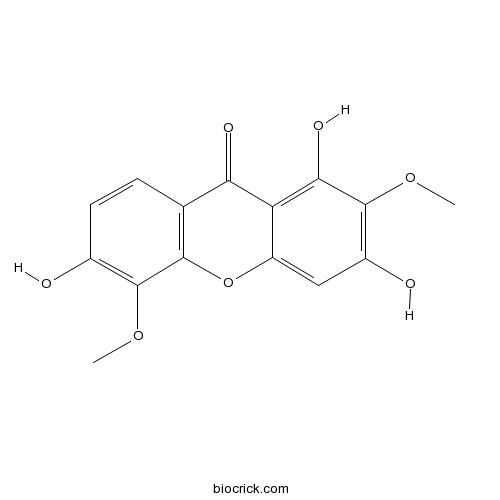
1,3,6-Trihydroxy-2,5-dimethoxyxanthoneCAS# 345287-92-5 |
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 345287-92-5 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 5480343 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C15H12O7 | M.Wt | 304.25 |
| Type of Compound | Xanthones | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | Soluble in Chloroform,Dichloromethane,Ethyl Acetate,DMSO,Acetone,etc. | ||
| Chemical Name | 1,3,6-trihydroxy-2,5-dimethoxyxanthen-9-one | ||
| SMILES | COC1=C(C=CC2=C1OC3=CC(=C(C(=C3C2=O)O)OC)O)O | ||
| Standard InChIKey | YAPFVXIBUYNNQM-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C15H12O7/c1-20-14-8(17)5-9-10(12(14)19)11(18)6-3-4-7(16)15(21-2)13(6)22-9/h3-5,16-17,19H,1-2H3 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | 1. 1,3,6-Trihydroxy-2,5-dimethoxyxanthone shows antimutagenic potential, in particular preventing mutations caused by aflatoxin B1 (AFB1) and benzo[a]pyrene (B[a]P). 2. 1,3,6-Trihydroxy-2,5-dimethoxyxanthone may have antifungal activity. |
| Targets | Antifection |

1,3,6-Trihydroxy-2,5-dimethoxyxanthone Dilution Calculator

1,3,6-Trihydroxy-2,5-dimethoxyxanthone Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 3.2868 mL | 16.4339 mL | 32.8677 mL | 65.7354 mL | 82.1693 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.6574 mL | 3.2868 mL | 6.5735 mL | 13.1471 mL | 16.4339 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.3287 mL | 1.6434 mL | 3.2868 mL | 6.5735 mL | 8.2169 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0657 mL | 0.3287 mL | 0.6574 mL | 1.3147 mL | 1.6434 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0329 mL | 0.1643 mL | 0.3287 mL | 0.6574 mL | 0.8217 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- Myricanol triacetate
Catalog No.:BCN5281
CAS No.:34509-52-9
- Pseudoephedrine Hydrochloride; Threo-Ephedrine Hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC8241
CAS No.:345-78-8
- SSR 69071
Catalog No.:BCC2369
CAS No.:344930-95-6
- Araloside X
Catalog No.:BCN2467
CAS No.:344911-90-6
- Leukadherin 1
Catalog No.:BCC6332
CAS No.:344897-95-6
- 17-ODYA
Catalog No.:BCC6717
CAS No.:34450-18-5
- PJ34
Catalog No.:BCC1865
CAS No.:344458-19-1
- PJ34 hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC2210
CAS No.:344458-15-7
- Nortrachelogenin
Catalog No.:BCN5280
CAS No.:34444-37-6
- Amycomycin
Catalog No.:BCN1824
CAS No.:344362-08-9
- Alpha-Onocerin diacetate
Catalog No.:BCN6700
CAS No.:34434-99-6
- Prudomestin
Catalog No.:BCN5279
CAS No.:3443-28-5
- Arnicolide C
Catalog No.:BCN7978
CAS No.:34532-67-7
- Arnicolide D
Catalog No.:BCN7975
CAS No.:34532-68-8
- Beta,beta-Dimethylacrylalkannin
Catalog No.:BCN2767
CAS No.:34539-65-6
- 6,7-Dehydroferruginol
Catalog No.:BCN3218
CAS No.:34539-84-9
- Madecassoside
Catalog No.:BCN1012
CAS No.:34540-22-2
- Loperamide HCl
Catalog No.:BCC4380
CAS No.:34552-83-5
- SNS-032 (BMS-387032)
Catalog No.:BCC1152
CAS No.:345627-80-7
- SF1670
Catalog No.:BCC5482
CAS No.:345630-40-2
- D-(+)-Mannose
Catalog No.:BCC8311
CAS No.:3458-28-4
- Ketotifen Fumarate
Catalog No.:BCC4531
CAS No.:34580-14-8
- Boc-Asp-OtBu
Catalog No.:BCC3073
CAS No.:34582-32-6
- SB 611812
Catalog No.:BCC6257
CAS No.:345892-71-9
Lipoxygenase inhibitory constituents from Periploca aphylla.[Pubmed:15387640]
J Nat Prod. 2004 Sep;67(9):1450-4.
Bisflavan-3-ols 1 and 2 and norterpenoid 3 have been isolated from the methanolic extract of the whole plant of Periploca aphylla. Their structures have been assigned on the basis of spectroscopic analysis including 1D and 2D NMR techniques. In addition, o-phthalic acid bis(2-ethylnonyl) ester (4), 1,3,6-Trihydroxy-2,5-dimethoxyxanthone (5), and (+)-lyoniresinol (6) have been reported for the first time from this species. Compounds 1-3 displayed evident inhibitory potential against the enzyme lipoxygenase in a concentration-dependent fashion with IC(50) values 19.7, 13.5, and 150.1 microM, respectively.
Xanthone and antifungal constituents from Monnina obtusifolia.[Pubmed:7765695]
Phytochemistry. 1994 Oct;37(3):875-8.
Three biphenyls and four xanthones have been isolated from the aerial parts of Monnina obtusifolia. The structures were established on the basis of their spectral data and that of some derivatives. The biphenyls have been isolated previously from the same genus. 1,3,6-Trihydroxy-2,5-dimethoxyxanthone is a new natural product, whereas the other xanthones have been described in other species. The antifungal activity of the isolated compounds has been determined.
Estrogenic and chemopreventive activities of xanthones and flavones of Syngonanthus (Eriocaulaceae).[Pubmed:23891669]
Steroids. 2013 Nov;78(11):1053-63.
The possible benefits of some bioactive flavones and xanthones present in plants of the genus Syngonanthus prompted us to screen them for estrogenic activity. However, scientific research has shown that such substances may have undesirable properties, such as mutagenicity, carcinogenicity and toxicity, which restrict their use as therapeutic agents. Hence, the aim of this study was to assess the estrogenicity and mutagenic and antimutagenic properties. We used recombinant yeast assay (RYA), with the strain BY4741 of Saccharomyces cerevisiae, and Ames test, with strains TA100, TA98, TA97a and TA102 of Salmonella typhimirium, to evaluate estrogenicity, mutagenicity and antimutagenicity of methanolic extracts of Syngonanthus dealbatus (S.d.), Syngonanthus macrolepsis (S.m.), Syngonanthus nitens (S.n.) and Syngonanthus suberosus (S.s.), and of 9 compounds isolated from them (1=luteolin, 2=mix of A-1,3,6-trihydroxy-2-methoxyxanthone and B-1,3,6-Trihydroxy-2,5-dimethoxyxanthone, 3=1,5,7-trihydroxy-3,6-dimethoxyxanthone, 4=1,3,6,8-tetrahydroxy-2,5-dimethoxyxanthone, 5=1,3,6,8-tetrahydroxy-5-methoxyxanthone, 6=7-methoxyluteolin-8-C-beta-glucopyranoside, 7=7-methoxyluteolin-6-C-beta-glucopyranoside, 8=7,3'-dimethoxyluteolin-6-C-beta-glucopyranoside and 9=6-hydroxyluteolin). The results indicated the estrogenic potential of the S. nitens methanol extract and four of its isolated xanthones, which exhibited, respectively, 14.74+/-1.63 nM; 19.54+/-6.61; 7.20+/-0.37; 6.71+/-1.02 e 10.01+/-4.26 nM of estradiol-equivalents (EEQ). None of the extracts or isolated compounds showed mutagenicity in any of the test strains and all of them showed antimutagenic potential, in particular preventing mutations caused by aflatoxin B1 (AFB1) and benzo[a]pyrene (B[a]P). The results show that the xanthones, only isolated from the methanol extract of S. nitens capitula, probably were the responsible for its estrogenic activity and could be useful as phytoestrogens, providing a new opportunity to develop hormonal agents. In addition, flavones and xanthones could also be used as a new antimutagenic agent. Since, the mutagens are involved in the initiation and promotion of several human diseases, including cancer, the significance of novel bioactive phytocompounds in counteracting these pro-mutagenic and carcinogenic effects is now gaining credence.


