AIDAPotent, selective group I mGlu antagonist CAS# 168560-79-0 |
- SAMS Peptide
Catalog No.:BCC5745
CAS No.:125911-68-4
- YLF-466D
Catalog No.:BCC4086
CAS No.:1273323-67-3
- RSVA 405
Catalog No.:BCC8016
CAS No.:140405-36-3
- TCS-PIM-1-4a
Catalog No.:BCC5461
CAS No.:327033-36-3
- PT 1
Catalog No.:BCC7846
CAS No.:331002-70-1
- A-769662
Catalog No.:BCC2080
CAS No.:844499-71-4
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 168560-79-0 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 6919177 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C11H11NO4 | M.Wt | 221.21 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Synonyms | UPF 523 | ||
| Solubility | Soluble to 100 mM in 1.1eq. NaOH | ||
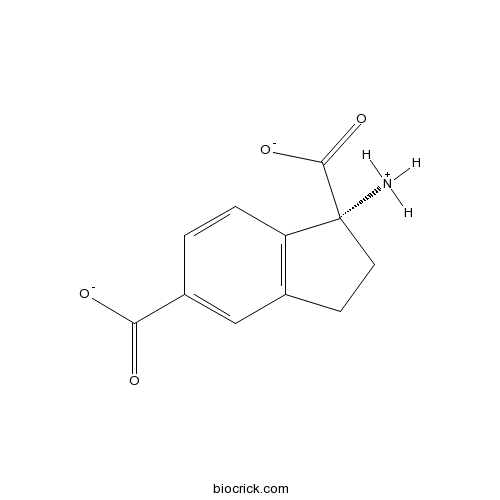
| Chemical Name | (1R)-1-azaniumyl-2,3-dihydroindene-1,5-dicarboxylate | ||
| SMILES | C1CC(C2=C1C=C(C=C2)C(=O)[O-])(C(=O)[O-])[NH3+] | ||
| Standard InChIKey | LSTPKMWNRWCNLS-LLVKDONJSA-M | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C11H11NO4/c12-11(10(15)16)4-3-6-5-7(9(13)14)1-2-8(6)11/h1-2,5H,3-4,12H2,(H,13,14)(H,15,16)/p-1/t11-/m1/s1 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | A relatively potent and selective antagonist of group I metabotropic glutamate receptors (mGlu1a), having no effect on group II (mGlu2) or group III (mGlu4) receptors expressed individually in baby hamster kidney cells. Has no effect on ionotropic glutamate receptors. Centrally active following systemic administration in vivo. |

AIDA Dilution Calculator

AIDA Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 4.5206 mL | 22.603 mL | 45.2059 mL | 90.4118 mL | 113.0148 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.9041 mL | 4.5206 mL | 9.0412 mL | 18.0824 mL | 22.603 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.4521 mL | 2.2603 mL | 4.5206 mL | 9.0412 mL | 11.3015 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0904 mL | 0.4521 mL | 0.9041 mL | 1.8082 mL | 2.2603 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0452 mL | 0.226 mL | 0.4521 mL | 0.9041 mL | 1.1301 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- H-Asp(OMe)-OH.HCl
Catalog No.:BCC2889
CAS No.:16856-13-6
- Fosbretabulin (Combretastatin A4 Phosphate (CA4P)) Disodium
Catalog No.:BCC4600
CAS No.:168555-66-6
- Dehydrogeijerin
Catalog No.:BCN7531
CAS No.:16850-91-2
- Z-D-Val-OH
Catalog No.:BCC2732
CAS No.:1685-33-2
- SHU 9119
Catalog No.:BCC6019
CAS No.:168482-23-3
- Epifriedelanol
Catalog No.:BCN1104
CAS No.:16844-71-6
- Rhodiocyanoside A
Catalog No.:BCN7852
CAS No.:168433-86-1
- Compound 401
Catalog No.:BCC7622
CAS No.:168425-64-7
- Tacrine hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC6869
CAS No.:1684-40-8
- Oxymatrine
Catalog No.:BCN1103
CAS No.:16837-52-8
- Asiaticoside
Catalog No.:BCN1011
CAS No.:16830-15-2
- 3-Epidehydropachymic acid
Catalog No.:BCN3644
CAS No.:168293-15-0
- TPEN
Catalog No.:BCC7913
CAS No.:16858-02-9
- Conivaptan HCl
Catalog No.:BCC3756
CAS No.:168626-94-6
- Ezatiostat
Catalog No.:BCC3638
CAS No.:168682-53-9
- H-Tyr-OtBu
Catalog No.:BCC3128
CAS No.:16874-12-7
- SGC707
Catalog No.:BCC6543
CAS No.:1687736-54-4
- Z-Tyr(tBu)-OH.DCHA
Catalog No.:BCC2745
CAS No.:16879-90-6
- RS 67333 hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC5693
CAS No.:168986-60-5
- RS 67506 hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC6878
CAS No.:168986-61-6
- Tropanyl phenylacetate
Catalog No.:BCN1927
CAS No.:1690-22-8
- 4'-O-Methylcoumestrol
Catalog No.:BCN7226
CAS No.:1690-62-6
- (2R,4R)-APDC
Catalog No.:BCC6969
CAS No.:169209-63-6
- MSPG
Catalog No.:BCC6819
CAS No.:169209-64-7
Quorum sensing network in clinical strains of A. baumannii: AidA is a new quorum quenching enzyme.[Pubmed:28328989]
PLoS One. 2017 Mar 22;12(3):e0174454.
Acinetobacter baumannii is an important pathogen that causes nosocomial infections generally associated with high mortality and morbidity in Intensive Care Units (ICUs). Currently, little is known about the Quorum Sensing (QS)/Quorum Quenching (QQ) systems of this pathogen. We analyzed these mechanisms in seven clinical isolates of A. baumannii. Microarray analysis of one of these clinical isolates, Ab1 (A. baumannii ST-2_clon_2010), previously cultured in the presence of 3-oxo-C12-HSL (a QS signalling molecule) revealed a putative QQ enzyme (alpha/ss hydrolase gene, AIDA). This QQ enzyme was present in all non-motile clinical isolates (67% of which were isolated from the respiratory tract) cultured in nutrient depleted LB medium. Interestingly, this gene was not located in the genome of the only motile clinical strain growing in this medium (A. baumannii strain Ab421_GEIH-2010 [Ab7], isolated from a blood sample). The AIDA protein expressed in E. coli showed QQ activity. Finally, we observed downregulation of the AIDA protein (QQ system attenuation) in the presence of H2O2 (ROS stress). In conclusion, most of the A. baumannii clinical strains were not surface motile (84%) and were of respiratory origin (67%). Only the pilT gene was involved in surface motility and related to the QS system. Finally, a new QQ enzyme (alpha/ss hydrolase gene, AIDA protein) was detected in these strains.
Multicentre open-label randomised controlled trial to compare colistin alone with colistin plus meropenem for the treatment of severe infections caused by carbapenem-resistant Gram-negative infections (AIDA): a study protocol.[Pubmed:27098822]
BMJ Open. 2016 Apr 20;6(4):e009956.
INTRODUCTION: The emergence of antibiotic-resistant bacteria has driven renewed interest in older antibacterials, including colistin. Previous studies have shown that colistin is less effective and more toxic than modern antibiotics. In vitro synergy studies and clinical observational studies suggest a benefit of combining colistin with a carbapenem. A randomised controlled study is necessary for clarification. METHODS AND ANALYSIS: This is a multicentre, investigator-initiated, open-label, randomised controlled superiority 1:1 study comparing colistin monotherapy with colistin-meropenem combination therapy for infections caused by carbapenem-resistant Gram-negative bacteria. The study is being conducted in 6 centres in 3 countries (Italy, Greece and Israel). We include patients with hospital-associated and ventilator-associated pneumonia, bloodstream infections and urosepsis. The primary outcome is treatment success at day 14, defined as survival, haemodynamic stability, stable or improved respiratory status for patients with pneumonia, microbiological cure for patients with bacteraemia and stability or improvement of the Sequential Organ Failure Assessment (SOFA) score. Secondary outcomes include 14-day and 28-day mortality as well as other clinical end points and safety outcomes. A sample size of 360 patients was calculated on the basis of an absolute improvement in clinical success of 15% with combination therapy. Outcomes will be assessed by intention to treat. Serum colistin samples are obtained from all patients to obtain population pharmacokinetic models. Microbiological sampling includes weekly surveillance samples with analysis of resistance mechanisms and synergy. An observational trial is evaluating patients who met eligibility requirements but were not randomised in order to assess generalisability of findings. ETHICS AND DISSEMINATION: The study was approved by ethics committees at each centre and informed consent will be obtained for all patients. The trial is being performed under the auspices of an independent data and safety monitoring committee and is included in a broad dissemination strategy regarding revival of old antibiotics. TRIAL REGISTRATION NUMBER: NCT01732250 and 2012-004819-31; Pre-results.
CaMKII-mediated displacement of AIDA-1 out of the postsynaptic density core.[Pubmed:27477489]
FEBS Lett. 2016 Sep;590(17):2934-9.
Ankyrin repeat and sterile alpha motif domain-containing protein 1B (ANKS1B, also known as AIDA-1) is a major component of the postsynaptic density (PSD) in excitatory neurons where it concentrates at the electron-dense core under basal conditions and moves out during activity. This study investigates the molecular mechanism underlying activity-induced displacement of AIDA-1. Experiments with PSD fractions from brain indicate phosphorylation of AIDA-1 upon activation of endogenous CaMKII. Immuno-electron microscopy studies show that treatment of hippocampal neurons with NMDA results in an ~ 30 nm shift in the median distance of the AIDA-1 label from the postsynaptic membrane, an effect that is blocked by the CaMKII inhibitor tatCN21. CaMKII-mediated redistribution of AIDA-1 is similar to that observed for SynGAP. CaMKII-mediated removal of two abundant PSD-95-binding proteins from the PSD core during activity is expected to initiate a molecular reorganization at the PSD.
Pharmacological characterization of 1-aminoindan-1,5-dicarboxylic acid, a potent mGluR1 antagonist.[Pubmed:9152378]
J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1997 May;281(2):721-9.
We examined the pharmacological profile of 1-aminoindan-1,5-dicarboxylic acid (AIDA), a rigid (carboxyphenyl)glycine derivative acting on metabotropic glutamate receptors (mGluRs). In cells transfected with mGluR1a, AIDA competitively antagonized the stimulatory responses of glutamate and (1S,3R)-1-aminocyclopentane-1,3-dicarboxylic acid [(1S,3R)-ACPD] on phosphoinositide hydrolysis (pA2 = 4.21). In cells transfected with mGluR5a, AIDA displayed a much weaker antagonist effect. In transfected cells expressing mGluR2, AIDA (< or = 1 mM) did not affect the inhibition of forskolin-stimulated adenylate cyclase activity induced by (1S,3R)-ACPD, but at large concentrations, it displayed a modest agonist activity. In rat hippocampal or striatal slices, AIDA (0.1-1 mM) reduced the effects of (1S,3R)-ACPD on phospholipase C but not on adenylate cyclase responses, whereas (+)-alpha-methyl-4-carboxyphenylglycine (0.3-1 mM) was an antagonist on both transduction systems. In addition, AIDA (0.3-1 mM) had no effect on mGluRs coupled to phospholipase D, whereas (+)-alpha-methyl-4-carboxy-phenylglycine (0.5-1 mM) acted as an agonist with low intrinsic activity. In rat cortical slices, AIDA antagonized the stimulatory (mGluR1-mediated) effect of (1S,3R)-ACPD on the depolarization-induced outflow of D-[3H]aspartate, disclosing an inhibitory effect ascribable to (1S,3R)-ACPD activating mGluR2 and/or mGluR4. Finally, mice treated with AIDA (0.1-10 nmol i.c.v.) had an increased pain threshold and difficulties in initiating a normal ambulatory behavior. Taken together, these data suggest that AIDA is a potent, selective and competitive mGluR1 a antagonist.
Class I mGlu receptor antagonist 1-aminoindan-1,5-dicarboxylic acid blocks contextual but not cue conditioning in rats.[Pubmed:9196260]
Eur J Pharmacol. 1997 May 20;326(2-3):105-8.
It is widely believed that metabotropic glutamate (mGlu) receptors play a potential role in memory formation. However, the particular function of different classes of mGluRs, or even subtypes, remains elusive. We show here that intraperitoneal injection of the class I selective antagonist 1-aminoindan-1,5-dicarboxylic acid (AIDA) in concentrations of 0.18 or 1.8 mg/kg 25 min prior to acquisition training blocks hippocampus-dependent contextual, but not hippocampus-independent cue, conditioning in rats. These data provide the first evidence for a specific role of mGlu receptors, class I in particular, in hippocampus-dependent learning tasks.


