Ajuforrestin BCAS# 708277-48-9 |
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 708277-48-9 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 162343338.0 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C20H22O4 | M.Wt | 326.39 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | Soluble in Chloroform,Dichloromethane,Ethyl Acetate,DMSO,Acetone,etc. | ||
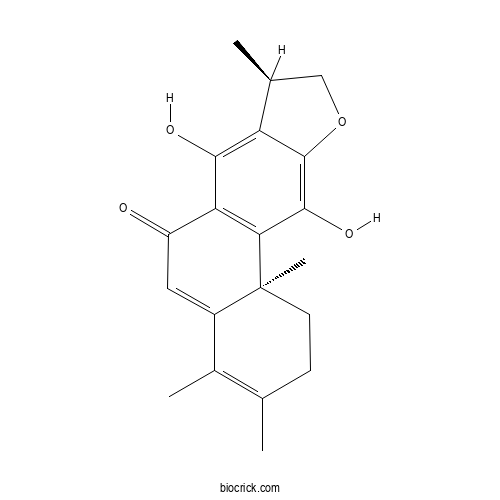
| Chemical Name | (8R,11bS)-7,11-dihydroxy-3,4,8,11b-tetramethyl-1,2,8,9-tetrahydronaphtho[2,1-f][1]benzofuran-6-one | ||
| SMILES | CC1COC2=C(C3=C(C(=O)C=C4C3(CCC(=C4C)C)C)C(=C12)O)O | ||
| Standard InChIKey | YOJNWDYXALZJGT-FVINQWEUSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C20H22O4/c1-9-5-6-20(4)12(11(9)3)7-13(21)15-16(20)18(23)19-14(17(15)22)10(2)8-24-19/h7,10,22-23H,5-6,8H2,1-4H3/t10-,20-/m0/s1 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||

Ajuforrestin B Dilution Calculator

Ajuforrestin B Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 3.0638 mL | 15.3191 mL | 30.6382 mL | 61.2764 mL | 76.5955 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.6128 mL | 3.0638 mL | 6.1276 mL | 12.2553 mL | 15.3191 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.3064 mL | 1.5319 mL | 3.0638 mL | 6.1276 mL | 7.6595 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0613 mL | 0.3064 mL | 0.6128 mL | 1.2255 mL | 1.5319 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0306 mL | 0.1532 mL | 0.3064 mL | 0.6128 mL | 0.766 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- Pseudoginsenoside F8
Catalog No.:BCX1333
CAS No.:69884-01-1
- β-D-Glucopyranoside, (3β,12β)-20-[(6-O-α-L-arabinofuranosyl-β-D-glucopyranosyl)oxy]-12-hydroxydammar-24-en-3-yl 2-O-β-D-glucopyranosyl-, 6-acetate
Catalog No.:BCX1332
CAS No.:1613477-95-4
- Pseudoginsenoside RC1
Catalog No.:BCX1331
CAS No.:102805-32-3
- Quinquenoside III
Catalog No.:BCX1330
CAS No.:208764-53-8
- Multiflorin A
Catalog No.:BCX1329
CAS No.:1350028-90-8
- Multiflorin B
Catalog No.:BCX1328
CAS No.:52657-01-9
- 6-Methylrhein
Catalog No.:BCX1327
CAS No.:401621-27-0
- Methyllycaconitine
Catalog No.:BCX1326
CAS No.:21019-30-7
- Lycaconitine
Catalog No.:BCX1325
CAS No.:25867-19-0
- Anhydronotoptol
Catalog No.:BCX1324
CAS No.:88206-51-3
- Decuroside V
Catalog No.:BCX1323
CAS No.:96648-59-8
- 5-MethoxyPinocembroside
Catalog No.:BCX1322
CAS No.:1450878-89-3
- Ilexoside XLVIII
Catalog No.:BCX1335
CAS No.:129095-76-7
- Gosferol
Catalog No.:BCX1336
CAS No.:37551-62-5
- rel-(+)-(1R,2Z,7Z,10S,11S)-10-(Acetyloxy)-7,12,12-trimethylbicyclo[9.1.0]dodeca-2,7-dien-4-one
Catalog No.:BCX1337
CAS No.:886439-01-6
- Phloyoside I
Catalog No.:BCX1338
CAS No.:139757-58-7
- Dracaenoside F
Catalog No.:BCX1339
CAS No.:109460-83-5
- Linderanine C
Catalog No.:BCX1340
CAS No.:139681-96-2
- Paratocarpin K
Catalog No.:BCX1341
CAS No.:170900-13-7
- 3'-Methoxycoumestrol
Catalog No.:BCX1342
CAS No.:13360-66-2
- 8-Geranyl daidzein
Catalog No.:BCX1343
CAS No.:1072940-16-9
- 6β-Hydroxy-7-epiloganin
Catalog No.:BCX1344
CAS No.:125410-28-8
- 9-epi-Phlomiol
Catalog No.:BCX1345
CAS No.:1621720-47-5
- 5, 9-epi-Phlomiol
Catalog No.:BCX1346
CAS No.:1621908-70-0
A newly developed UPLC-MS/MS method for simultaneous quantitative analysis of ajuforrestin A, ajuforrestin B, ajugamacrin and 8-O-acetylharpagide derived from Ajuga plants in mice blood and the in vivo pharmacokinetics.[Pubmed:38456836]
Drug Dev Ind Pharm. 2024 Apr;50(4):354-362.
OBJECTIVE: To develop a sensitive and fast detection method via ultra-performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry (UPLC-MS/MS) to assess the concentration of ajuforrestin A, Ajuforrestin B, ajugamacrin and 8-O-Acetylharpagide primarily derived from Ajuga plants in mice blood and their pharmacokinetics. METHODS: Single protein precipitation with high-proportioned acetonitrile is chosen for sample clean-up. The UPLC HSS T3 (2.1 mm x 100 mm, 1.8 microm) column with a mobile phase in gradient elution mode at the flow rate of 0.4 mL/min was used for sample separation. Acetonitrile was selected as the organic phase solution and water containing 0.1% formic acid was chosen as the aqueous solution. A tandem mass spectrometer containing an electrospray ionization (ESI) source in the positive ionization mode was used to detect four compounds via multiple reaction monitoring (MRM). RESULTS: The calibration curves (5-1000 ng/mL) of four compounds were linear with correlation coefficients > 0.997. The matrix effects, accuracy, precision, and recovery were all within permissible scope. CONCLUSIONS: In this approach, the corresponding pharmacokinetic parameters were successfully clarified in mouse for the first time, which provided a theoretical basis for the improvement of the standard of Ajuga plants and the safety of clinical medication. Furthermore, this method may provide the UPLC-MS/MS evidence for the differentiation of the main close relative varieties of genus Ajuga according to these plants contain different mixtures of the four marker compounds.
Antifeedant, cytotoxic, and anti-inflammatory neo-clerodane diterpenoids in the peltate glandular trichomes and fresh leaves of Ajuga forrestii.[Pubmed:33721797]
Phytochemistry. 2021 Jun;186:112731.
The Lamiaceae plant Ajuga forrestii Diels is a traditional Chinese herbal medicine with abundant glandular trichomes (GTs), but their chemistry and biological functions remain uninvestigated. Here, a panel of six highly functionalized neo-clerodane diterpenoids was localized to the peltate GTs of A. forrestii using laser microdissection coupled with HPLC analysis, indicating that the GTs of A. forrestii are an excellent material for the elucidation of the yet unclear biosynthetic pathway of natural neo-clerodane diterpenoids. In addition, four undescribed neo-clerodane diterpenoids with an acyclic C-9 side chain including two pairs of 1:1 mixture of inseparable diastereomers, ajuforrestins D-G, were isolated from the fresh leaves of A. forrestii together with six known compounds. The structures of the undescribed compounds were elucidated by spectroscopic (including 1D and 2D NMR and HR-ESI-MS) analyses. Biological assays indicated that the major GT compound ajugacumbin B and undescribed ajuforrestins D/E showed antifeedant activity against Helicoverpa armigera, suggesting that neo-clerodanes in A. forrestii should be involved in plant defence against insects. Moreover, the abietane diterpenoid Ajuforrestin B exhibited significant anti-inflammatory activity on the secretion of interleukin-2 (IL-2) and cytotoxicity against three cancer cell lines, NCI-H1975, HepG2 and MCF-7, suggesting that Ajuforrestin B could positively contribute to the therapeutic effects of this traditional Chinese medicine.


