3-n-ButylphthalideCAS# 6066-49-5 |
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 6066-49-5 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 61361 | Appearance | Oil |
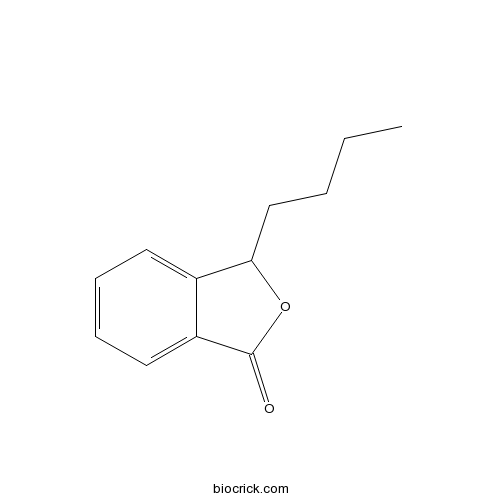
| Formula | C12H14O2 | M.Wt | 190.24 |
| Type of Compound | Miscellaneous | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Synonyms | 3-n-Butylphthalide; 3-Butylphthalide | ||
| Solubility | DMSO : ≥ 56 mg/mL (294.37 mM) *"≥" means soluble, but saturation unknown. | ||
| Chemical Name | 3-butyl-3H-2-benzofuran-1-one | ||
| SMILES | CCCCC1C2=CC=CC=C2C(=O)O1 | ||
| Standard InChIKey | HJXMNVQARNZTEE-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Dl-3-n-Butylphthalide has antihypertensive effects, may slow the progression of hypertensive nephropathy by a variety of mechanisms.3-n-Butylphthalide is effective for improving cognitive and global functioning in patients with subcortical VCIND and exhibits good safety, this effect might be mediated by preventing the decline of the central cholinergic system. |
| Targets | Bcl-2/Bax | Caspase | HO-1 | IkB | Nrf2 | p65 | NF-kB | TGF-β/Smad | IKK |
| In vitro | Bioactivation of 3-n-butylphthalide via sulfation of its major metabolite 3-hydroxy-NBP: mediated mainly by sulfotransferase 1A1.[Pubmed: 24468743]Drug Metab Dispos. 2014 Apr;42(4):774-81.3-n-Butylphthalide (NBP) [(±)-3-butyl-1(3H)-isobenzofuranone] is an anti-cerebral-ischemia drug. Moderate hepatotoxicity has been observed in clinical applications. One of the major metabolites, 3-N-acetylcysteine-3-n-Butylphthalide, has been detected in human urine, indicating the formation of a reactive metabolite. |
| In vivo | The effects of DL-3-n-butylphthalide in patients with vascular cognitive impairment no dementia caused by subcortical ischemic small vessel disease: A multicentre, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial.[Pubmed: 26086183]Alzheimers Dement. 2015 Jun 15.Vascular cognitive impairment without dementia is very common among the aged and tends to progress to dementia, but there have been no proper large-scale intervention trials dedicated to it. Vascular cognitive impairment without dementia caused by subcortical ischemic small vessel disease (hereinafter, subcortical Vascular cognitive impairment without dementia) represents a relatively homogeneous disease process and is a suitable target for therapeutic trials investigating Vascular cognitive impairment without dementia. Preclinical trials showed that dl-3-n-Butylphthalide (NBP) is effective for cognitive impairment of vascular origin.
The edaravone and 3-n-butylphthalide ring-opening derivative 10b effectively attenuates cerebral ischemia injury in rats.[Pubmed: 26073328]Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2015 Jun 15. Compound 10b is a hybrid molecule of edaravone and a ring-opening derivative of 3-n-Butylphthalide (NBP). The aim of this study was to examine the effects of compound 10b on brain damage in rats after focal cerebral ischemia. |
| Animal Research | Improvement of cognitive deficits in SAMP8 mice by 3-n-butylphthalide.[Pubmed: 24512016]Protective effect of 3-n-butylphthalide against hypertensive nephropathy in spontaneously hypertensive rats.[Pubmed: 25352064]Mol Med Rep. 2015 Feb;11(2):1448-54.Previous studies have demonstrated that a natural product of celery seeds, 3‑n‑butylphthalide (NBP), has significant antihypertensive effects that are widely utilized in Chinese traditional medicine. Neurol Res. 2014 Mar;36(3):224-33.The herbal extract 3-n-Butylphthalide (NBP) is used in clinical practice for ischemic patients in China. It has been shown to have various neuroprotective effects both in vitro and in vivo. |

3-n-Butylphthalide Dilution Calculator

3-n-Butylphthalide Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 5.2565 mL | 26.2826 mL | 52.5652 mL | 105.1304 mL | 131.413 mL |
| 5 mM | 1.0513 mL | 5.2565 mL | 10.513 mL | 21.0261 mL | 26.2826 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.5257 mL | 2.6283 mL | 5.2565 mL | 10.513 mL | 13.1413 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.1051 mL | 0.5257 mL | 1.0513 mL | 2.1026 mL | 2.6283 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0526 mL | 0.2628 mL | 0.5257 mL | 1.0513 mL | 1.3141 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
Butylphthalide(3-n-Butylphthalide) is an anti-cerebral-ischemia drug; first isolated from the seeds of celery, showed efficacy in animal models of stroke. IC50 value: Target: 3-n-butylphthalide alleviates oxidative stress caused by chronic cerebral ischemia, improves cholinergic function, and inhibits amyloid beta accumulation, thereby improving cerebral neuronal injury and cognitive deficits [2]. Intragastric NBP administration to 4-month-old SAMP8 mice for 2 months significantly improved spatial learning and memory ability. Moreover, the loss of choline acetyltransferase (ChAT)-positive neurons in the medial septal nucleus and the vertical limb of the diagonal band in SAMP8 mice was slowed down, as was the decline in the protein and mRNA expression of ChAT in the hippocampus, cerebral cortex, and forebrain [4].
References:
[1]. Cui LY, et al. Ninety-day administration of dl-3-n-butylphthalide for acute ischemic stroke: a randomized, double-blind trial. Chin Med J (Engl). 2013;126(18):3405-10.
[2]. Zhao W, et al. 3-N-butylphthalide improves neuronal morphology after chronic cerebral ischemia. Neural Regen Res. 2014 Apr 1;9(7):719-26.
[3]. Wang X, et al. Design, synthesis and biological evaluation of hydrogen sulfide releasing derivatives of 3-n-butylphthalide as potential antiplatelet and antithrombotic agents. Org Biomol Chem. 2014 Aug 21;12(31):5995-6004.
[4]. Wang F, et al. Improvement of cognitive deficits in SAMP8 mice by 3-n-butylphthalide. Neurol Res. 2014 Mar;36(3):224-33.
- Dihydromollugin
Catalog No.:BCN8247
CAS No.:60657-93-4
- Danaidone
Catalog No.:BCN1966
CAS No.:6064-85-3
- Bifonazole
Catalog No.:BCC4766
CAS No.:60628-96-8
- MEK162 (ARRY-162, ARRY-438162)
Catalog No.:BCC1148
CAS No.:606143-89-9
- AZD6244 (Selumetinib)
Catalog No.:BCC3624
CAS No.:606143-52-6
- Momor-cerebroside I
Catalog No.:BCN4120
CAS No.:606125-07-9
- MK-0773
Catalog No.:BCC1754
CAS No.:606101-58-0
- Homopterocarpin
Catalog No.:BCN4615
CAS No.:606-91-7
- Cinnabarinic acid
Catalog No.:BCC7865
CAS No.:606-59-7
- Toyocamycin
Catalog No.:BCC8047
CAS No.:606-58-6
- 2,4'-Dihydroxybenzophenone
Catalog No.:BCN3358
CAS No.:606-12-2
- Pamabrom
Catalog No.:BCC1835
CAS No.:606-04-2
- HOSu
Catalog No.:BCC2845
CAS No.:6066-82-6
- Isopicropodophyllone
Catalog No.:BCN8316
CAS No.:60660-50-6
- 3-Hydroxy-1,5-diphenyl-1-pentanone
Catalog No.:BCN3536
CAS No.:60669-64-9
- FC 131
Catalog No.:BCC7917
CAS No.:606968-52-9
- Sesamin
Catalog No.:BCN4123
CAS No.:607-80-7
- Myristicin
Catalog No.:BCN2730
CAS No.:607-91-0
- Physoperuvine
Catalog No.:BCN1402
CAS No.:60723-27-5
- SB 772077B dihydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC6116
CAS No.:607373-46-6
- AZ 10606120 dihydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC6005
CAS No.:607378-18-7
- Canthin-6-one N-oxide
Catalog No.:BCN2992
CAS No.:60755-87-5
- 2-Hydroxy-1,8-cineole
Catalog No.:BCN4121
CAS No.:60761-00-4
- ent-Kauran-17,19-dioic acid
Catalog No.:BCN4122
CAS No.:60761-79-7
The edaravone and 3-n-butylphthalide ring-opening derivative 10b effectively attenuates cerebral ischemia injury in rats.[Pubmed:26073328]
Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2015 Aug;36(8):917-27.
AIM: Compound 10b is a hybrid molecule of edaravone and a ring-opening derivative of 3-n-Butylphthalide (NBP). The aim of this study was to examine the effects of compound 10b on brain damage in rats after focal cerebral ischemia. METHODS: SD rats were subjected to 2-h-middle cerebral artery occlusion (MCAO). At the onset of reperfusion, the rats were orally treated with NBP (60 mg/kg), edaravone (3 mg/kg), NBP (60 mg/kg)+edaravone (3 mg/kg), or compound 10b (70, 140 mg/kg). The infarct volume, motor behavior deficits, brain water content, histopathological alterations, and activity of GSH, SOD, and MDA were analyzed 24 h after reperfusion. The levels of relevant proteins in the ipsilateral striatum were examined using immunoblotting. RESULTS: Administration of compound 10b (70 or 140 mg/kg) significantly reduced the infarct volume and neurological deficits in MCAO rats. The neuroprotective effects of compound 10b were more pronounced compared to NBP, edaravone or NBP+edaravone. Furthermore, compound 10b significantly upregulated the protein levels of the cytoprotective molecules Bcl-2, HO-1, Nrf2, Trx, P-NF-kappaB p65, and IkappaB-alpha, while decreasing the expression of Bax, caspase 3, caspase 9, Txnip, NF-kappaB p65, and P-IkappaB-alpha. CONCLUSION: Oral administration of compound 10b effectively attenuates rat cerebral ischemia injury.
Protective effect of 3-n-butylphthalide against hypertensive nephropathy in spontaneously hypertensive rats.[Pubmed:25352064]
Mol Med Rep. 2015 Feb;11(2):1448-54.
Previous studies have demonstrated that a natural product of celery seeds, 3nbutylphthalide (NBP), has significant antihypertensive effects that are widely utilized in Chinese traditional medicine. The present study aimed to investigate the effects of NBP on hypertensive nephropathy, as well as the mechanisms underlying this disease in spontaneously hypertensive rats (SHRs). SHRs were treated orally with saline, NBP (15 or 30 mg/kg) or losartan (10 mg/kg) daily for 20 weeks, during which time blood pressure was measured every four weeks. At the end of the 20week treatment, blood and urine samples were collected for biochemical analysis, and kidney tissues were obtained for histopathological analysis and immunohistochemistry. Enzymelinked immunosorbent assays and western blotting were used to analyze the expression of transforming growth factor (TGF)beta1 in blood and kidney tissues, respectively. The results showed that NBP effectively attenuated progression of hypertensive nephropathy by decreasing urinary albumin excretion and blood urea nitrogen levels. It significantly decreased blood pressure (although less markedly than losartan) and the incidence of glomerulosclerosis. In addition, it alleviated tubular impairment and significantly decreased oxidative stress, as well as the expression of proinflammatory cytokines and TGF-beta1 in kidney tissues. In conclusion, the results suggested that NBP may slow the progression of hypertensive nephropathy by a variety of mechanisms.
The effects of DL-3-n-butylphthalide in patients with vascular cognitive impairment without dementia caused by subcortical ischemic small vessel disease: A multicentre, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial.[Pubmed:26086183]
Alzheimers Dement. 2016 Feb;12(2):89-99.
INTRODUCTION: Vascular cognitive impairment without dementia is very common among the aged and tends to progress to dementia, but there have been no proper large-scale intervention trials dedicated to it. Vascular cognitive impairment without dementia caused by subcortical ischemic small vessel disease (hereinafter, subcortical Vascular cognitive impairment without dementia) represents a relatively homogeneous disease process and is a suitable target for therapeutic trials investigating Vascular cognitive impairment without dementia. Preclinical trials showed that dl-3-n-Butylphthalide (NBP) is effective for cognitive impairment of vascular origin. METHODS: In this randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial, we enrolled patients aged 50-70 years who had a diagnosis of subcortical Vascular cognitive impairment without dementia at 15 academic medical centers in China. Inclusion criteria included a clinical dementia rating >/=0.5 on at least one domain and global score /=20 (primary school) or >/=24 (junior school or above); and brain magnetic resonance imaging consistent with subcortical ischemic small vessel disease. Patients were randomly assigned to NBP 200 mg three times daily or matched placebo (1:1) for 24 weeks according to a computer-generated randomization protocol. All patients and study personnel were masked to treatment assignment. Primary outcome measures were the changes in Alzheimer's disease assessment scale-cognitive subscale (ADAS-cog) and clinician's interview-based impression of change plus caregiver input (CIBIC-plus) after 24 weeks. All patients were monitored for adverse events (AEs). Outcome measures were analyzed for both the intention-to-treat (ITT) population and the per protocol population. RESULTS: This study enrolled 281 patients. NBP showed greater effects than placebo on ADAS-cog (NBP change -2.46 vs. placebo -1.39; P = .03; ITT) and CIBIC-plus (80 [57.1%] vs. 59 [42.1%] patients improved; P = .01; ITT). NBP-related AE were uncommon and primarily consisted of mild gastrointestinal symptoms. DISCUSSION: Over the 6-month treatment period, NBP was effective for improving cognitive and global functioning in patients with subcortical vascular cognitive impairment without dementia and exhibited good safety.
Bioactivation of 3-n-butylphthalide via sulfation of its major metabolite 3-hydroxy-NBP: mediated mainly by sulfotransferase 1A1.[Pubmed:24468743]
Drug Metab Dispos. 2014 Apr;42(4):774-81.
3-n-Butylphthalide (NBP) [(+/-)-3-butyl-1(3H)-isobenzofuranone] is an anti-cerebral-ischemia drug. Moderate hepatotoxicity has been observed in clinical applications. One of the major metabolites, 3-N-acetylcysteine-NBP, has been detected in human urine, indicating the formation of a reactive metabolite. We elucidated the formation mechanism of the reactive metabolite and its association with the hepatotoxicity of NBP. The in vitro incubations revealed that 3-glutathione-NBP (3-GSH-NBP) was observed only in fresh rat liver homogenate rather than in liver microsomes, liver cytosol, or liver 9,000g supernatant supplemented with NADPH and GSH. We also detected 3-GSH-NBP when 3'-phosphoadenosine-5'-phosphosulfate was added in GSH-fortified human liver cytosol (HLC). The formation of 3-GSH-NBP was 39.3-fold higher using 3-hydroxy-NBP (3-OH-NBP) as the substrate than NBP. The sulfotransferase (SULT) inhibitors DCNP (2,6-dichloro-4-nitrophenol) and quercetin suppressed 3-GSH-NBP formation in HLC by 75 and 82%, respectively, suggesting that 3-OH-NBP sulfation was involved in 3-GSH-NBP formation. Further SULT phenotyping revealed that SULT1A1 is the major isoform responsible for the sulfation. Dose-dependent toxicity was observed in primary rat hepatocytes exposed to 3-OH-NBP, with an IC50 of approximately 168 muM. Addition of DCNP and quercetin significantly increased cell viability, whereas l-buthionine-sulfoximine (a GSH depleter) decreased cell viability. Overall, our study revealed the underlying mechanism for the bioactivation of NBP is as follows. NBP is first oxidized to 3-OH-NBP and further undergoes sulfation to form 3-OH-NBP sulfate. The sulfate spontaneously cleaves off, generating highly reactive electrophilic cations, which can bind either to GSH to detoxify or to hepatocellular proteins to cause undesirable side effects.
Improvement of cognitive deficits in SAMP8 mice by 3-n-butylphthalide.[Pubmed:24512016]
Neurol Res. 2014 Mar;36(3):224-33.
The herbal extract 3-n-Butylphthalide (NBP) is used in clinical practice for ischemic patients in China. It has been shown to have various neuroprotective effects both in vitro and in vivo. In the present study, the effects of NBP on learning and memory decline in the senescence-accelerated mouse prone-8 (SAMP8) animal model were investigated. Intragastric NBP administration to 4-month-old SAMP8 mice for 2 months significantly improved spatial learning and memory ability. Moreover, the loss of choline acetyltransferase (ChAT)-positive neurons in the medial septal nucleus and the vertical limb of the diagonal band in SAMP8 mice was slowed down, as was the decline in the protein and mRNA expression of ChAT in the hippocampus, cerebral cortex, and forebrain. These results demonstrated that NBP treatment starting at the age of 4 months protected from the learning/memory deficits with aging of SAMP8 mice, and that this effect might be mediated by preventing the decline of the central cholinergic system.


