AST-1306EGFR/HER2 inhibitor CAS# 897383-62-9 |
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 897383-62-9 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 24739943 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C24H18ClFN4O2 | M.Wt | 448.88 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | >22.5mg/mL in DMSO | ||
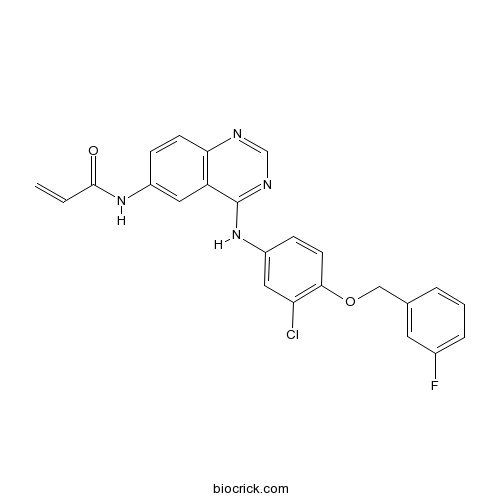
| Chemical Name | N-[4-[3-chloro-4-[(3-fluorophenyl)methoxy]anilino]quinazolin-6-yl]prop-2-enamide | ||
| SMILES | C=CC(=O)NC1=CC2=C(C=C1)N=CN=C2NC3=CC(=C(C=C3)OCC4=CC(=CC=C4)F)Cl | ||
| Standard InChIKey | MVZGYPSXNDCANY-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C24H18ClFN4O2/c1-2-23(31)29-17-6-8-21-19(11-17)24(28-14-27-21)30-18-7-9-22(20(25)12-18)32-13-15-4-3-5-16(26)10-15/h2-12,14H,1,13H2,(H,29,31)(H,27,28,30) | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | AST1306 is a selective, irreversible EGFR and ErbB2 inhibitor with IC50s of 0.5 and 3 nM, respectively.In Vitro:AST1306 induces a significant, concentration-dependent inhibition of the growth of HIH3T3-EGFR T790M/L858R cells. In addition, AST1306 effectively inhibits EGFR phosphorylation in HIH3T3-EGFR T790M/L858R cells. AST1306 inhibits the growth of NCI-H1975 cells that harbor the EGFR T790M/L858R mutation in a concentration-dependent manner, and blocks phosphorylation of EGFR and downstream pathways as well. AST1306 inhibits the phosphorylation of EGFR and ErbB2, and downstream signaling in human cancer cells. AST1306 inhibits the proliferation of human cancer cells, with ErbB2-overexpressing cells exhibiting more sensitivity[1].In Vivo:AST1306 potently suppresses tumor growth in ErbB2-overexpressing adenocarcinoma xenograft and FVB-2/Nneu transgenic breast cancer mouse models, but weakly inhibits the growth of EGFR-overexpressing tumor xenografts. Tumor growth inhibition induced by a single dose of AST1306 in the SK-OV-3 xenograft model is accompanied by a rapid (within 2 h) and sustained (≥24 h) inhibition of both EGFR and ErbB2, consistent with an irreversible inhibition mechanism[1]. References: | |||||

AST-1306 Dilution Calculator

AST-1306 Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.2278 mL | 11.1388 mL | 22.2777 mL | 44.5553 mL | 55.6942 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.4456 mL | 2.2278 mL | 4.4555 mL | 8.9111 mL | 11.1388 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.2228 mL | 1.1139 mL | 2.2278 mL | 4.4555 mL | 5.5694 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0446 mL | 0.2228 mL | 0.4456 mL | 0.8911 mL | 1.1139 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0223 mL | 0.1114 mL | 0.2228 mL | 0.4456 mL | 0.5569 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
AST1306 is a novel inhibitor of EGFR and HER2 (IC50 = 0.5 nM and 3 nM respectively)
EGFR (epidermal growth factor receptor) is a cell-surface receptor tyrosine kinase. The receptor activation leads to dimerization and tyrosine autophosphorylation. It induces a cascade of downstream cellular responses such as modification in gene expression, cell proliferation and cytoskeletal rearrangement etc. HER2 is a member of the epidermal growth factor and is associated with breast and ovarian cancers.
AST1306 selectively blocked EGFR and HER2 kinase activities in a cell-free assay. The tyrosine kinase activity of EGFR mutant T790M/L858R was also inhibited by AST1306 in intact cell and cell-free assays. In addition, AST1306 attenuated the EGFR and HER2 phosphorylation and downstream substrates. [1]
In ErbB2-overexpressing xenograft and FVB-2/Nneu transgenic mouse model, AST1306 potently inhibited tumor growth. In SK-OV-3 xenograft model, AST1306 caused a quick and long-lasting (≥24h) inhibition of EGFR and HER2. [1]
Reference:
1. Xie H, Lin L, Tong L et al. AST1306, a novel irreversible inhibitor of the epidermal growth factor receptor 1 and 2, exhibits antitumor activity both in vitro and in vivo. PLoS One. 2011;6(7):e21487.
- 7-O-Acetyl-4-O-demethylpolysyphorin
Catalog No.:BCN3984
CAS No.:89706-39-8
- KX2-391
Catalog No.:BCC5080
CAS No.:897016-82-9
- Androstadienedione
Catalog No.:BCC8824
CAS No.:897-06-3
- VX-11e
Catalog No.:BCC2051
CAS No.:896720-20-0
- BMH-21
Catalog No.:BCC5580
CAS No.:896705-16-1
- AT9283
Catalog No.:BCC2173
CAS No.:896466-04-9
- trans-3-Oxo-alpha-ionol
Catalog No.:BCN3385
CAS No.:896107-70-3
- Imiquimod maleate
Catalog No.:BCC4197
CAS No.:896106-16-4
- 2-Acetamidoethyl phosphate
Catalog No.:BCN1760
CAS No.:89603-45-2
- Chamaejasmenin A
Catalog No.:BCN3044
CAS No.:89595-71-1
- Chamaejasmenin C
Catalog No.:BCN3043
CAS No.:89595-70-0
- Mogroside VI
Catalog No.:BCN2578
CAS No.:89590-98-7
- Toremifene
Catalog No.:BCC2010
CAS No.:89778-26-7
- Toremifene Citrate
Catalog No.:BCC4487
CAS No.:89778-27-8
- Tazobactam acid
Catalog No.:BCC9160
CAS No.:89786-04-9
- 2,3,24-Trihydroxy-12-ursen-28-oic acid
Catalog No.:BCN1314
CAS No.:89786-83-4
- Myrianthic acid
Catalog No.:BCN7130
CAS No.:89786-84-5
- Aceclofenac
Catalog No.:BCC5233
CAS No.:89796-99-6
- 5-Ethyltio-1H-Tetrazole
Catalog No.:BCC2844
CAS No.:89797-68-2
- PF-3758309
Catalog No.:BCC1853
CAS No.:898044-15-0
- YS-035 hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC6639
CAS No.:89805-39-0
- Esculentoside D
Catalog No.:BCN5013
CAS No.:89808-50-4
- XL228
Catalog No.:BCC2058
CAS No.:898280-07-4
- 4-(4-(5-(Aminomethyl)-2-oxooxazolidin-3-yl)phenyl)morpholin-3-one hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC8647
CAS No.:898543-06-1
miR-551b regulates epithelial-mesenchymal transition and metastasis of gastric cancer by inhibiting ERBB4 expression.[Pubmed:28501849]
Oncotarget. 2017 Jul 11;8(28):45725-45735.
Epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) is an important biological process that is characteristic of malignant tumor cells with metastatic potential. We investigated the role of miR-551b in EMT and metastasis in gastric cancer (GC). We found that low miR-551b levels were associated with EMT, metastasis and a poor prognosis in GC patients. Further, two GC cell lines, MNK45 and SGC7901, exhibited lower miR-551b levels than the GES normal stomach cell line. Exposing MNK45 and SGC7901 cells to TGF-beta1 resulted in cell morphology changes characteristic of EMT, which was confirmed by Western blot analysis demonstrating low E-Cadherin and high N-Cadherin and Vimentin levels. Treatment with miR-551b mimics inhibited these EMT changes as well as Transwell migration and invasiveness. We identified ERBB4 as a potential target of miR-551b based on patient data from the TCGA. ERBB4 was upregulated in GC specimens, and its high expression correlated with a poor prognosis of GC patients. Dual luciferase assays revealed that miR-551b directly inhibited ERBB4 by binding to its 3'UTR. Moreover, treatment with miR-551b mimics or the ERBB4 inhibitor AST-1306 inhibited EMT in the GC cell lines. Finally, nude mice xenografted with GC cancer cell lines expressing miR-551b mimics exhibited smaller tumors and longer survival than mice engrafted with control GC cancer cells. These data indicate that miR-551b inhibits EMT and metastasis in GC by inhibiting ERBB4. miR-551b and ERBB4 are thus potential therapeutic targets for the treatment of GC.


