KNK437stress-induced HSP synthesis inhibitor CAS# 218924-25-5 |
- KN-92 hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC1681
CAS No.:1431698-47-3
- A-317491
Catalog No.:BCC1320
CAS No.:475205-49-3
- Ivermectin
Catalog No.:BCC1251
CAS No.:70288-86-7
- A 438079 hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC1317
CAS No.:899431-18-6
- A 438079
Catalog No.:BCC1316
CAS No.:899507-36-9
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 218924-25-5 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 46195007 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C13H11NO4 | M.Wt | 245.23 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | DMSO : ≥ 34 mg/mL (138.65 mM) *"≥" means soluble, but saturation unknown. | ||
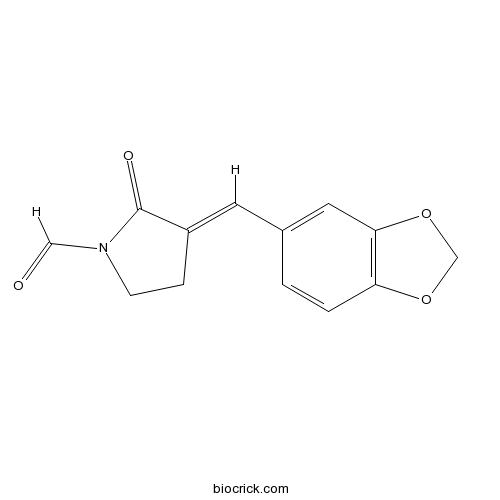
| Chemical Name | (3E)-3-(1,3-benzodioxol-5-ylmethylidene)-2-oxopyrrolidine-1-carbaldehyde | ||
| SMILES | C1CN(C(=O)C1=CC2=CC3=C(C=C2)OCO3)C=O | ||
| Standard InChIKey | LZGGUFLRKIMBDQ-BJMVGYQFSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C13H11NO4/c15-7-14-4-3-10(13(14)16)5-9-1-2-11-12(6-9)18-8-17-11/h1-2,5-7H,3-4,8H2/b10-5+ | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | KNK437 is a HSP inhibitor, and inhibits the induction of HSP105, HSP70, and HSP40.In Vitro:KNK437 inhibits the activation of several HSPs including HSP105, HSP70, and HSP40 in COLO 320DM (human colon carcinoma) cells. KNK437 (100 μM) inhibits thermotolerance in COLO 320DM cells after the first heat treatment. KNK437 shows inhibitory effects on thermotolerance dose-dependently in COLO 320DM cells (0-200 μM) and HeLa S3 cells (100, 200 μM)[1]. KNK437 (100 μM) exhibits inhibitory activities against the methylation of H3-Lys4 before or after heat-treatment in HSC4 cells and KB cells, but does not affect that of H3 Lys9. KNK437 also suppresses the expression of HSP70[3].In Vivo:KNK437 is a weakly toxic agent. KNK437 (62.5-400 mg/kg) recovers bodyweight losses of tumor-free CD-1 (ICR) mice. KNK437 (200 mg/kg) alone shows no antitumor effects and does not increase the thermosensitivity of nontolerant tumors. KNK437 improves the antitumor effects of fractionated heat treatment at 44°C at 200 mg/kg in a synergistic manner. KNK437 (200 mg/kg, i.p.) suppresses the induction of thermotolerance when administrated 6 h before the initial heating[2]. References: | |||||

KNK437 Dilution Calculator

KNK437 Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 4.0778 mL | 20.389 mL | 40.778 mL | 81.5561 mL | 101.9451 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.8156 mL | 4.0778 mL | 8.1556 mL | 16.3112 mL | 20.389 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.4078 mL | 2.0389 mL | 4.0778 mL | 8.1556 mL | 10.1945 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0816 mL | 0.4078 mL | 0.8156 mL | 1.6311 mL | 2.0389 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0408 mL | 0.2039 mL | 0.4078 mL | 0.8156 mL | 1.0195 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
KNK437 is a benzylidene lactam compound that inhibits stress-induced HSPs (heat shock proteins) synthesis.
HSPs (heat shock proteins) are chaperones that their expressions are increased under various cellular stresses including temperature rise. It plays a vital role in regulating protein folding and associated with cancer and cardiovascular diseases.
KNK437 inhibits the acquisition of thermotolerance and the induction of various HSPs in human colon carcinoma cells (COLO 320DM) in a dose-dependent manner. KNK437 also blocks the acquisition of thermotolerance that developed by sodium arsenite. [1]
KNK437 exerts low toxicity in vivo. In C3H/He mice transplanted with SCC VII cells, the concentration of KNK437 in the tumors gradually increases and reaches a peak 6 hours after i.p. injection. Hsp72 were synthesized 8 h after hyperthermia at 44 oC for 10 minutes, and their synthesis is inhibited by administration of KNK437 6 hours before hyperthermia. [2]
References:
1. Yokota S, Kitahara M, Nagata K. Benzylidene lactam compound, KNK437, a novel
inhibitor of acquisition of thermotolerance and heat shock protein induction in
human colon carcinoma cells. Cancer Res. 2000 Jun 1;60(11):2942-8.
2. Koishi M, Yokota S, Mae T et al. The effects of KNK437, a novel inhibitor of heat shock protein
synthesis, on the acquisition of thermotolerance in a murine transplantable tumor in vivo. Clin Cancer Res. 2001 Jan;7(1):215-9.
- Euphorbia factor L8
Catalog No.:BCN3785
CAS No.:218916-53-1
- 5,15-Diacetyl-3-benzoyllathyrol
Catalog No.:BCN1196
CAS No.:218916-52-0
- Euphorbia factor L2
Catalog No.:BCN3783
CAS No.:218916-51-9
- Ciwujiatone
Catalog No.:BCN7598
CAS No.:218901-26-9
- Taraxeryl acetate
Catalog No.:BCN4937
CAS No.:2189-80-2
- 1-Phenyloctane
Catalog No.:BCN2227
CAS No.:2189-60-8
- Boc-Orn-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3427
CAS No.:21887-64-9
- Horminone
Catalog No.:BCN4936
CAS No.:21887-01-4
- Lycorine chloride
Catalog No.:BCN1220
CAS No.:2188-68-3
- Boc-Arg(NO2)-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3065
CAS No.:2188-18-3
- 12-Hydroxyisodrimenin
Catalog No.:BCN4935
CAS No.:218780-16-6
- Boc- ß-HoIle-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3236
CAS No.:218608-82-3
- Z-Trp(Boc)-OH.DCHA
Catalog No.:BCC2749
CAS No.:218938-57-9
- Boc-ß-HoGlu(OBzl)-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3233
CAS No.:218943-30-7
- 2,3-Dihydro-3-methoxywithaferin A
Catalog No.:BCN7943
CAS No.:21902-96-5
- 3'-Methoxydaidzein
Catalog No.:BCN4082
CAS No.:21913-98-4
- Ac-YVAD-AFC
Catalog No.:BCC4022
CAS No.:219137-85-6
- Hydroxyzine 2HCl
Catalog No.:BCC4519
CAS No.:2192-20-3
- 2-Hydroxy-3,4,5,6-tetramethoxychalcone
Catalog No.:BCN1489
CAS No.:219298-74-5
- H-ß-HoIle-OH.HCl
Catalog No.:BCC3235
CAS No.:219310-10-8
- Boc-Nle-OH.DCHA
Catalog No.:BCC3297
CAS No.:21947-32-0
- trans-Cinnamic anhydride
Catalog No.:BCN7914
CAS No.:21947-71-7
- Boc-Cys(Trt)-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3380
CAS No.:21947-98-8
- Littorine
Catalog No.:BCN1917
CAS No.:21956-47-8
KNK437, a benzylidene lactam compound, sensitises prostate cancer cells to the apoptotic effect of hyperthermia.[Pubmed:21204621]
Int J Hyperthermia. 2011;27(1):63-73.
Hyperthermia is known to serve as a powerful tool in the treatment of prostate cancer which is commonly diagnosed in men. Quercetin and KNK437, Hsp70 inhibitors, play an important role in blocking thermotolerance in some cancer cells. In the present study we investigated the effects of KNK437 and quercetin on the acquisition of thermotolerance and heat-induced apoptosis. Also, it was examined whether the possible mechanism triggering apoptotic pathway included caspase-3 activation in prostate cancer cells. For this purpose, PC-3 and LNCaP cells were treated with hyperthermia following pretreatment with or without KNK437 or quercetin. Thermotolerance was investigated by colony formation assay in these cells, while Hsp70 mRNA levels were measured by real time RT-PCR. Sandwich ELISA was used for detection of Hsp70 protein levels. Apoptosis was detected by flow cytometric annexin V binding assay and by western blot analysis of procaspase-3 and cleaved poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase levels. In our study, KNK437 and quercetin inhibited thermotolerance in a dose-dependent manner in PC-3 cells. KNK437 and quercetin decreased heat-induced accumulation of Hsp70 mRNA and protein in PC-3 and LNCaP cells. KNK437 and quercetin pretreatment enhanced the apoptotic effect of hyperthermia in both cells. We found that KNK437 was more effective than quercetin in inducing apoptotic cell death, activation of caspase-3, and cleavage of PARP in prostate cancer cells. We suggest that KNK437 is a useful agent for enhancing the efficiency of hyperthermic therapy which has less toxic side-effects in prostate cancer.
KNK437 downregulates heat shock protein 27 of pancreatic cancer cells and enhances the cytotoxic effect of gemcitabine.[Pubmed:21124027]
Chemotherapy. 2011;57(1):12-6.
BACKGROUND: Our previous proteomic study demonstrated that expression of heat shock protein 27 (HSP27) is upregulated in gemcitabine (GEM)-resistant pancreatic cancer cells and that it suppressed the cytotoxic effect of GEM on the cells. This report describes the benefits of a treatment strategy combining the HSP inhibitor KNK437 with GEM for GEM-resistant pancreatic cancer cells. METHODS: We used 2 human pancreatic cancer cell lines, GEM-sensitive KLM1 and GEM-resistant KLM1-R. KLM1-R was treated with KNK437, and we examined the expression of HSP27 by Western blotting. The cytotoxicity of GEM and KNK437 for KLM1-R was investigated by 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-5-(3-carboxymethoxyphenyl)-2-(4-sulfophenyl)-2H-tetr azolium assay. RESULTS: The expression of HSP27 in KLM1-R was dramatically reduced by KNK437. In addition, the in vitro antitumor cytotoxic effect of GEM on KLM1-R was enhanced by combination treatment with KNK437 compared to GEM alone. CONCLUSION: This study supports the potential therapeutic benefits of a treatment strategy combining KNK437 with GEM.
KNK437, abrogates hypoxia-induced radioresistance by dual targeting of the AKT and HIF-1alpha survival pathways.[Pubmed:22521642]
Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2012 May 11;421(3):538-43.
KNK437 is a benzylidene lactam compound known to inhibit stress-induced synthesis of heat shock proteins (HSPs). HSPs promote radioresistance and play a major role in stabilizing hypoxia inducible factor-1alpha (HIF-1alpha). HIF-1alpha is widely responsible for tumor resistance to radiation under hypoxic conditions. We hypothesized that KNK437 sensitizes cancer cells to radiation and overrides hypoxia-induced radioresistance via destabilizing HIF-1alpha. Treatment of human cancer cells MDA-MB-231 and T98G with KNK437 sensitized them to ionizing radiation (IR). Surprisingly, IR did not induce HSPs in these cell lines. As hypothesized, KNK437 abrogated the accumulation of HIF-1alpha in hypoxic cells. However, there was no induction of HSPs under hypoxic conditions. Moreover, the proteosome inhibitor MG132 did not restore HIF-1alpha levels in KNK437-treated cells. This suggested that the absence of HIF-1alpha in hypoxic cells was not due to the enhanced protein degradation. HIF-1alpha is mainly regulated at the level of post-transcription and AKT is known to modulate the translation of HIF-1alpha mRNA. Interestingly, pre-treatment of cells with KNK437 inhibited AKT signaling. Furthermore, down regulation of AKT by siRNA abrogated HIF-1alpha levels under hypoxia. Interestingly, KNK437 reduced cell survival in hypoxic conditions and inhibited hypoxia-induced resistance to radiation. Taken together, these data suggest that KNK437 is an effective radiosensitizer that targets multiple pro-survival stress response pathways.
An in vitro model to consider the effect of 2 mM glutamine and KNK437 on endotoxin-stimulated release of heat shock protein 70 and inflammatory mediators.[Pubmed:26706024]
Nutrition. 2016 Mar;32(3):375-83.
OBJECTIVE: Glutamine has been shown to promote the release of heat shock protein 70 (HSP70) both within experimental in vitro models of sepsis and in adults with septic shock. This study aimed to investigate the effects of 2 mM glutamine and an inhibitor of HSP70 (KNK437) on the release of HSP70 and inflammatory mediators in healthy adult volunteers. METHODS: An in vitro whole blood endotoxin stimulation assay was used. RESULTS: The addition of 2 mM glutamine significantly increased HSP70 levels over time (P < 0.05). HSP70 release had a positive correlation at 4 h with IL-1 beta (r = 0.51, P = 0.03) and an inverse correlation with TNF-alpha (r = -0.56, P = 0.02) and IL-8 levels (r = -0.52, P = 0.03), and there were no significant correlations between HSP70 and IL6 or IL-10 or glutamine. Glutamine supplementation significantly (P < 0.05) attenuated the release of IL-10 at 4 h and IL-8 at 24 h, compared with conditions without glutamine. In endotoxin-stimulated blood there were no significant differences in the release of IL-6, TNF-alpha, and IL-1 beta with glutamine supplementation at 4 and 24 h. However, glutamine supplementation (2 mM) appeared to attenuate the release of inflammatory mediators (IL-1 beta, IL-6, TNF-alpha), although this effect was not statistically significant. The addition of KNK437, a HSP70 inhibitor, significantly diminished HSP70 release, which resulted in lower levels of inflammatory mediators (P < 0.05). CONCLUSION: Glutamine supplementation promotes HSP70 release in an experimental model of sepsis. After the addition of KNK437, the effects of glutamine on HSP70 and inflammatory mediator release appear to be lost, suggesting that HSP70 in part orchestrates the inflammatory mediator response to sepsis. The clinical implications require further investigation.


