AKT Kinase InhibitorCAS# 842148-40-7 |
- GDC-0068 (RG7440)
Catalog No.:BCC1271
CAS No.:1001264-89-6
- AZD5363
Catalog No.:BCC1073
CAS No.:1143532-39-1
- AT7867 dihydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC1378
CAS No.:1431697-86-7
- Perifosine
Catalog No.:BCC3673
CAS No.:157716-52-4
- AT7867
Catalog No.:BCC2536
CAS No.:857531-00-1
- CCT128930
Catalog No.:BCC3904
CAS No.:885499-61-6
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 842148-40-7 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 25023726 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C16H19N7O3 | M.Wt | 357.37 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | DMSO : 16.67 mg/mL (46.65 mM; Need ultrasonic) H2O : < 0.1 mg/mL (insoluble) | ||
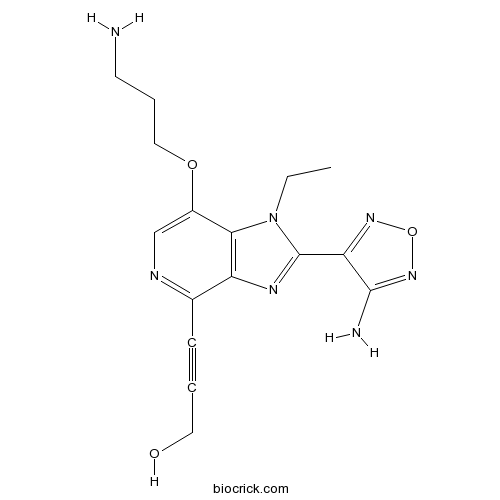
| Chemical Name | 3-[2-(4-amino-1,2,5-oxadiazol-3-yl)-7-(3-aminopropoxy)-1-ethylimidazo[4,5-c]pyridin-4-yl]prop-2-yn-1-ol | ||
| SMILES | CCN1C2=C(C(=NC=C2OCCCN)C#CCO)N=C1C3=NON=C3N | ||
| Standard InChIKey | LWLOLQIXHMFYND-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C16H19N7O3/c1-2-23-14-11(25-8-4-6-17)9-19-10(5-3-7-24)12(14)20-16(23)13-15(18)22-26-21-13/h9,24H,2,4,6-8,17H2,1H3,(H2,18,22) | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | AKT Kinase Inhibitor is an Akt kinase inhibitor. References: | |||||

AKT Kinase Inhibitor Dilution Calculator

AKT Kinase Inhibitor Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.7982 mL | 13.9911 mL | 27.9822 mL | 55.9644 mL | 69.9555 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.5596 mL | 2.7982 mL | 5.5964 mL | 11.1929 mL | 13.9911 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.2798 mL | 1.3991 mL | 2.7982 mL | 5.5964 mL | 6.9956 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.056 mL | 0.2798 mL | 0.5596 mL | 1.1193 mL | 1.3991 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.028 mL | 0.1399 mL | 0.2798 mL | 0.5596 mL | 0.6996 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
AKT Kinase Inhibitor
- Canagliflozin
Catalog No.:BCC3696
CAS No.:842133-18-0
- Cyclosomatostatin
Catalog No.:BCC7693
CAS No.:84211-54-1
- Sudan I
Catalog No.:BCN8378
CAS No.:842-07-9
- 7 8-Dihydroxy-4-Phenylcoumarin
Catalog No.:BCC8289
CAS No.:842-01-3
- Ac-Glu(OtBu)-OH
Catalog No.:BCC2921
CAS No.:84192-88-1
- 6-Fluoro-3-(4-piperidinyl)-1,2-benzisoxazole hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC8772
CAS No.:84163-13-3
- R406
Catalog No.:BCC3876
CAS No.:841290-81-1
- R406 (free base)
Catalog No.:BCC2553
CAS No.:841290-80-0
- Triptotriterpenic acid A
Catalog No.:BCN6780
CAS No.:84108-17-8
- Wilforlide A acetate
Catalog No.:BCN4384
CAS No.:84104-80-3
- Wilforlide A
Catalog No.:BCN4383
CAS No.:84104-71-2
- 1-Benzhydrylpiperazine
Catalog No.:BCC8453
CAS No.:841-77-0
- Raclopride
Catalog No.:BCC7184
CAS No.:84225-95-6
- 5-O-Methylvisammioside
Catalog No.:BCN4954
CAS No.:84272-85-5
- Aliarin
Catalog No.:BCN3919
CAS No.:84294-77-9
- Pterosin D 3-O-glucoside
Catalog No.:BCN4567
CAS No.:84299-80-9
- 4,4'-Cyclohexylidenebisphenol
Catalog No.:BCC8663
CAS No.:843-55-0
- Rabdosin B
Catalog No.:BCN3236
CAS No.:84304-92-7
- Bedaquiline
Catalog No.:BCC5246
CAS No.:843663-66-1
- Mifepristone
Catalog No.:BCC4486
CAS No.:84371-65-3
- Adoxosidic acid
Catalog No.:BCN7593
CAS No.:84375-46-2
- Neuromedin S (rat)
Catalog No.:BCC6055
CAS No.:843782-19-4
- Bretazenil
Catalog No.:BCC7711
CAS No.:84379-13-5
- alpha-Arbutin
Catalog No.:BCN8336
CAS No.:84380-01-8
Didymin Alleviates Hepatic Fibrosis Through Inhibiting ERK and PI3K/Akt Pathways via Regulation of Raf Kinase Inhibitor Protein.[Pubmed:27997902]
Cell Physiol Biochem. 2016;40(6):1422-1432.
BACKGROUND: Didymin has been reported to have anti-cancer potential. However, the effect of didymin on liver fibrosis remains illdefined. METHODS: Hepatic fibrosis was induced by CCl4 in rats. The effects of didymin on liver pathology and collagen accumulation were observed by hematoxylin-eosin and Masson's trichrome staining, respectively. Serum transaminases activities and collagen-related indicators levels were determined by commercially available kits. Moreover, the effects of didymin on hepatic stellate cell apoptosis and cell cycle were analyzed by flow cytometry. Mitochondrial membrane potential was detected by using rhodamine-123 dye. The expression of Raf kinase inhibitor protein (RKIP) and the phosphorylation of the ERK/MAPK and PI3K/Akt pathways were assessed by Western blot. RESULTS: Didymin significantly ameliorated chronic liver injury and collagen deposition. It strongly inhibited hepatic stellate cells proliferation, induced apoptosis and caused cell cycle arrest in G2/M phase. Moreover, didymin notably attenuated mitochondrial membrane potential, accompanied by release of cytochrome C. Didymin significantly inhibited the ERK/MAPK and PI3K/Akt pathways. The effects of didymin on the collagen accumulation in rats and on the biological behaviors of hepatic stellate cells were largely abolished by the specific RKIP inhibitor locostatin. CONCLUSION: Didymin alleviates hepatic fibrosis by inhibiting ERK/MAPK and PI3K/Akt pathways via regulation of RKIP expression.
PAK1 Is a Novel Therapeutic Target in Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor-Resistant Lung Adenocarcinoma Activated by the PI3K/AKT Signaling Regardless of EGFR Mutation.[Pubmed:27178741]
Clin Cancer Res. 2016 Nov 1;22(21):5370-5382.
PURPOSE: EGFR mutation as a biomarker has documented that EGFR-mutant patients will derive clinical benefit from tyrosine kinase inhibitor (TKI) treatment. Unfortunately, most patients show TKI resistance and tumor recurrence after therapy. Therefore, we expected that an adjuvant biomarker other than EGFR mutation is needed for predicting TKI resistance. EXPERIMENTAL DESIGN: Molecular manipulations were performed to verify whether TKI resistance mediated by p21-activated kinase (PAK1) could be through increasing Mcl-1 protein stability via the PI3K/AKT/C/EBP-beta/miR-145 cascade. Xenograft mouse models were used to confirm the mechanistic action of PAK1 on TKI resistance. Forty-six tumor tissues from patients with lung adenocarcinoma who received TKI therapy were collected to evaluate PAK1 and E-cadherin mRNA expressions by real-time PCR. The association of PAK1 and E-cadherin mRNA expressions with tumor response to TKI treatment and outcomes was evaluated. RESULTS: We demonstrate that PAK1 confers TKI resistance in EGFR-mutant cells as well as in EGFR-wild-type cells. Mechanistically, the positive feedback loop of PAK1/PI3K/AKT/C/EBP-beta/miR-145 cascades persistently activates the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway to protect Mcl-1 degradation by Fbw7, which results, in turn, in TKI resistance and cell invasion via epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition due to a decrease in E-cadherin expression. The mechanism underlying the cell model is further confirmed in xenograft tumors. Among patients, high-PAK1 or low-E-cadherin tumors more commonly exhibited an unfavorable response to TKI and poorer outcome compared with low-PAK1 or low-E-cadherin tumors. CONCLUSIONS: The combination of TKI with AKT inhibitor might confer TKI sensitivity and in turn improve outcomes in patients with lung adenocarcinoma who harbored high PAK1 mRNA-expressing tumors. Clin Cancer Res; 22(21); 5370-82. (c)2016 AACR.
Selective elimination of neuroblastoma cells by synergistic effect of Akt kinase inhibitor and tetrathiomolybdate.[Pubmed:28244639]
J Cell Mol Med. 2017 Sep;21(9):1859-1869.
Neuroblastoma is the most common extracranial solid tumour of infancy. Pathological activation of glucose consumption, glycolysis and glycolysis-activating Akt kinase occur frequently in neuroblastoma cells, and these changes correlate with poor prognosis of patients. Therefore, several inhibitors of glucose utilization and the Akt kinase activity are in preclinical trials as potential anti-cancer drugs. However, metabolic plasticity of cancer cells might undermine efficacy of this approach. In this work, we identified oxidative phosphorylation as compensatory mechanism preserving viability of neuroblastoma cells with inhibited glucose uptake/Akt kinase. It was oxidative phosphorylation that maintained intracellular level of ATP and proliferative capacity of these cells. The oxidative phosphorylation inhibitors (rotenone, tetrathiomolybdate) synergized with inhibitor of the Akt kinase/glucose uptake in down-regulation of both viability of neuroblastoma cells and clonogenic potential of cells forming neuroblastoma spheroids. Interestingly, tetrathiomolybdate acted as highly specific inhibitor of oxygen consumption and activator of lactate production in neuroblastoma cells, but not in normal fibroblasts and neuronal cells. Moreover, the reducing effect of tetrathiomolybdate on cell viability and the level of ATP in the cells with inhibited Akt kinase/glucose uptake was also selective for neuroblastoma cells. Therefore, efficient elimination of neuroblastoma cells requires inhibition of both glucose uptake/Akt kinase and oxidative phosphorylation activities. The use of tetrathiomolybdate as a mitochondrial inhibitor contributes to selectivity of this combined treatment, preferentially targeting neuroblastoma cells.


