AceclofenacCAS# 89796-99-6 |
- Etifoxine
Catalog No.:BCC1560
CAS No.:21715-46-8
- Etomidate
Catalog No.:BCC1150
CAS No.:33125-97-2
- Etifoxine hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC1561
CAS No.:56776-32-0
- Flumazenil
Catalog No.:BCC1259
CAS No.:78755-81-4
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 89796-99-6 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 71771 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C16H13Cl2NO4 | M.Wt | 354.18 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | DMSO : 100 mg/mL (282.34 mM; Need ultrasonic) H2O : < 0.1 mg/mL (insoluble) | ||
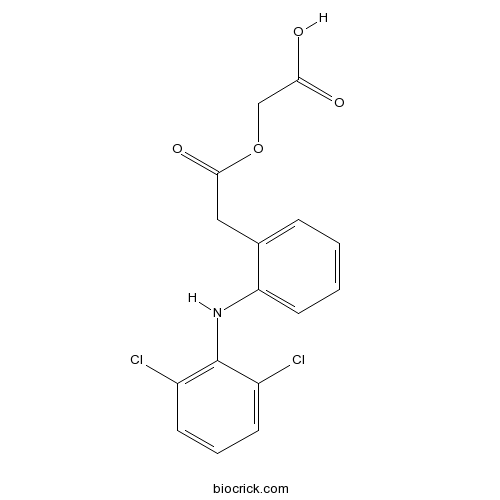
| Chemical Name | 2-[2-[2-(2,6-dichloroanilino)phenyl]acetyl]oxyacetic acid | ||
| SMILES | C1=CC=C(C(=C1)CC(=O)OCC(=O)O)NC2=C(C=CC=C2Cl)Cl | ||
| Standard InChIKey | MNIPYSSQXLZQLJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C16H13Cl2NO4/c17-11-5-3-6-12(18)16(11)19-13-7-2-1-4-10(13)8-15(22)23-9-14(20)21/h1-7,19H,8-9H2,(H,20,21) | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||

Aceclofenac Dilution Calculator

Aceclofenac Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.8234 mL | 14.1171 mL | 28.2342 mL | 56.4685 mL | 70.5856 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.5647 mL | 2.8234 mL | 5.6468 mL | 11.2937 mL | 14.1171 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.2823 mL | 1.4117 mL | 2.8234 mL | 5.6468 mL | 7.0586 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0565 mL | 0.2823 mL | 0.5647 mL | 1.1294 mL | 1.4117 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0282 mL | 0.1412 mL | 0.2823 mL | 0.5647 mL | 0.7059 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
Aceclofenac is a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) analog of Diclofenac. Target: COX Aceclofenac is a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) analog of Diclofenac. It is used for the relief of pain and inflammation in rheumatoid arthritis, osteoarthritis and ankylosing spondylitis. Aceclofenac has higher anti-inflammatory action than conventional NSAIDs. It is a cytokine inhibitor. Aceclofenac works by blocking the action of a substance in the body called cyclo-oxygenase. Cyclo-oxygenase is involved in the production of prostaglandins (chemicals in the body) which cause pain, swelling and inflammation. Aceclofenac is the glycolic acid ester of diclofenac [1].
References:
[1]. http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Aceclofenac
- Myrianthic acid
Catalog No.:BCN7130
CAS No.:89786-84-5
- 2,3,24-Trihydroxy-12-ursen-28-oic acid
Catalog No.:BCN1314
CAS No.:89786-83-4
- Tazobactam acid
Catalog No.:BCC9160
CAS No.:89786-04-9
- Toremifene Citrate
Catalog No.:BCC4487
CAS No.:89778-27-8
- Toremifene
Catalog No.:BCC2010
CAS No.:89778-26-7
- AST-1306
Catalog No.:BCC3727
CAS No.:897383-62-9
- 7-O-Acetyl-4-O-demethylpolysyphorin
Catalog No.:BCN3984
CAS No.:89706-39-8
- KX2-391
Catalog No.:BCC5080
CAS No.:897016-82-9
- Androstadienedione
Catalog No.:BCC8824
CAS No.:897-06-3
- VX-11e
Catalog No.:BCC2051
CAS No.:896720-20-0
- BMH-21
Catalog No.:BCC5580
CAS No.:896705-16-1
- AT9283
Catalog No.:BCC2173
CAS No.:896466-04-9
- 5-Ethyltio-1H-Tetrazole
Catalog No.:BCC2844
CAS No.:89797-68-2
- PF-3758309
Catalog No.:BCC1853
CAS No.:898044-15-0
- YS-035 hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC6639
CAS No.:89805-39-0
- Esculentoside D
Catalog No.:BCN5013
CAS No.:89808-50-4
- XL228
Catalog No.:BCC2058
CAS No.:898280-07-4
- 4-(4-(5-(Aminomethyl)-2-oxooxazolidin-3-yl)phenyl)morpholin-3-one hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC8647
CAS No.:898543-06-1
- 3-Epichromolaenide
Catalog No.:BCN7241
CAS No.:89913-53-1
- 3-O-Acetyl-alpha-boswellic acid
Catalog No.:BCN2671
CAS No.:89913-60-0
- Beta-Carboline-1-propanoic acid
Catalog No.:BCN5805
CAS No.:89915-39-9
- Gymnoside III
Catalog No.:BCN8218
CAS No.:899430-03-6
- A 438079 hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC1317
CAS No.:899431-18-6
- Platycoside K
Catalog No.:BCN3242
CAS No.:899447-64-4
Efficacy and safety of aceclofenac in osteoarthritis: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials.[Pubmed:28293447]
Eur J Rheumatol. 2017 Mar;4(1):11-18.
OBJECTIVE: To analyze the effects on pain, function, and safety of Aceclofenac compared with other nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) or pain relief medications in patients with osteoarthritis. MATERIAL AND METHODS: Two investigators independently searched the database. We included randomized controlled trials evaluating efficacy and/or safety of Aceclofenac compared with control interventions (NSAIDs or acetaminophen) in patients with osteoarthritis. We did not include placebo, opioid analgesics, NSAID combinations, and topical analgesics for the control groups. We summarized the efficacy data as standardized mean differences (SMD) with 95% confidence intervals (CI) and safety outcomes as risk ratios (RR) with 95% CI using the inverse variance random effect model. We assessed the heterogeneity by the I(2) test. We used the GRADE approach to evaluate the quality of the evidence for all outcome parameters. RESULTS: We included 9 trials (8 double blind and 1 single blind) that evaluated pain (7 trials), function (8 trials) and safety (7 trials). We observed no significant difference in pain reduction between Aceclofenac and control interventions [SMD: -0.30 (-0.62, 0.01); I(2)=88%; GRADE evidence- low]. Aceclofenac was more beneficial than control interventions in improving physical function [SMD: -0.27 (-0.50, -0.03); I(2)=88%; GRADE evidence- low]. We observed less gastrointestinal adverse events for Aceclofenac than in control interventions [RR 0.69 (95% CI: 0.57, 0.83); I(2)=12%; GRADE evidence- moderate]. We observed no difference in overall adverse events occurrence and dropout rate between Aceclofenac and control interventions. CONCLUSION: We observed that Aceclofenac was beneficial over control analgesics for function improvement and to minimize gastrointestinal adverse events. Our findings could be biased due to the heterogeneity of the sample, the fact that the trials were small and methodological issues.
Efficacy and Safety of Different Aceclofenac Treatments for Chronic Lower Back Pain: Prospective, Randomized, Single Center, Open-Label Clinical Trials.[Pubmed:28332372]
Yonsei Med J. 2017 May;58(3):637-643.
PURPOSE: Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are a mainstay for medical treatment of chronic lower back pain (CLBP). Increased dose intervals for medication have been associated with increased patient adherence to prescriptions. The purpose of this clinical trial was to compare the efficacy and safety of a once daily dose of Aceclofenac controlled release (CR) and a twice daily dose of Aceclofenac for CLBP management. MATERIALS AND METHODS: A prospective, randomized, single center, open-label clinical trial was performed to compare the efficacy and safety of Aceclofenac CR (200 mg once daily) to Aceclofenac dose (100 mg twice daily). Fifty patients in each group were enrolled for the study. The primary end point was Visual Analogue Scale (VAS) change at baseline to that at 2 weeks after medication and safety profiles. Also, change in quality of life measured by EuroQoL 5D (EQ-5D) and Oswestry Disability Index (ODI) functional score for the lumbar spine were also assessed. RESULTS: Within groups at pre- and post-treatment, there were significant VAS reductions for Aceclofenac CR and Aceclofenac (p=0.028). EQ-5D increased significantly in both groups (p=0.037). ODI scores decreased significantly in both groups (p=0.012). However, there were no significant differences between Aceclofenac CR and Aceclofenac at pre- and post-treatment. Patients with Aceclofenac CR showed significant increases in heartburn and indigestion and adverse gastrointestinal effects, compared to Aceclofenac. CONCLUSION: In patients with CLBP, Aceclofenac CR and Aceclofenac demonstrated significant symptomatic pain relief, improvement in quality of life and functional scores. Aceclofenac CR slightly increased gastrointestinal adverse effects, such as heartburn and indigestion.
Aceclofenac cocrystal nanoliposomes for rheumatoid arthritis with better dermatokinetic attributes: a preclinical study.[Pubmed:28186461]
Nanomedicine (Lond). 2017 Mar;12(6):615-638.
AIM: The aim of present research was to complex Aceclofenac with lysine (LYS) and the developed Aceclofenac-LYS cocrystal was encapsulated in lipid bilayers of liposomes by employing dual carrier approach for the treatment of pain-related disorders in rheumatoid arthritis (RA). MATERIALS & METHODS: The developed carriers were characterized for particle size, drug release, ex vivo and in vivo studies, dermatokinetic modeling, complete freund's adjuvant (CFA)-induced RA rat model, radiant heat tail-flick method, formalin-induced paw-licking model, paw edema model and xylene-induced ear edema model in mice. RESULTS: The developed nanoliposomes offered nanometric size, controlled drug release and enhanced drug permeation. Further, hydrogel incorporated nanoproduct was found to be rheologically acceptable and substantially compatible with rodent skin. CONCLUSION: The studies indicated the superiority of LYS-conjugated liposome-entrapped nanocarriers for improved management of conditions like RA over the marketed product.
Modulation of microenvironmental pH for dual release and reduced in vivo gastrointestinal bleeding of aceclofenac using hydroxypropyl methylcellulose-based bilayered matrix tablet.[Pubmed:28263912]
Eur J Pharm Sci. 2017 May 1;102:85-93.
This study was designed to develop a once-daily controlled-release matrix tablet of Aceclofenac 200mg (AFC-CR) with dual release characteristics and to investigate the role of an alkalizer in enhancing drug solubility and reducing the occurrence of gastroduodenal mucosal lesions. Two formulation approaches were employed, namely a monolithic matrix tablet and a bilayered tablet. In vitro dissolution studies of AFC-CR tablets were carried out in simulated intestinal fluid (pH6.8 buffer). The in vivo pharmacokinetic studies and drug safety of the immediate-release reference tablet Airtal(R) 100mg (Daewoong Co., Korea) and the optimized AFC-CR tablet were compared in beagle dogs under fasted condition. The optimally selected AFC-CR formulation displayed the desired dual release characteristics in simulated intestinal fluid with satisfactory micromeritic properties. The swelling action of the optimal matrix tablet, which was visualized by near-infrared (NIR) chemical imaging, occurred rapidly following hydration. Incorporation of sodium carbonate (Na2CO3) was found to enhance the release rate of the AFC-CR bilayered tablets at early stages and increase the microenvironmental pH (pHM). A pharmacokinetic study in beagle dogs indicated a higher drug plasma concentration and a sustained-release pattern for the AFC-CR tablet compared to the Airtal(R) tablet. AFC-CR was also superior to Airtal(R) in terms of in vivo drug safety, since no beagle dog receiving AFC-CR experienced gastrointestinal bleeding. The significant enhancement of drug safety was attributed to the size reduction and the increase of pHM of drug particles by means of incorporation of the alkalizer. These findings provide a scientific rationale for developing a novel controlled-release matrix tablet with enhanced patient compliance and better pain control.


