AP26113Anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK) inhibitor CAS# 1197958-12-5 |
- LDK378
Catalog No.:BCC3691
CAS No.:1032900-25-6
- LDK378 dihydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC1694
CAS No.:1380575-43-8
- TAE684 (NVP-TAE684)
Catalog No.:BCC3660
CAS No.:761439-42-3
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 1197958-12-5 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 57390074 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C26H34ClN6O2P | M.Wt | 529.01 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Synonyms | ALK-IN-1; 3DGD69C6PV | ||
| Solubility | DMSO : 50 mg/mL (94.52 mM; Need ultrasonic) | ||
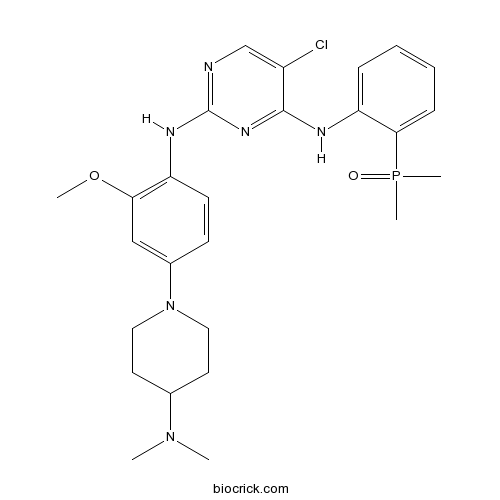
| Chemical Name | 5-chloro-2-N-[4-[4-(dimethylamino)piperidin-1-yl]-2-methoxyphenyl]-4-N-(2-dimethylphosphorylphenyl)pyrimidine-2,4-diamine | ||
| SMILES | CN(C)C1CCN(CC1)C2=CC(=C(C=C2)NC3=NC=C(C(=N3)NC4=CC=CC=C4P(=O)(C)C)Cl)OC | ||
| Standard InChIKey | OVDSPTSBIQCAIN-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C26H34ClN6O2P/c1-32(2)18-12-14-33(15-13-18)19-10-11-21(23(16-19)35-3)30-26-28-17-20(27)25(31-26)29-22-8-6-7-9-24(22)36(4,5)34/h6-11,16-18H,12-15H2,1-5H3,(H2,28,29,30,31) | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | AP26113 is a potent inhibitor of ALK with IC50 of 0.62 nM. | ||||||
| Targets | ALK | FER | ROS/ROS1 | FLT3 | FES/FPS | ||
| IC50 | 0.62 nM | 1.3 nM | 1.9 nM | 2.1 nM | 3.4 nM | ||

AP26113 Dilution Calculator

AP26113 Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 1.8903 mL | 9.4516 mL | 18.9032 mL | 37.8065 mL | 47.2581 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.3781 mL | 1.8903 mL | 3.7806 mL | 7.5613 mL | 9.4516 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.189 mL | 0.9452 mL | 1.8903 mL | 3.7806 mL | 4.7258 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0378 mL | 0.189 mL | 0.3781 mL | 0.7561 mL | 0.9452 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0189 mL | 0.0945 mL | 0.189 mL | 0.3781 mL | 0.4726 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
AP26113 is a novel, synthetic, orally available small-molecule inhibitor of anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK), which is a receptor tyrosine kinase in the insulin receptor superfamily, with half maximal inhibitory concentration IC50 ranging from 5 nmol/l to 11 nmol/l. AP26113 is also capable of inhibiting the ALK tyrosine kinase gatekeeper mutation L1196M (IC50: 15 nmol/l to 45 nmol/L), mutant epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) containing the gatekeeper T790M mutation and c-ros oncogene 1 (ROS1). Moreover, AP26113 has been found to be active against H3122 cells (both sensitive and resistant) and Ba/F3 cells harboring native or mutant EML4-ALK (IC50: 10 nM and 24 nM respectively).
References:
[1]Solomon B, Wilner KD, Shaw AT. Current status of targeted therapy for anaplastic lymphoma kinase-rearranged non-small cell lung cancer. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2014 Jan;95(1):15-23. doi: 10.1038/clpt.2013.200. Epub 2013 Oct 3.
[2]Katayama R1, Khan TM, Benes C, Lifshits E, Ebi H, Rivera VM, Shakespeare WC, Iafrate AJ, Engelman JA, Shaw AT. Therapeutic strategies to overcome crizotinib resistance in non-small cell lung cancers harboring the fusion oncogene EML4-ALK. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2011 May 3;108(18):7535-40. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1019559108. Epub 2011 Apr 18.
- 3-Furfuryl 2-pyrrolecarboxylate
Catalog No.:BCN6086
CAS No.:119767-00-9
- 29-Norlanosta-8,24-diene-1alpha,2alpha,3beta-triol
Catalog No.:BCN7984
CAS No.:119765-92-3
- Baohuoside VI
Catalog No.:BCC8129
CAS No.:119760-73-5
- Tautomycetin
Catalog No.:BCC7320
CAS No.:119757-73-2
- Schizanthine M
Catalog No.:BCN1939
CAS No.:119736-78-6
- Schizanthine G
Catalog No.:BCN1938
CAS No.:119736-74-2
- SB 206553 hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC7143
CAS No.:1197334-04-5
- SDZ 205-557 hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC7246
CAS No.:1197334-02-3
- Sazetidine A dihydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC7468
CAS No.:1197329-42-2
- TGR5 Receptor Agonist
Catalog No.:BCC4195
CAS No.:1197300-24-5
- Baohuoside VII
Catalog No.:BCN2889
CAS No.:119730-89-1
- Fupenzic acid
Catalog No.:BCN6085
CAS No.:119725-20-1
- Mirin
Catalog No.:BCC5986
CAS No.:1198097-97-0
- Sodium Channel inhibitor 1
Catalog No.:BCC1959
CAS No.:1198117-23-5
- Cerdulatinib (PRT062070)
Catalog No.:BCC8068
CAS No.:1198300-79-6
- Coptisine sulfate
Catalog No.:BCN2286
CAS No.:1198398-71-8
- Phyperunolide E
Catalog No.:BCN7292
CAS No.:1198400-52-0
- Esomeprazole magnesium salt
Catalog No.:BCC5430
CAS No.:1198768-91-0
- Posaconazole hydrate
Catalog No.:BCC4234
CAS No.:1198769-38-8
- CGRP 8-37 (human)
Catalog No.:BCC5724
CAS No.:119911-68-1
- 7-O-Methylmorroniside
Catalog No.:BCN7293
CAS No.:119943-46-3
- Peroxy Orange 1
Catalog No.:BCC6336
CAS No.:1199576-10-7
- 1,2-Didehydrotanshinone IIA
Catalog No.:BCN3143
CAS No.:119963-50-7
- INT-777
Catalog No.:BCC5390
CAS No.:1199796-29-6
Discovery of Brigatinib (AP26113), a Phosphine Oxide-Containing, Potent, Orally Active Inhibitor of Anaplastic Lymphoma Kinase.[Pubmed:27144831]
J Med Chem. 2016 May 26;59(10):4948-64.
In the treatment of echinoderm microtubule-associated protein-like 4 (EML4)-anaplastic lymphoma kinase positive (ALK+) non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC), secondary mutations within the ALK kinase domain have emerged as a major resistance mechanism to both first- and second-generation ALK inhibitors. This report describes the design and synthesis of a series of 2,4-diarylaminopyrimidine-based potent and selective ALK inhibitors culminating in identification of the investigational clinical candidate brigatinib. A unique structural feature of brigatinib is a phosphine oxide, an overlooked but novel hydrogen-bond acceptor that drives potency and selectivity in addition to favorable ADME properties. Brigatinib displayed low nanomolar IC50s against native ALK and all tested clinically relevant ALK mutants in both enzyme-based biochemical and cell-based viability assays and demonstrated efficacy in multiple ALK+ xenografts in mice, including Karpas-299 (anaplastic large-cell lymphomas [ALCL]) and H3122 (NSCLC). Brigatinib represents the most clinically advanced phosphine oxide-containing drug candidate to date and is currently being evaluated in a global phase 2 registration trial.
The Potent ALK Inhibitor Brigatinib (AP26113) Overcomes Mechanisms of Resistance to First- and Second-Generation ALK Inhibitors in Preclinical Models.[Pubmed:27780853]
Clin Cancer Res. 2016 Nov 15;22(22):5527-5538.
PURPOSE: Non-small cell lung cancers (NSCLCs) harboring ALK gene rearrangements (ALK(+)) typically become resistant to the first-generation anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK) tyrosine kinase inhibitor (TKI) crizotinib through development of secondary resistance mutations in ALK or disease progression in the brain. Mutations that confer resistance to second-generation ALK TKIs ceritinib and alectinib have also been identified. Here, we report the structure and first comprehensive preclinical evaluation of the next-generation ALK TKI brigatinib. EXPERIMENTAL DESIGN: A kinase screen was performed to evaluate the selectivity profile of brigatinib. The cellular and in vivo activities of ALK TKIs were compared using engineered and cancer-derived cell lines. The brigatinib-ALK co-structure was determined. RESULTS: Brigatinib potently inhibits ALK and ROS1, with a high degree of selectivity over more than 250 kinases. Across a panel of ALK(+) cell lines, brigatinib inhibited native ALK (IC50, 10 nmol/L) with 12-fold greater potency than crizotinib. Superior efficacy of brigatinib was also observed in mice with ALK(+) tumors implanted subcutaneously or intracranially. Brigatinib maintained substantial activity against all 17 secondary ALK mutants tested in cellular assays and exhibited a superior inhibitory profile compared with crizotinib, ceritinib, and alectinib at clinically achievable concentrations. Brigatinib was the only TKI to maintain substantial activity against the most recalcitrant ALK resistance mutation, G1202R. The unique, potent, and pan-ALK mutant activity of brigatinib could be rationalized by structural analyses. CONCLUSIONS: Brigatinib is a highly potent and selective ALK inhibitor. These findings provide the molecular basis for the promising activity being observed in ALK(+), crizotinib-resistant patients with NSCLC being treated with brigatinib in clinical trials. Clin Cancer Res; 22(22); 5527-38. (c)2016 AACR.
Treatment Efficacy and Resistance Mechanisms Using the Second-Generation ALK Inhibitor AP26113 in Human NPM-ALK-Positive Anaplastic Large Cell Lymphoma.[Pubmed:25421750]
Mol Cancer Res. 2015 Apr;13(4):775-83.
UNLABELLED: ALK is a tyrosine kinase receptor involved in a broad range of solid and hematologic tumors. Among 70% to 80% of ALK(+) anaplastic large cell lymphomas (ALCL) are caused by the aberrant oncogenic fusion protein NPM-ALK. Crizotinib was the first clinically relevant ALK inhibitor, now approved for the treatment of late-stage and metastatic cases of lung cancer. However, patients frequently develop drug resistance to Crizotinib, mainly due to the appearance of point mutations located in the ALK kinase domain. Fortunately, other inhibitors are available and in clinical trial, suggesting the potential for second-line therapies to overcome Crizotinib resistance. This study focuses on the ongoing phase I/II trial small-molecule tyrosine kinase inhibitor (TKI) AP26113, by Ariad Pharmaceuticals, which targets both ALK and EGFR. Two NPM-ALK(+) human cell lines, KARPAS-299 and SUP-M2, were grown in the presence of increasing concentrations of AP26113, and eight lines were selected that demonstrated resistance. All lines show IC50 values higher (130 to 1,000-fold) than the parental line. Mechanistically, KARPAS-299 populations resistant to AP26113 show NPM-ALK overexpression, whereas SUP-M2-resistant cells harbor several point mutations spanning the entire ALK kinase domain. In particular, amino acid substitutions: L1196M, S1206C, the double F1174V+L1198F and L1122V+L1196M mutations were identified. The knowledge of the possible appearance of new clinically relevant mechanisms of drug resistance is a useful tool for the management of new TKI-resistant cases. IMPLICATIONS: This work defines reliable ALCL model systems of AP26113 resistance and provides a valuable tool in the management of all cases of relapse upon NPM-ALK-targeted therapy.


