INT-777TGR5 receptor agonist, potent and selective CAS# 1199796-29-6 |
- GW1929
Catalog No.:BCC1611
CAS No.:196808-24-9
- Balaglitazone
Catalog No.:BCC1395
CAS No.:199113-98-9
- Inolitazone dihydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC1653
CAS No.:223132-38-5
- Aleglitazar
Catalog No.:BCC1337
CAS No.:475479-34-6
- L-165041
Catalog No.:BCC1687
CAS No.:79558-09-1
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 1199796-29-6 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 45483949 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C27H46O5 | M.Wt | 450.65 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Synonyms | S-EMCA | ||
| Solubility | Ethanol : ≥ 50 mg/mL (110.95 mM) DMSO : ≥ 31 mg/mL (68.79 mM) *"≥" means soluble, but saturation unknown. | ||
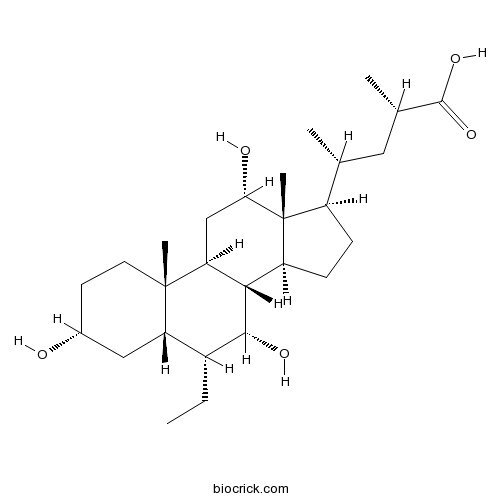
| Chemical Name | (2S,4R)-4-[(3R,5S,6R,7R,8R,9S,10S,12S,13R,14S,17R)-6-ethyl-3,7,12-trihydroxy-10,13-dimethyl-2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,11,12,14,15,16,17-tetradecahydro-1H-cyclopenta[a]phenanthren-17-yl]-2-methylpentanoic acid | ||
| SMILES | CCC1C2CC(CCC2(C3CC(C4(C(C3C1O)CCC4C(C)CC(C)C(=O)O)C)O)C)O | ||
| Standard InChIKey | NPBCMXATLRCCLF-IRRLEISYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C27H46O5/c1-6-17-20-12-16(28)9-10-26(20,4)21-13-22(29)27(5)18(14(2)11-15(3)25(31)32)7-8-19(27)23(21)24(17)30/h14-24,28-30H,6-13H2,1-5H3,(H,31,32)/t14-,15+,16-,17-,18-,19+,20+,21+,22+,23+,24-,26+,27-/m1/s1 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | INT-777 is a potent TGR5 agonist with EC50 of 0.82 μM.In Vitro:INT-777 is a novel potent and selective TGR5 agonist with remarkable in vivo activity[1]. INT-777 (3 μM) increases ATP production in the human enteroendocrine cell line NCI-H716 in a cAMP-dependent manner[2]. INT-777 (10 μM) lowers Isc and increases TEER when added on the serosal side of seromuscular stripped distal colon segments. INT-777 effect on basal secretion is reduced in neuron-free and TTX-treated mucosal-submucosal preparations[3].In Vivo:INT-777 (1 μM/min/kg, p.o.) has a potent choleretic effect, prevents carboxyl CoA activation and subsequent conjugation, thereby favoring its cholehepatic shunt pathway with a ductular absorption and a potent choleretic effect in HF-fed TGR5-Tg male mice[1]. INT-777 (30 mg/kg/day, p.o.) increases energy expenditure and reduces hepatic steatosis and obesity upon high fat feeding, and improves insulin sensitivity, in TGR5-Tg mice[2]. References: | |||||
| Cell experiment [1]: | |
| Cell lines | RAW264.7 cells |
| Preparation method | Limited solubility. General tips for obtaining a higher concentration: Please warm the tube at 37 ℃ for 10 minutes and/or shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while. Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. |
| Reacting condition | 37oC |
| Applications | Combined LPS-INT-777 treatment significantly attenuates the transient increase in mRNA levels for Tnfa, monocyte chemoattractant protein 1 (Mcp-1), Il-6, and Il-1b. INT-777 also markedly diminishes p65 translocation via TGR5 activation; in contrast to the unchanged the phosphorylation of c-Jun. |
| Animal experiment [1]: | |
| Animal models | TGR5 genetic models |
| Dosage form | 30 mg/kg/day. |
| Application | INT-777 inhibits atherosclerosis through activation of TGR5 in leukocytes. In Ldlr-/- mice transplanted with bone marrow of Tgr5+/+ mice, INT-777 treatment causes less vascular lesion, indicating the solid inhibitory effect of INT-777 on development of atherosclerosis. |
| Other notes | Please test the solubility of all compounds indoor, and the actual solubility may slightly differ with the theoretical value. This is caused by an experimental system error and it is normal. |
| References: 1. Pols TW, Nomura M, Harach T et al. TGR5 activation inhibits atherosclerosis by reducing macrophage inflammation and lipid loading. Cell Metab. 2011 Dec 7;14(6):747-57. | |

INT-777 Dilution Calculator

INT-777 Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.219 mL | 11.0951 mL | 22.1902 mL | 44.3803 mL | 55.4754 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.4438 mL | 2.219 mL | 4.438 mL | 8.8761 mL | 11.0951 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.2219 mL | 1.1095 mL | 2.219 mL | 4.438 mL | 5.5475 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0444 mL | 0.2219 mL | 0.4438 mL | 0.8876 mL | 1.1095 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0222 mL | 0.111 mL | 0.2219 mL | 0.4438 mL | 0.5548 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
INT-777 (S-EMCA) is a potent and selective agonist of TGR5 receptor with EC50 value of 0.82 μM [1].
TGR5 receptor is a G protein-coupled receptor and functions as a cell surface receptor for bile acids. TGR5 receptor plays an important role in the regulation of energy homeostasis by bile acids and suppression of macrophage functions [1].
INT-777 (S-EMCA) is a potent and selective TGR5 receptor agonist [1]. In macrophages, INT-777 inhibited proinflammatory cytokine production by TGR5-induced cAMP signaling and subsequent NF-kB inhibition [2]. In pancreatic β cell line MIN6, INT-777 selectively activated Gαs and increased intracellular cAMP and Ca2+. INT-777 also increased phosphoinositide (PI) hydrolysis and insulin release, which was dependent on Gs/cAMP/Ca2+ pathway [3]. In human podocytes with high glucose, INT-777 induced mitochondrial biogenesis, increased fatty acid β-oxidation and decreased oxidative stress [4].
In Ldlr- /- Tgr5+/+ mice, INT-777 activated TGR5 and attenuated atherosclerosis, which was associated with less plaque macrophage content and decreased intraplaque inflammation [2]. In diabetic db/db mice, INT-777 decreased mitochondrial H2O2 production and increased SOD2 activity, then reduced proteinuria, mesangial expansion, podocyte injury, fibrosis, and CD68 macrophage infiltration in the kidney [4].
References:
[1]. Pellicciari R, Gioiello A, Macchiarulo A, et al. Discovery of 6alpha-ethyl-23(S)-methylcholic acid (S-EMCA, INT-777) as a potent and selective agonist for the TGR5 receptor, a novel target for diabesity. J Med Chem, 2009, 52(24): 7958-7961.
[2]. Pols TW, Nomura M, Harach T, et al. TGR5 activation inhibits atherosclerosis by reducing macrophage inflammation and lipid loading. Cell Metab, 2011, 14(6): 747-757.
[3]. Kumar DP, Rajagopal S, Mahavadi S, et al. Activation of transmembrane bile acid receptor TGR5 stimulates insulin secretion in pancreatic β cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 2012, 427(3): 600-605.
[4]. Wang XX, Edelstein MH, Gafter U, et al. G Protein-Coupled Bile Acid Receptor TGR5 Activation Inhibits Kidney Disease in Obesity and Diabetes. J Am Soc Nephrol, 2015. pii: ASN.2014121271.
- 1,2-Didehydrotanshinone IIA
Catalog No.:BCN3143
CAS No.:119963-50-7
- Peroxy Orange 1
Catalog No.:BCC6336
CAS No.:1199576-10-7
- 7-O-Methylmorroniside
Catalog No.:BCN7293
CAS No.:119943-46-3
- CGRP 8-37 (human)
Catalog No.:BCC5724
CAS No.:119911-68-1
- Posaconazole hydrate
Catalog No.:BCC4234
CAS No.:1198769-38-8
- Esomeprazole magnesium salt
Catalog No.:BCC5430
CAS No.:1198768-91-0
- Phyperunolide E
Catalog No.:BCN7292
CAS No.:1198400-52-0
- Coptisine sulfate
Catalog No.:BCN2286
CAS No.:1198398-71-8
- Cerdulatinib (PRT062070)
Catalog No.:BCC8068
CAS No.:1198300-79-6
- Sodium Channel inhibitor 1
Catalog No.:BCC1959
CAS No.:1198117-23-5
- Mirin
Catalog No.:BCC5986
CAS No.:1198097-97-0
- AP26113
Catalog No.:BCC1069
CAS No.:1197958-12-5
- Unedone
Catalog No.:BCN6759
CAS No.:1199815-09-2
- Sulfuretin
Catalog No.:BCN4725
CAS No.:120-05-8
- Scoparone
Catalog No.:BCN6088
CAS No.:120-08-1
- Veratraldehyde
Catalog No.:BCN6089
CAS No.:120-14-9
- Tropine benzilate
Catalog No.:BCN1921
CAS No.:3736-36-5
- Clorofene
Catalog No.:BCC8919
CAS No.:120-32-1
- 3-Amino-4-methoxybenzanilide
Catalog No.:BCC8613
CAS No.:120-35-4
- Desoxyanisoin
Catalog No.:BCN2264
CAS No.:120-44-5
- Ethylparaben
Catalog No.:BCN6094
CAS No.:120-47-8
- Benzyl benzoate
Catalog No.:BCN8521
CAS No.:120-51-4
- Isosafrole
Catalog No.:BCC3976
CAS No.:120-58-1
- 2'-Methylacetanilide
Catalog No.:BCC8581
CAS No.:120-66-1
Reduction of epithelial secretion in male rat distal colonic mucosa by bile acid receptor TGR5 agonist, INT-777: role of submucosal neurons.[Pubmed:27259385]
Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2016 Nov;28(11):1663-1676.
BACKGROUND: Recent evidence from rat neuron-free mucosa study suggests that the membrane bile acid receptor TGR5 decreases colonic secretion under basal and stimulated conditions. As submucosal neurons are key players in secretory processes and highly express TGR5, we investigated their role in TGR5 agonist-induced inhibition of secretion and the pathways recruited. METHODS: TGR5 expression and localization were assessed in rat proximal (pC) and distal (dC) colon by qPCR and immunohistochemistry with double labeling for cholinergic neurons in whole-mount preparations. The influence of a selective (INT-777) or weak (ursodeoxycholic acid, UDCA) TGR5 agonist on colonic secretion was assessed in Ussing chambers, in dC preparation removing seromuscular +/- submucosal tissues, in the presence of different inhibitors of secretion pathways. KEY RESULTS: TGR5 mRNA is expressed in full thickness dC and pC and immunoreactivity is located in colonocytes and pChAT-positive neurons. Addition of INT-777, and less potently UDCA, decreased colonic secretion in seromuscular stripped dC by -58.17+/- 2.6%. INT-777 effect on basal secretion was reduced in neuron-free and TTX-treated mucosal-submucosal preparations. Atropine, hexamethonium, indomethacin, and L-NAME all reduced significantly INT-777's inhibitory effect while the 5-HT4 antagonist, RS-39604, and lidocaine abolished it. INT-777 inhibited stimulated colonic secretion induced by nicotine, but not cisapride, carbachol or PGE2. CONCLUSIONS & INFERENCES: TGR5 activation inhibits basal and stimulated distal colonic secretion in rats by acting directly on epithelial cells and also inhibiting submucosal neurons. This could represent a counter-regulatory mechanism, at the submucosal level, of the known prosecretory effect of bile acids in the colon.
Discovery of 6alpha-ethyl-23(S)-methylcholic acid (S-EMCA, INT-777) as a potent and selective agonist for the TGR5 receptor, a novel target for diabesity.[Pubmed:20014870]
J Med Chem. 2009 Dec 24;52(24):7958-61.
In the framework of the design and development of TGR5 agonists, we reported that the introduction of a C(23)(S)-methyl group in the side chain of bile acids such as chenodeoxycholic acid (CDCA) and 6-ethylchenodeoxycholic acid (6-ECDCA, INT-747) affords selectivity for TGR5. Herein we report further lead optimization efforts that have led to the discovery of 6alpha-ethyl-23(S)-methylcholic acid (S-EMCA, INT-777) as a novel potent and selective TGR5 agonist with remarkable in vivo activity.


