Leukadherin 1CD11b/CD18 activator CAS# 344897-95-6 |
- Levomefolate calcium
Catalog No.:BCC1702
CAS No.:151533-22-1
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 344897-95-6 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 5342077 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C22H15NO4S2 | M.Wt | 421.49 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | DMSO : 5 mg/mL (11.86 mM; Need ultrasonic) | ||
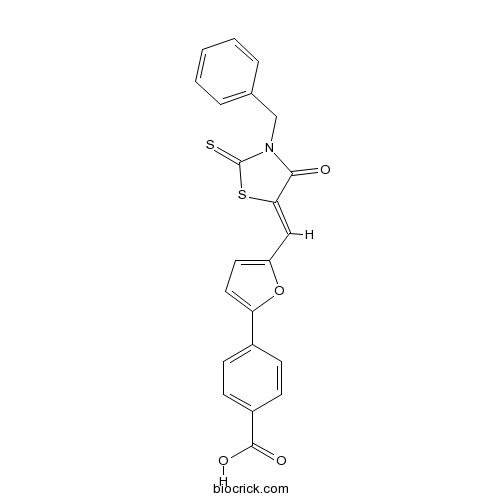
| Chemical Name | 4-[5-[(Z)-(3-benzyl-4-oxo-2-sulfanylidene-1,3-thiazolidin-5-ylidene)methyl]furan-2-yl]benzoic acid | ||
| SMILES | C1=CC=C(C=C1)CN2C(=O)C(=CC3=CC=C(O3)C4=CC=C(C=C4)C(=O)O)SC2=S | ||
| Standard InChIKey | AEZGRQSLKVNPCI-UNOMPAQXSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C22H15NO4S2/c24-20-19(29-22(28)23(20)13-14-4-2-1-3-5-14)12-17-10-11-18(27-17)15-6-8-16(9-7-15)21(25)26/h1-12H,13H2,(H,25,26)/b19-12- | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Allosteric activator of CD11b/CD18. Increases CD11b/CD18-dependent cell adhesion to fibrinogen (EC50 = 4 μM). Decreases leukocyte motility and transendothelial migration; reduces inflammation. Also activates complement receptor 3 (CR3), and promotes CR3-dependent leukocyte adhesion to fibrinogen-coated surfaces. |

Leukadherin 1 Dilution Calculator

Leukadherin 1 Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.3725 mL | 11.8627 mL | 23.7254 mL | 47.4507 mL | 59.3134 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.4745 mL | 2.3725 mL | 4.7451 mL | 9.4901 mL | 11.8627 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.2373 mL | 1.1863 mL | 2.3725 mL | 4.7451 mL | 5.9313 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0475 mL | 0.2373 mL | 0.4745 mL | 0.949 mL | 1.1863 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0237 mL | 0.1186 mL | 0.2373 mL | 0.4745 mL | 0.5931 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
Leukadherin 1 is an activator of CD11b/CD18 [1].
CD11b/CD18 is a cell surface adhesion receptor that mediates immune functions and leukocyte migration and is expressed primarily in the cells of the innate immune system.
Leukadherin 1 is a CD11b/CD18 activator. Leukadherin 1 increased CD11b/CD18-dependent cell adhesion to fibrinogen with EC50 value of 4 μM [1]. Leukadherin 1 increased CD11b/CD18-dependent cell adhesion to its ligand ICAM-1. In K562 cells, leukadherin 1 increased the binding of CD11b/CD18 to ICAM-1 through the formation of long membrane tethers [2].
In the acute peritonitis mice model, leukadherin 1 significantly reduced neutrophil accumulation by 40% [1]. In a MHC mismatched orthotopic kidney transplantation mouse model, leukadherin 1 reduced interstitial leukocyte infiltration, glomerular damage, neointimal hyperplasia and prolonged survival from 48.5% (CsA only) to 100% (CsA and LA1) [3]. In newborn rats exposed to hyperoxia (85% O2), leukadherin 1 reduced both macrophage and neutrophil infiltration in the lungs [4].
References:
[1]. Maiguel D, Faridi MH, Wei C, et al. Small molecule-mediated activation of the integrin CD11b/CD18 reduces inflammatory disease. Sci Signal, 2011, 4(189): ra57.
[2]. Celik E1, Faridi MH, Kumar V, et al. Agonist leukadherin-1 increases CD11b/CD18-dependent adhesion via membrane tethers. Biophys J, 2013, 105(11): 2517-2527.
[3]. Khan SQ, Guo L, Cimbaluk DJ, et al. A small molecule b2 integrin agonist improves chronic kidney allograft survival by reducing leukocyte recruitment and accompanying vasculopathy. Front Med (Lausanne), 2014, 1: 45.
[4]. Jagarapu J, Kelchtermans J, Rong M, et al. Leukadherin-1 Attenuates Hyperoxia-induced Lung Injury in Neonatal Rats. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol, 2015.
- 17-ODYA
Catalog No.:BCC6717
CAS No.:34450-18-5
- PJ34
Catalog No.:BCC1865
CAS No.:344458-19-1
- PJ34 hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC2210
CAS No.:344458-15-7
- Nortrachelogenin
Catalog No.:BCN5280
CAS No.:34444-37-6
- Amycomycin
Catalog No.:BCN1824
CAS No.:344362-08-9
- Alpha-Onocerin diacetate
Catalog No.:BCN6700
CAS No.:34434-99-6
- Prudomestin
Catalog No.:BCN5279
CAS No.:3443-28-5
- Tirandamycin A
Catalog No.:BCN1861
CAS No.:34429-70-4
- Ligularine
Catalog No.:BCN2090
CAS No.:34429-54-4
- Ikshusterol
Catalog No.:BCN5278
CAS No.:34427-61-7
- Lyoniside
Catalog No.:BCN5277
CAS No.:34425-25-7
- 2,3-dihydrosciadopitysin
Catalog No.:BCN4034
CAS No.:34421-19-7
- Araloside X
Catalog No.:BCN2467
CAS No.:344911-90-6
- SSR 69071
Catalog No.:BCC2369
CAS No.:344930-95-6
- Pseudoephedrine Hydrochloride; Threo-Ephedrine Hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC8241
CAS No.:345-78-8
- Myricanol triacetate
Catalog No.:BCN5281
CAS No.:34509-52-9
- 1,3,6-Trihydroxy-2,5-dimethoxyxanthone
Catalog No.:BCN7216
CAS No.:345287-92-5
- Arnicolide C
Catalog No.:BCN7978
CAS No.:34532-67-7
- Arnicolide D
Catalog No.:BCN7975
CAS No.:34532-68-8
- Beta,beta-Dimethylacrylalkannin
Catalog No.:BCN2767
CAS No.:34539-65-6
- 6,7-Dehydroferruginol
Catalog No.:BCN3218
CAS No.:34539-84-9
- Madecassoside
Catalog No.:BCN1012
CAS No.:34540-22-2
- Loperamide HCl
Catalog No.:BCC4380
CAS No.:34552-83-5
- SNS-032 (BMS-387032)
Catalog No.:BCC1152
CAS No.:345627-80-7
Agonist leukadherin-1 increases CD11b/CD18-dependent adhesion via membrane tethers.[Pubmed:24314082]
Biophys J. 2013 Dec 3;105(11):2517-27.
Integrin CD11b/CD18 is a key adhesion receptor that mediates leukocyte migration and immune functions. Leukadherin-1 (LA1) is a small molecule agonist that enhances CD11b/CD18-dependent cell adhesion to its ligand ICAM-1. Here, we used single-molecule force spectroscopy to investigate the biophysical mechanism by which LA1-activated CD11b/CD18 mediates leukocyte adhesion. Between the two distinct populations of CD11b/CD18:ICAM-1 complex that participate in cell adhesion, the cytoskeleton(CSK)-anchored elastic elements and the membrane tethers, we found that LA1 enhanced binding of CD11b/CD18 on K562 cells to ICAM-1 via the formation of long membrane tethers, whereas Mn(2+) additionally increased ICAM-1 binding via CSK-anchored bonds. LA1 activated wild-type and LFA1(-/-) neutrophils also showed longer detachment distances and time from ICAM-1-coated atomic force microscopy tips, but significantly lower detachment force, as compared to the Mn(2+)-activated cells, confirming that LA1 primarily increased membrane-tether bonds to enhance CD11b/CD18:ICAM-1 binding, whereas Mn(2+) induced additional CSK-anchored bond formation. The results suggest that the two types of agonists differentially activate integrins and couple them to the cellular machinery, providing what we feel are new insights into signal mechanotransduction by such agents.
Efficacy of Leukadherin-1 in the Prevention of Hyperoxia-Induced Lung Injury in Neonatal Rats.[Pubmed:25909334]
Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2015 Dec;53(6):793-801.
Lung inflammation plays a key role in the pathogenesis of bronchopulmonary dysplasia (BPD), a chronic lung disease of premature infants. The challenge in BPD management is the lack of effective and safe antiinflammatory agents. Leukadherin-1 (LA1) is a novel agonist of the leukocyte surface integrin CD11b/CD18 that enhances leukocyte adhesion to ligands and vascular endothelium and thus reduces leukocyte transendothelial migration and influx to the injury sites. Its functional significance in preventing hyperoxia-induced neonatal lung injury is unknown. We tested the hypothesis that administration of LA1 is beneficial in preventing hyperoxia-induced neonatal lung injury, an experimental model of BPD. Newborn rats were exposed to normoxia (21% O2) or hyperoxia (85% O2) and received twice-daily intraperitoneal injection of LA1 or placebo for 14 days. Hyperoxia exposure in the presence of the placebo resulted in a drastic increase in the influx of neutrophils and macrophages into the alveolar airspaces. This increased leukocyte influx was accompanied by decreased alveolarization and angiogenesis and increased pulmonary vascular remodeling and pulmonary hypertension (PH), the pathological hallmarks of BPD. However, administration of LA1 decreased macrophage infiltration in the lungs during hyperoxia. Furthermore, treatment with LA1 improved alveolarization and angiogenesis and decreased pulmonary vascular remodeling and PH. These data indicate that leukocyte recruitment plays an important role in the experimental model of BPD induced by hyperoxia. Targeting leukocyte trafficking using LA1, an integrin agonist, is beneficial in preventing lung inflammation and protecting alveolar and vascular structures during hyperoxia. Thus, targeting integrin-mediated leukocyte recruitment and inflammation may provide a novel strategy in preventing and treating BPD in preterm infants.
The complement receptor 3 (CD11b/CD18) agonist Leukadherin-1 suppresses human innate inflammatory signalling.[Pubmed:27118513]
Clin Exp Immunol. 2016 Sep;185(3):361-71.
Complement receptor 3 (CR3, CD11b/CD18) is a multi-functional receptor expressed predominantly on myeloid and natural killer (NK) cells. The R77H variant of CD11b, encoded by the ITGAM rs1143679 polymorphism, is associated robustly with development of the autoimmune disease systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) and impairs CR3 function, including its regulatory role on monocyte immune signalling. The role of CR3 in NK cell function is unknown. Leukadherin-1 is a specific small-molecule CR3 agonist that has shown therapeutic promise in animal models of vascular injury and inflammation. We show that Leukadherin-1 pretreatment reduces secretion of interferon (IFN)-gamma, tumour necrosis factor (TNF) and macrophage inflammatory protein (MIP)-1beta by monokine-stimulated NK cells. It was associated with a reduction in phosphorylated signal transducer and activator of transcription (pSTAT)-5 following interleukin (IL)-12 + IL-15 stimulation (P < 0.02) and increased IL-10 secretion following IL-12 + IL-18 stimulation (P < 0.001). Leukadherin-1 pretreatment also reduces secretion of IL-1beta, IL-6 and TNF by Toll-like receptor (TLR)-2 and TLR-7/8-stimulated monocytes (P < 0.01 for all). The R77H variant did not affect NK cell response to Leukadherin-1 using ex-vivo cells from homozygous donors; nor did the variant influence CR3 expression by these cell types, in contrast to a recent report. These data extend our understanding of CR3 biology by demonstrating that activation potently modifies innate immune inflammatory signalling, including a previously undocumented role in NK cell function. We discuss the potential relevance of this to the pathogenesis of SLE. Leukadherin-1 appears to mediate its anti-inflammatory effect irrespective of the SLE-risk genotype of CR3, providing further evidence to support its evaluation of Leukadherin-1 as a potential therapeutic for autoimmune disease.
Complement receptor 3 influences toll-like receptor 7/8-dependent inflammation: implications for autoimmune diseases characterized by antibody reactivity to ribonucleoproteins.[Pubmed:23386618]
J Biol Chem. 2013 Mar 29;288(13):9077-83.
Toll-like receptor (TLR) signaling is an important component in the inflammatory response generated in diseases characterized by autoantibody reactivity to proteins such as SSA/Ro in complex with endogenous nucleic acids. Complement receptor 3 (CR3), a genetic variant of which has been identified as a risk factor in systemic lupus erythematosus, has been shown to induce tolerogenic responses in dendritic cells and suppress TLR4 responses in a murine sepsis model. Accordingly, this study addressed the hypothesis that activation of CR3, influenced by genotype of CD11b, negatively regulates TLR7/8-dependent effector function. Allosteric activation of CD11b via pretreatment with the small molecule, leukadhedrin 1 (LA1), significantly attenuated TLR7/8-induced (hY3 RNA, R848) secretion of TNFalpha in THP-1 cells and human macrophages isolated from donors homozygous for the ancestral common ITGAM allele at rs1143679. This inhibition was accompanied by profound degradation of the adaptor protein MyD88, an effect not observed with direct inhibition of TLR ligation by an antagonist oligonucleotide. In contrast, the addition of LA1 after incubation with the TLR agonists did not result in MyD88 degradation and subsequent attenuation of TNFalpha secretion. In TLR7/8-stimulated macrophages isolated from donors heterozygous for the CD11b variant, pretreatment with LA1 did not down-regulate TNFalpha release. These novel findings support a negative cross-talk between CR3 and TLR pathways likely to be induced by antibodies reactive with ribonucleoproteins and point to the development of CR3-specific agonists as potential therapeutics for diseases such as neonatal lupus.
Small molecule-mediated activation of the integrin CD11b/CD18 reduces inflammatory disease.[Pubmed:21900205]
Sci Signal. 2011 Sep 6;4(189):ra57.
The integrin CD11b/CD18 (also known as Mac-1), which is a heterodimer of the alpha(M) (CD11b) and beta(2) (CD18) subunits, is critical for leukocyte adhesion and migration and for immune functions. Blocking integrin-mediated leukocyte adhesion, although beneficial in experimental models, has had limited success in treating inflammatory diseases in humans. Here, we used an alternative strategy of inhibiting leukocyte recruitment by activating CD11b/CD18 with small-molecule agonists, which we term leukadherins. These compounds increased the extent of CD11b/CD18-dependent cell adhesion of transfected cells and of primary human and mouse neutrophils, which resulted in decreased chemotaxis and transendothelial migration. Leukadherins also decreased leukocyte recruitment and reduced arterial narrowing after injury in rats. Moreover, compared to a known integrin antagonist, leukadherins better preserved kidney function in a mouse model of experimental nephritis. Leukadherins inhibited leukocyte recruitment by increasing leukocyte adhesion to the inflamed endothelium, which was reversed with a blocking antibody. Thus, we propose that pharmacological activation of CD11b/CD18 offers an alternative therapeutic approach for inflammatory diseases.


