg(-1) oxalate for PV, PM, and PE respectively, with higher As inducing greater phytate exudation and no phytate being detected in tomato exudates. PV treated with phytate+FeAsO4 had higher As and Fe contents and larger biomass than phytate or FeAsO4 treatment, which were 340 vs 20 and 130 mg kg(-1) As in the fronds and 7900 vs 1600 and 4100 mg kg(-1) Fe in the roots. We hypothesized that As-induced phytate exudation helped PV to take up Fe and As from insoluble FeAsO4 and promoted PV growth. Our study suggests that phytate exudation may be special to fern plants, which may play an important role in enhancing As and nutrient uptake by plants, thereby increasing their efficiency in phytoremediation of As-contaminated soils.
Changes in gametophyte physiology of Pteris multifida induced by the leaf leachate treatment of the invasive Bidens pilosa.[Pubmed: 26490937]
In recent years, the response of fern gametophytes to environment has raised much attention. However, studies on the influence of plant invasion to fern gametophytes are scarce. Allelopathy plays an important role in biological invasion. Hence, it is necessary to study the allelopathic effects of invasive plants on fern gametophytes and elucidate the mechanisms by which invasive plants cause phytotoxicity. As one of the main invasive plants in China, Bidens pilosa exhibits allelopathic effects on spermatophyte growth. Field investigation shows that many ferns are threatened by the invasion of B. pilosa. The distribution of Pteris multifida overlaps with that of B. pilosa in China. To examine the potential involvement of allelopathic mechanisms of B. pilosa leaves, changes in the physiology in P. multifida gametophytes are analyzed. We found that cell membrane and antioxidant enzyme activities as well as photosynthesis pigment contents of the gametophytes were affected by B. pilosa leachates. Gametophytes of P. multifida exposed to B. pilosa had increased damages to cell membranes, expressed in thiobarbituric acid reacting substance (TBARS) concentrations, malondialdehyde (MDA), electrolyte leakage (membrane permeability), and degree of injury. Enzyme activities, assessed by superoxide dismutase (SOD) and catalase (CAT) as well as guaiacol peroxidase (GPX) enhanced with the increase in leachate concentration after 2-day exposure. Meanwhile, lower chlorophyll a (Chl a), chlorophyll b (Chl b), carotenoid (Car), and the total chlorophyll were measured as leachate concentrations increased. At day 10, leaf leachates of B. pilosa exhibited the greatest inhibition. These results suggest that the observed inhibitory or stimulatory effects on the physiology studied can have an adverse effect on P. multifida and that allelopathic interference seems to have involved in this process.


