1-PhenyloctaneCAS# 2189-60-8 |
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 2189-60-8 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 16607 | Appearance | Oil |
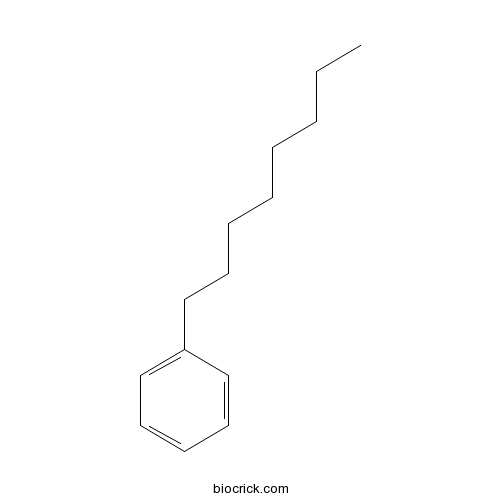
| Formula | C14H22 | M.Wt | 190.32 |
| Type of Compound | Miscellaneous | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | Soluble in Chloroform,Dichloromethane,Ethyl Acetate,DMSO,Acetone,etc. | ||
| Chemical Name | octylbenzene | ||
| SMILES | CCCCCCCCC1=CC=CC=C1 | ||
| Standard InChIKey | CDKDZKXSXLNROY-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | 1-Phenyloctane, 1-phenyldecane, 1-methylnaphthalene, and 2-methylnaphthalene, are four potential laser-induced fluorescence (LIF) tracers for diesel engine applications. |
| In vitro | Characterization of four potential laser-induced fluorescence tracers for diesel engine applications.[Pubmed: 24513750]Appl Opt. 2013 Nov 20;52(33):8001-7.
|
| Structure Identification | Chem Commun (Camb). 2014 Sep 18;50(72):10456-9.Comparative STM studies of mixed ligand monolayers on gold nanoparticles in air and in 1-phenyloctane.[Pubmed: 25068154]Scanning tunnelling microscopy (STM) studies have found stripe-like domains on gold nanoparticles (NPs) coated with certain binary mixtures of ligand molecules. The majority of these NPs' properties have been investigated for particles in solvents. Yet, most STM studies are for NPs in a dry state. Images of the same particles in air and liquid have not been obtained yet. Chirality. 2012 Feb;24(2):155-66.Organization of the enantiomeric and racemic forms of an amphiphilic resorcinol derivative at the air-water and graphite-1-phenyloctane interfaces.[Pubmed: 22180286]This article describes a study of the outcome of racemate condensation in different types of monolayers. |

1-Phenyloctane Dilution Calculator

1-Phenyloctane Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 5.2543 mL | 26.2715 mL | 52.5431 mL | 105.0862 mL | 131.3577 mL |
| 5 mM | 1.0509 mL | 5.2543 mL | 10.5086 mL | 21.0172 mL | 26.2715 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.5254 mL | 2.6272 mL | 5.2543 mL | 10.5086 mL | 13.1358 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.1051 mL | 0.5254 mL | 1.0509 mL | 2.1017 mL | 2.6272 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0525 mL | 0.2627 mL | 0.5254 mL | 1.0509 mL | 1.3136 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- Boc-Orn-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3427
CAS No.:21887-64-9
- Horminone
Catalog No.:BCN4936
CAS No.:21887-01-4
- Lycorine chloride
Catalog No.:BCN1220
CAS No.:2188-68-3
- Boc-Arg(NO2)-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3065
CAS No.:2188-18-3
- 12-Hydroxyisodrimenin
Catalog No.:BCN4935
CAS No.:218780-16-6
- Boc- ß-HoIle-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3236
CAS No.:218608-82-3
- Bardoxolone methyl
Catalog No.:BCC1400
CAS No.:218600-53-4
- Bardoxolone
Catalog No.:BCC1399
CAS No.:218600-44-3
- Falcarinol
Catalog No.:BCN3938
CAS No.:21852-80-2
- Octahydroisoindole
Catalog No.:BCN2275
CAS No.:21850-12-4
- BDNF (human)
Catalog No.:BCC5944
CAS No.:218441-99-7
- Macrocarpal K
Catalog No.:BCN4934
CAS No.:218290-59-6
- Taraxeryl acetate
Catalog No.:BCN4937
CAS No.:2189-80-2
- Ciwujiatone
Catalog No.:BCN7598
CAS No.:218901-26-9
- Euphorbia factor L2
Catalog No.:BCN3783
CAS No.:218916-51-9
- 5,15-Diacetyl-3-benzoyllathyrol
Catalog No.:BCN1196
CAS No.:218916-52-0
- Euphorbia factor L8
Catalog No.:BCN3785
CAS No.:218916-53-1
- KNK437
Catalog No.:BCC6399
CAS No.:218924-25-5
- Z-Trp(Boc)-OH.DCHA
Catalog No.:BCC2749
CAS No.:218938-57-9
- Boc-ß-HoGlu(OBzl)-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3233
CAS No.:218943-30-7
- 2,3-Dihydro-3-methoxywithaferin A
Catalog No.:BCN7943
CAS No.:21902-96-5
- 3'-Methoxydaidzein
Catalog No.:BCN4082
CAS No.:21913-98-4
- Ac-YVAD-AFC
Catalog No.:BCC4022
CAS No.:219137-85-6
- Hydroxyzine 2HCl
Catalog No.:BCC4519
CAS No.:2192-20-3
Characterization of four potential laser-induced fluorescence tracers for diesel engine applications.[Pubmed:24513750]
Appl Opt. 2013 Nov 20;52(33):8001-7.
Four potential laser-induced fluorescence (LIF) tracers, 1-Phenyloctane, 1-phenyldecane, 1-methylnaphthalene, and 2-methylnaphthalene, are characterized for diesel engine applications. These tracers, embedded in the diesel primary reference fuels n-C(1)(6)H(3)(4) and iso-C(1)(6)H(3)(4), match the relevant physical properties of commercial diesel fuel much better than the commonly used toluene/iso-octane/n-heptane tracer-fuel system does. The temperature and pressure dependencies of the fluorescence intensities and spectra were measured in a flow cell in nitrogen for each candidate tracer molecule. The results show that the signal intensities of the methylnaphthalenes are about two orders of magnitude higher than for 1-Phenyloctane and 1-phenyldecane and show a strong temperature but no pressure, dependence. An analysis of the fluorescence spectrum of 1-methylnaphthalene shows that it also can be used for two-color detection LIF thermometry by choosing appropriate optical filters.
Comparative STM studies of mixed ligand monolayers on gold nanoparticles in air and in 1-phenyloctane.[Pubmed:25068154]
Chem Commun (Camb). 2014 Sep 18;50(72):10456-9.
Scanning tunnelling microscopy (STM) studies have found stripe-like domains on gold nanoparticles (NPs) coated with certain binary mixtures of ligand molecules. The majority of these NPs' properties have been investigated for particles in solvents. Yet, most STM studies are for NPs in a dry state. Images of the same particles in air and liquid have not been obtained yet. In this work, a judicious choice of ligand molecules led to NPs with close-to-ideal STM imaging conditions in air and in 1-Phenyloctane (PO). Large datasets under both conditions were acquired and rapidly evaluated through power spectral density (PSD) analysis. The result is a quantitative comparison of stripe-like domains in air and PO on the same NPs. PSD analysis determines a characteristic length-scale for these domains of ~1.0 nm in air and in PO showing persistence of striped domains in these two media. A length scale of ~0.7 nm for homoligand NPs was found.
Organization of the enantiomeric and racemic forms of an amphiphilic resorcinol derivative at the air-water and graphite-1-phenyloctane interfaces.[Pubmed:22180286]
Chirality. 2012 Feb;24(2):155-66.
This article describes a study of the outcome of racemate condensation in different types of monolayers. The study was performed on a resorcinol surfactant bearing an octadecyl chain and a lactate group which formed a monolayer at the interface of graphite and 1-Phenyloctane as well as a Langmuir film at the air-water interface. Control experiments with the enantiopure materials provided the characteristics of the chiral organizations. The results obtained on the racemate show that on graphite the molecule forms chiral domains, indicating that spontaneous resolution takes place at the surface, a phenomenon that has been rationalized using molecular modeling. The X-ray crystal structure of the DMSO solvate of one of the enantiomers shows a similar type of packing to this monolayer. On the other hand, in the Langmuir layer it appears that the formation of a racemic compound is favoured, as it is in the solid state in three dimensions. The work shows how the symmetry restrictions in different environments can have a critical influence on the outcome of racemate organization, and underline the tendency of graphite to favour symmetry breaking in monolayers formed at its surface.


