SulfuretinCAS# 120-05-8 |
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 120-05-8 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 5281295 | Appearance | Yellow powder |
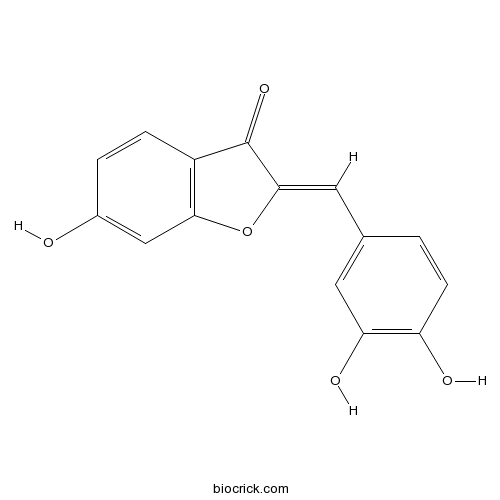
| Formula | C15H10O5 | M.Wt | 270.24 |
| Type of Compound | Flavonoids | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | Soluble in Chloroform,Dichloromethane,Ethyl Acetate,DMSO,Acetone,etc. | ||
| Chemical Name | (2Z)-2-[(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)methylidene]-6-hydroxy-1-benzofuran-3-one | ||
| SMILES | C1=CC(=C(C=C1C=C2C(=O)C3=C(O2)C=C(C=C3)O)O)O | ||
| Standard InChIKey | RGNXWPVNPFAADO-NSIKDUERSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C15H10O5/c16-9-2-3-10-13(7-9)20-14(15(10)19)6-8-1-4-11(17)12(18)5-8/h1-7,16-18H/b14-6- | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | 1. Sulfuretin may have therapeutic value in preventing or delaying the progression of rheumatoid arthritis. 2. Sulfuretin has therapeutical effect on leukemia, due to its potent apoptotic activity through the extrinsic pathway driven by a Fas-mediated caspase-8-dependent pathway. 3. Sulfuretin is a potent anti-oxidant, has protective effect against t-BHP-induced oxidative damage in human liver-derived HepG2 cells is attributable to its ability to scavenge ROS and up-regulate the activity of HO-1 through the Nrf2/ARE and JNK/ERK signaling pathways. 4. Sulfuretin may have a potential role for neuroprotection, possibly through inhibition of phosphorylation of MAPK, PI3K/Akt, and GSK-3β, which leads to mitochondrial protection, NF-κB modulations and subsequent suppression of apoptosis via ROS-dependent pathwaysand, may be used as a therapeutic agent for PD. |
| Targets | PI3K | Akt | GSK-3 | NF-kB | p38MAPK | ERK | JNK | ROS | HO-1 | Nrf2 | JNK | Caspase | P450 (e.g. CYP17) | TNF-α |

Sulfuretin Dilution Calculator

Sulfuretin Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 3.7004 mL | 18.5021 mL | 37.0041 mL | 74.0083 mL | 92.5104 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.7401 mL | 3.7004 mL | 7.4008 mL | 14.8017 mL | 18.5021 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.37 mL | 1.8502 mL | 3.7004 mL | 7.4008 mL | 9.251 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.074 mL | 0.37 mL | 0.7401 mL | 1.4802 mL | 1.8502 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.037 mL | 0.185 mL | 0.37 mL | 0.7401 mL | 0.9251 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- Unedone
Catalog No.:BCN6759
CAS No.:1199815-09-2
- INT-777
Catalog No.:BCC5390
CAS No.:1199796-29-6
- 1,2-Didehydrotanshinone IIA
Catalog No.:BCN3143
CAS No.:119963-50-7
- Peroxy Orange 1
Catalog No.:BCC6336
CAS No.:1199576-10-7
- 7-O-Methylmorroniside
Catalog No.:BCN7293
CAS No.:119943-46-3
- CGRP 8-37 (human)
Catalog No.:BCC5724
CAS No.:119911-68-1
- Posaconazole hydrate
Catalog No.:BCC4234
CAS No.:1198769-38-8
- Esomeprazole magnesium salt
Catalog No.:BCC5430
CAS No.:1198768-91-0
- Phyperunolide E
Catalog No.:BCN7292
CAS No.:1198400-52-0
- Coptisine sulfate
Catalog No.:BCN2286
CAS No.:1198398-71-8
- Cerdulatinib (PRT062070)
Catalog No.:BCC8068
CAS No.:1198300-79-6
- Sodium Channel inhibitor 1
Catalog No.:BCC1959
CAS No.:1198117-23-5
- Scoparone
Catalog No.:BCN6088
CAS No.:120-08-1
- Veratraldehyde
Catalog No.:BCN6089
CAS No.:120-14-9
- Tropine benzilate
Catalog No.:BCN1921
CAS No.:3736-36-5
- Clorofene
Catalog No.:BCC8919
CAS No.:120-32-1
- 3-Amino-4-methoxybenzanilide
Catalog No.:BCC8613
CAS No.:120-35-4
- Desoxyanisoin
Catalog No.:BCN2264
CAS No.:120-44-5
- Ethylparaben
Catalog No.:BCN6094
CAS No.:120-47-8
- Benzyl benzoate
Catalog No.:BCN8521
CAS No.:120-51-4
- Isosafrole
Catalog No.:BCC3976
CAS No.:120-58-1
- 2'-Methylacetanilide
Catalog No.:BCC8581
CAS No.:120-66-1
- N,N'-Bis(salicylidene)-1,3-propanediamine
Catalog No.:BCC9063
CAS No.:120-70-7
- 1,2-Benzenediol
Catalog No.:BCN6103
CAS No.:120-80-9
Sulfuretin-induced miR-30C selectively downregulates cyclin D1 and D2 and triggers cell death in human cancer cell lines.[Pubmed:23318178]
Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2013 Feb 15;431(3):572-8.
Sulfuretin (3',4',6'-trihydroxyaurone), one of the key flavonoids isolated from Rhus verniciflua, is known to suppress inflammation and oxidative stress. However, the anti-cancer properties of Sulfuretin as well as its mechanism of action remain poorly understood. Here, we show that the expression of miR-30C is markedly enhanced in Sulfuretin-stimulated cells, consequently promoting apoptosis and cell cycle arrest in human cancer cell lines. The transient transfection of pre-miR-30C resulted in greater than 70% growth inhibition in PC-3 cells and provided strong evidence that miR-30C selectively suppresses the expression of cyclin D1 and D2, but not cyclin D3. Target validation analysis revealed that 3'-UTR of cyclin D2 is a direct target of miR-30C, whereas suppression by miR-30C of cyclin D1 may occur through indirect mRNA regulation. In addition, silencing miR-30C expression partially reversed Sulfuretin-induced cell death. Taken together, our data suggest that miR-30C, a tumor suppressor miRNA, contributes to anti-cancer properties of Sulfuretin by negatively regulating cyclin D1 and D2, providing important implications of Sulfuretin and miR-30C for the therapeutic intervention of human cancers.
Sulfuretin, a major flavonoid isolated from Rhus verniciflua, ameliorates experimental arthritis in mice.[Pubmed:22521292]
Life Sci. 2012 May 22;90(19-20):799-807.
AIM: Sulfuretin, a major flavonoid isolated from Rhus verniciflua, is known to have anti-inflammatory effects. However, the mechanisms underlying the anti-inflammatory effect of Sulfuretin on rheumatoid arthritis have not been elucidated. In this study we investigated whether Sulfuretin treatment modulates the severity of arthritis in an experimental model. MAIN METHODS: We evaluated the effects of Sulfuretin on tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-alpha)-treated human rheumatoid fibroblast-like synoviocytes (FLS) in vitro and on collagen-induced arthritis (CIA) mice in vivo. KEY FINDINGS: In vitro experiments demonstrated that Sulfuretin suppressed the chemokine production, matrix metalloproteinase secretion, and cell proliferation induced by tumor necrosis factor-alpha in rheumatoid FLS. In addition, Sulfuretin inhibited the osteoclast differentiation induced by macrophage colony-stimulating factor and receptor activator of NF-kappaB ligand in bone marrow macrophages. In mice with CIA, early intervention with Sulfuretin prevented joint destruction, as evidenced by a lower cumulative disease incidence and an absence of diverse disease features based on hind paw thickness, radiologic and histopathologic findings, and inflammatory cytokine levels. In mice with established arthritis, Sulfuretin treatment significantly reduced synovial inflammation and joint destruction. The in vitro and in vivo protective effects of Sulfuretin were mediated by inhibition of the NF-kappaB signaling pathway. SIGNIFICANCE: These results suggest that using Sulfuretin to block the NF-kappaB pathway in rheumatoid joints reduces both inflammatory responses and joint destruction. Therefore, Sulfuretin may have therapeutic value in preventing or delaying the progression of rheumatoid arthritis.
The cytoprotective effect of sulfuretin against tert-butyl hydroperoxide-induced hepatotoxicity through Nrf2/ARE and JNK/ERK MAPK-mediated heme oxygenase-1 expression.[Pubmed:24857917]
Int J Mol Sci. 2014 May 19;15(5):8863-77.
Sulfuretin is one of the major flavonoid components in Rhus verniciflua Stokes (Anacardiaceae) isolates. In this study, we investigated the protective effects of Sulfuretin against tert-butyl hydroperoxide (t-BHP)-induced oxidative injury. The results indicated that the addition of Sulfuretin before t-BHP treatment significantly inhibited cytotoxicity and reactive oxygen species (ROS) production in human liver-derived HepG2 cells. Sulfuretin up-regulated the activity of the antioxidant enzyme heme oxygenase (HO)-1 via nuclear factor E2-related factor 2 (Nrf2) translocation into the nucleus and increased the promoter activity of the antioxidant response element (ARE). Moreover, Sulfuretin exposure enhanced the phosphorylation of c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK) and extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2 (ERK1/2), which are members of the mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) family. Furthermore, cell treatment with a JNK inhibitor (SP600125) and ERK inhibitor (PD98059) reduced Sulfuretin-induced HO-1 expression and decreased its protective effects. Taken together, these results suggest that the protective effect of Sulfuretin against t-BHP-induced oxidative damage in human liver-derived HepG2 cells is attributable to its ability to scavenge ROS and up-regulate the activity of HO-1 through the Nrf2/ARE and JNK/ERK signaling pathways. Therefore, Sulfuretin could be advantageous as a bioactive source for the prevention of oxidative injury.
Sulfuretin inhibits 6-hydroxydopamine-induced neuronal cell death via reactive oxygen species-dependent mechanisms in human neuroblastoma SH-SY5Y cells.[Pubmed:24801546]
Neurochem Int. 2014 Jul;74:53-64.
Sulfuretin, a potent anti-oxidant, has been thought to provide health benefits by decreasing the risk of oxidative stress-related diseases. In this study, we investigated the mechanisms of Sulfuretin protection of neuronal cells from cell death induced by the Parkinson's disease (PD)-related neurotoxin 6-hydroxydopamine (6-OHDA). We examined whether Sulfuretin acts as an anti-oxidant to reduce oxidative stress and mitochondrial-mediated apoptotic cascade events in 6-OHDA-induced neurotoxicity in SH-SY5Y cells. We also investigated whether Sulfuretin specifically acts by inhibiting phosphorylation of mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK), phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K)/Akt, and glycogen synthase kinase-3beta (GSK-3beta) as well as activation of the nuclear factor-kappa B (NF-kappaB) pathway. Sulfuretin significantly inhibited neuronal cell death, neurotoxicity, apoptosis, and reactive oxygen species (ROS) production. Sulfuretin also strikingly attenuated 6-OHDA-induced mitochondrial dysfunction. Moreover, Sulfuretin significantly attenuated 6-OHDA-induced phosphorylation of c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK), p38, extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2 (ERK 1/2) MAPKs, PI3K/Akt, and GSK-3beta. Eventually, Sulfuretin inhibited 6-OHDA-induced NF-kappaB translocation to the nucleus induced by 6-OHDA. The results of the current study provide the first evidence that Sulfuretin protects SH-SY5Y cells against 6-OHDA-induced neuronal cell death, possibly through inhibition of phosphorylation of MAPK, PI3K/Akt, and GSK-3beta, which leads to mitochondrial protection, NF-kappaB modulations and subsequent suppression of apoptosis via ROS-dependent pathways. Thus, we conclude that Sulfuretin may have a potential role for neuroprotection and, therefore, may be used as a therapeutic agent for PD.
Sulfuretin from heartwood of Rhus verniciflua triggers apoptosis through activation of Fas, Caspase-8, and the mitochondrial death pathway in HL-60 human leukemia cells.[Pubmed:22492309]
J Cell Biochem. 2012 Sep;113(9):2835-44.
Sulfuretin, a flavonoid isolated from heartwood of Rhus verniciflua, has been reported to have anti-cancer activities but the underlying molecular mechanism was not clear. In this study, Sulfuretin induced apoptosis by activating caspases-8, -9, and -3 as well as cleavage of poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase. Furthermore, treatment with Sulfuretin caused mitochondrial dysfunctions, including the loss of mitochondrial membrane potential (DeltaPsi(m)), the release of cytochrome c to the cytosol, and the translocations of Bax and tBid. Sulfuretin also activated the extrinsic apoptosis pathway, that is, it increased the expressions of Fas and FasL, the activation of caspase-8, and the cleavage of Bid. Furthermore, blocking the FasL-Fas interaction with NOK-1 monoclonal antibody prevented the Sulfuretin-induced apoptosis. The therapeutical effect of Sulfuretin in leukemia is due to its potent apoptotic activity through the extrinsic pathway driven by a Fas-mediated caspase-8-dependent pathway.


