Salvia chinensis
Salvia chinensis
1. The products in our compound library are selected from thousands of unique natural products; 2. It has the characteristics of diverse structure, diverse sources and wide coverage of activities; 3. Provide information on the activity of products from major journals, patents and research reports around the world, providing theoretical direction and research basis for further research and screening; 4. Free combination according to the type, source, target and disease of natural product; 5. The compound powder is placed in a covered tube and then discharged into a 10 x 10 cryostat; 6. Transport in ice pack or dry ice pack. Please store it at -20 °C as soon as possible after receiving the product, and use it as soon as possible after opening.
Natural products/compounds from Salvia chinensis
- Cat.No. Product Name CAS Number COA
-
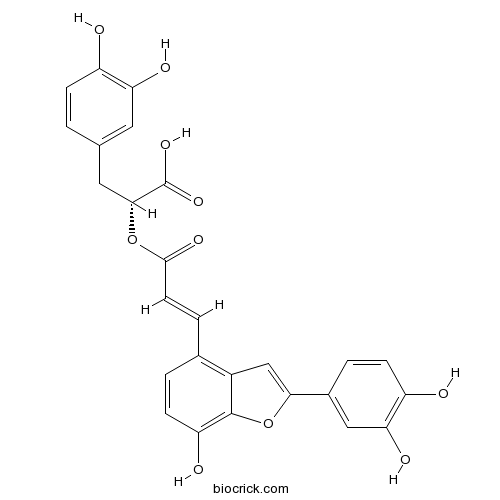
BCN5376
Salvianolic acid C115841-09-3
Instructions
-
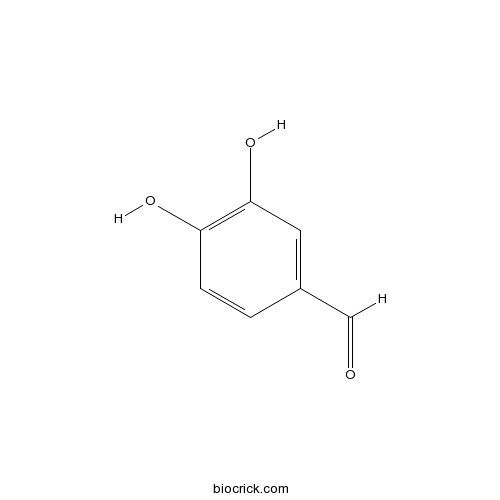
BCN6214
3,4-Dihydroxybenzaldehyde139-85-5
Instructions
-
BCN5893
Rosmarinic acid20283-92-5
Instructions

-
BCN8513
Danshensu76822-21-4
Instructions

-
BCN2823
Dimethyl lithospermate B875313-64-7
Instructions

-
BCN5951
Salvianolic acid A96574-01-5
Instructions

Polyphenol-rich extract of Salvia chinensis exhibits anticancer activity in different cancer cell lines, and induces cell cycle arrest at the G₀/G₁-phase, apoptosis and loss of mitochondrial membrane potential in pancreatic cancer cells.[Pubmed: 26165362]
Pancreatic cancer (PC) is one of the most aggressive types of human malignancy, which has an overall 5-year survival rate of <2%. PC is the fourth most common cause of cancer‑associated mortality in the western world. At present, there is almost no effective treatment available for the treatment of PC. The aim of the present study was to evaluate the anticancer potential of a polyphenol enriched extract obtained from Salvia chinensis, a Chinese medicinal plant. An MTT assay was used to evaluate the cell viability of five cancer cell lines and one normal cell line. In addition, the effects of the extract on apoptotic induction, cell cycle phase distribution, DNA damage and loss of mitochondrial membrane potential (ΛΨm) were evaluated in MiapaCa‑2 human PC cells. The effects of the extract on cell cycle phase distribution and ΛΨm were assessed by flow cytometry, using propidium iodide and rhodamine‑123 DNA‑binding fluorescent dyes, respectively. Fluorescence microscopy, using 4',6‑diamidino‑2‑phenylindole as a staining agent, was performed in order to detect the morphological changes of the MiapaCa‑2 cancer cells and the presence of apoptotic bodies following treatment with the extract. The results of the present study demonstrated that the polyphenol‑rich extract from S. chinensis induced potent cytotoxicity in the MCF‑7 human breast cancer cells, A549 human lung cancer cells, HCT‑116 and COLO 205 human colon cancer cells, and MiapaCa‑2 human PC cells. The Colo 205 and MCF‑7 cancer cell lines were the most susceptible to treatment with the extract, which exhibited increased rate of growth inhibition. Fluorescence microscopy revealed characteristic morphological features of apoptosis and detected the appearance of apoptotic bodies following treatment with the extract in the PC cells. Flow cytometric analysis demonstrated that the extract induced G0/G1 cell cycle arrest in a dose‑dependent manner. In addition, treatment with the extract induced a significant and concentration-dependent reduction in the ΛΨm of the PC cells.
Antitumor immunostimulatory activity of polysaccharides from Salvia chinensis Benth.[Pubmed: 25858511]
Salvia chinensis Benth (S. chinensis) is a traditional herb applied in the treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Polysaccharides abundantly exist in this plant. However, it remains poorly understood if polysaccharides from S. chinensis (PSSC) contribute to its anti-HCC activity.


