trans-Sinapic acidCAS# 7362-37-0 |
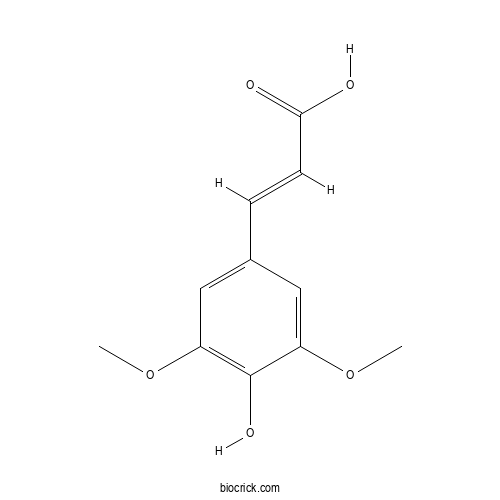
- Sinapic acid
Catalog No.:BCN3539
CAS No.:530-59-6
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 7362-37-0 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 637775 | Appearance | Light yellow powder |
| Formula | C11H12O5 | M.Wt | 224.21 |
| Type of Compound | Phenylpropanes | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Synonyms | trans-4-Hydroxy 3,5-dimethoxycinnamic acid; trans-Sinapinic acid | ||
| Solubility | Soluble in dioxane and methan | ||
| Chemical Name | (E)-3-(4-hydroxy-3,5-dimethoxyphenyl)prop-2-enoic acid | ||
| SMILES | COC1=CC(=CC(=C1O)OC)C=CC(=O)O | ||
| Standard InChIKey | PCMORTLOPMLEFB-ONEGZZNKSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C11H12O5/c1-15-8-5-7(3-4-10(12)13)6-9(16-2)11(8)14/h3-6,14H,1-2H3,(H,12,13)/b4-3+ | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||

trans-Sinapic acid Dilution Calculator

trans-Sinapic acid Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 4.4601 mL | 22.3005 mL | 44.601 mL | 89.2021 mL | 111.5026 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.892 mL | 4.4601 mL | 8.9202 mL | 17.8404 mL | 22.3005 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.446 mL | 2.2301 mL | 4.4601 mL | 8.9202 mL | 11.1503 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0892 mL | 0.446 mL | 0.892 mL | 1.784 mL | 2.2301 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0446 mL | 0.223 mL | 0.446 mL | 0.892 mL | 1.115 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- (RS)-Sakuranetin
Catalog No.:BCN0343
CAS No.:520-29-6
- Sabinene
Catalog No.:BCN0342
CAS No.:3387-41-5
- Rebaudioside O
Catalog No.:BCN0341
CAS No.:1220616-48-7
- Rebaudioside I
Catalog No.:BCN0340
CAS No.:1220616-34-1
- Sophoraflavanone B
Catalog No.:BCN0339
CAS No.:68682-02-0
- (S)-4',5,7-Trihydroxy-6-prenylflavanone
Catalog No.:BCN0338
CAS No.:68682-01-9
- Pinocembroside
Catalog No.:BCN0337
CAS No.:75829-43-5
- Naringenin chalcone
Catalog No.:BCN0336
CAS No.:25515-46-2
- 16-O-Methylcafestol
Catalog No.:BCN0335
CAS No.:108214-28-4
- 6-Methoxytricin
Catalog No.:BCN0334
CAS No.:76015-42-4
- (+)-Lupanine hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCN0333
CAS No.:1025-39-4
- Lavandulyl acetate
Catalog No.:BCN0332
CAS No.:25905-14-0
- Solanthrene
Catalog No.:BCN0345
CAS No.:26516-51-8
- Cannabisin G
Catalog No.:BCN0346
CAS No.:
- Tabersonine hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCN0347
CAS No.:29479-00-3
- Theacrine
Catalog No.:BCN0348
CAS No.:2309-49-1
- α,β-Thujone
Catalog No.:BCN0349
CAS No.:76231-76-0
- Tropine
Catalog No.:BCN0350
CAS No.:120-29-6
- (+/-)-Praeruptorin B
Catalog No.:BCN0351
CAS No.:73069-26-8
- Echiumine N-oxide
Catalog No.:BCN0352
CAS No.:685554-68-1
- 7-Acetylintermedine N-oxide
Catalog No.:BCN0353
CAS No.:685132-59-6
- Sinapine chloride
Catalog No.:BCN0354
CAS No.:6484-80-6
- Trichodesmine N-oxide
Catalog No.:BCN0355
CAS No.:55727-46-3
- Ruscogenin/Neoruscogenin mixture
Catalog No.:BCN0356
CAS No.:50933-59-0
Concentrations of Phenolic Acids Are Differently Genetically Determined in Leaves, Flowers, and Grain of Common Buckwheat (Fagopyrum esculentum Moench).[Pubmed:34205223]
Plants (Basel). 2021 Jun 3;10(6). pii: plants10061142.
Common buckwheat (Fagopyrum esculentum Moench) is a valuable source of proteins, B vitamins, manganese, tryptophan, phytochemicals with an antioxidant effect, and the natural flavonoid rutin. Due to its composition, buckwheat supports the human immune system, regulates blood cholesterol, and is suitable for patients with diabetes or celiac disease. The study aimed to compare the allocation of selected phenolic acids (neochlorogenic acid, chlorogenic acid, trans-caffeic acid, trans-p-coumaric acid, trans-Sinapic acid, trans-ferulic acid) and flavonoids (rutin, vitexin, quercetin, kaempferol) in the leaves, flowers, and grain of buckwheat cultivars of different origin. The content of individual phenolics was determined by the HPLC-DAD method. The results confirmed the determining role of cultivar on the relative content of chlorogenic acid, trans-caffeic acid, trans-Sinapic acid, vitexin, and kaempferol in buckwheat plants. A significantly negative correlation among concentrations of phenolic acids in different common buckwheat plant parts shows that there are different mechanisms of genetic influences on the concentration of phenolic substances in common buckwheat flowers, leaves, and grain. These differences should be taken into account when breeding buckwheat for a high concentration of selected phenolic substances.


