Alpha-pineneCAS# 80-56-8 |
- (-)-alpha-Pinene
Catalog No.:BCC8295
CAS No.:2437-95-8
- (1R)-(+)-Alpha-Pinene
Catalog No.:BCC8275
CAS No.:7785-70-8
- (1S)-(-)-α-Pinene
Catalog No.:BCN9076
CAS No.:7785-26-4
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 80-56-8 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 6654 | Appearance | Colorless liquid |
| Formula | C10H16 | M.Wt | 136.2 |
| Type of Compound | Monoterpenoids | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Synonyms | Acintene A; 2-Pinene; Sylvapine A | ||
| Solubility | Soluble in ethanol; insoluble in water | ||
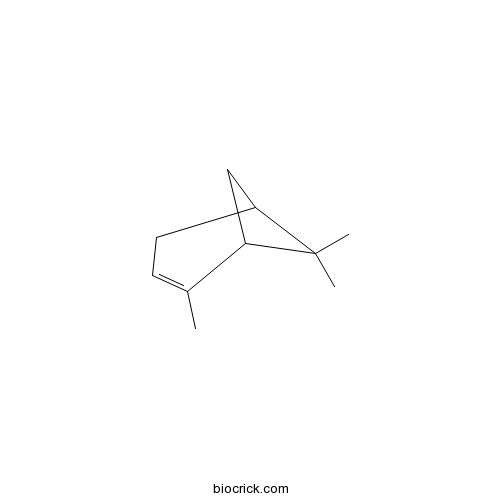
| Chemical Name | 4,6,6-trimethylbicyclo[3.1.1]hept-3-ene | ||
| SMILES | CC1=CCC2CC1C2(C)C | ||
| Standard InChIKey | GRWFGVWFFZKLTI-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Alpha-pinene inhibits the nuclear translocation of NF-kappa B induced by LPS in THP-1 cells, and this effect is partly due to the upregulation of I kappa B alpha expression. Alpha-pinene inhibits early root growth and causes oxidative damage in root tissue through enhanced generation of ROS, as indicated by increased lipid peroxidation, disruption of membrane integrity and elevated antioxidant enzyme levels. |
| Targets | NF-kB | p65 | ROS |
| In vitro | Effect of alpha-pinene on nuclear translocation of NF-kappa B in THP-1 cells.[Pubmed: 15066217]Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2004 Apr;25(4):480-4.
|
| Kinase Assay | alpha-Pinene inhibits growth and induces oxidative stress in roots.[Pubmed: 17028297 ]Ann Bot. 2006 Dec;98(6):1261-9.Determining the mode of action of allelochemicals is one of the challenging aspects in allelopathic studies. Recently, allelochemicals have been proposed to cause oxidative stress in target tissue and induce an antioxidant mechanism. Alpha-pinene, one of the common monoterpenoids emitted from several aromatic plants including forest trees, is known for its growth-inhibitory activity. However, its mechanism of action remains unexplored. |

Alpha-pinene Dilution Calculator

Alpha-pinene Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 7.3421 mL | 36.7107 mL | 73.4214 mL | 146.8429 mL | 183.5536 mL |
| 5 mM | 1.4684 mL | 7.3421 mL | 14.6843 mL | 29.3686 mL | 36.7107 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.7342 mL | 3.6711 mL | 7.3421 mL | 14.6843 mL | 18.3554 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.1468 mL | 0.7342 mL | 1.4684 mL | 2.9369 mL | 3.6711 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0734 mL | 0.3671 mL | 0.7342 mL | 1.4684 mL | 1.8355 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- Homatropine Methylbromide
Catalog No.:BCC4571
CAS No.:80-49-9
- Sulfamethoxypyridazine
Catalog No.:BCC4728
CAS No.:80-35-3
- Dapsone
Catalog No.:BCC5220
CAS No.:80-08-0
- Blumeatin B
Catalog No.:BCN4335
CAS No.:79995-67-8
- Fmoc-D-Ala-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3036
CAS No.:79990-15-1
- Quinovic acid 3-O-beta-D-glucoside
Catalog No.:BCN4334
CAS No.:79955-41-2
- Boc-His(Bom)-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3400
CAS No.:79950-65-5
- Idazoxan hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC6798
CAS No.:79944-56-2
- ML130 (Nodinitib-1)
Catalog No.:BCC4611
CAS No.:799264-47-4
- Forsythoside A
Catalog No.:BCN1195
CAS No.:79916-77-1
- Simvastatin
Catalog No.:BCN2569
CAS No.:79902-63-9
- 1,2,3,6-Tetragalloylglucose
Catalog No.:BCN2159
CAS No.:79886-50-3
- Tiglicacid
Catalog No.:BCN2976
CAS No.:80-59-1
- Sulfisoxazole Acetyl
Catalog No.:BCC5630
CAS No.:80-74-0
- Dihydrocholesterol
Catalog No.:BCN2749
CAS No.:80-97-7
- Soybean phospholipid
Catalog No.:BCN3888
CAS No.:8002-43-5
- Agatharesinol acetonide
Catalog No.:BCN4574
CAS No.:800389-33-7
- Boc-D-Phe(3-Cl)-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3169
CAS No.:80102-25-6
- H-D-Phe(2-Cl)-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3166
CAS No.:80126-50-7
- H-Phe(3-Cl)-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3168
CAS No.:80126-51-8
- H-D-Phe(3-Cl)-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3167
CAS No.:80126-52-9
- YC 170
Catalog No.:BCC1212
CAS No.:59946-73-5
- GSK256066
Catalog No.:BCC2285
CAS No.:801312-28-7
- L-Alanosine
Catalog No.:BCN7253
CAS No.:5854-93-3
Effect of alpha-pinene on nuclear translocation of NF-kappa B in THP-1 cells.[Pubmed:15066217]
Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2004 Apr;25(4):480-4.
AIM: To study the effects of Alpha-pinene on nuclear translocation of nuclear factor-kappa B (NF-kappa B) and the expression of the inhibitor of NF-kappa B (I kappa B alpha) in human monocyte THP-1 cell line. METHODS: THP-1 cells were incubated with Alpha-pinene (1, 10, and 100 mg/L, for 30 min) before being stimulated with lipopolysaccharide (LPS, 1 mg/L, 30 min). The location of NF-kappa B p65 subunit (NF-kappa B/p65) in THP-1 cells was detected by immunofluorescence and laser scanning confocal microscope (LSCM). The expression of NF-kappa B/p65 in nuclei and that of I kappa B alpha in cytoplasm were measured by Western-blot analysis. RESULTS: The majority of FITC-labelled NF-kappa B/p65 was located in the nuclei being stimulated with LPS. Whereas, no such fluorescence was seen in the nuclei of the groups pretreated with Alpha-pinene or control cells. Alpha-pinene pretreatment decreased the NF-kappa B/p65 nuclear translocation in LPS-stimulated THP-1 cells, and this effect was dose-dependent, but there was no reaction in LPS-unstimulated THP-1 cells. Alpha-pinene pretreatment increased I kappa B alpha protein level in cytoplasm, compared with that in LPS-stimulated THP-1 cells. CONCLUSION: In a dose-related fashion, Alpha-pinene inhibits the nuclear translocation of NF-kappa B induced by LPS in THP-1 cells, and this effect is partly due to the upregulation of I kappa B alpha expression.
alpha-Pinene inhibits growth and induces oxidative stress in roots.[Pubmed:17028297]
Ann Bot. 2006 Dec;98(6):1261-9.
BACKGROUND AND AIMS: Determining the mode of action of allelochemicals is one of the challenging aspects in allelopathic studies. Recently, allelochemicals have been proposed to cause oxidative stress in target tissue and induce an antioxidant mechanism. Alpha-pinene, one of the common monoterpenoids emitted from several aromatic plants including forest trees, is known for its growth-inhibitory activity. However, its mechanism of action remains unexplored. The aim of the present study was to determine the inhibitory effect of Alpha-pinene on root growth and generation of reactive oxygen species, as indicators of oxidative stress and changes in activities of antioxidant enzymes. METHODS: Effects of Alpha-pinene on early root growth were studied in five test species, Cassia occidentalis, Amaranthus viridis, Triticum aestivum, Pisum sativum and Cicer arietinum. Electrolyte leakage, lipid peroxidation, hydrogen peroxide generation, proline accumulation, and activities of the enzymes superoxide dismutase (SOD), ascorbate peroxidase (APX), guaiacol peroxidase (GPX), catalase (CAT) and glutathione reductase (GR) were studied in roots of C. occidentalis. KEY RESULTS: Alpha-pinene inhibited the radicle growth of all the test species. Exposure of C. occidentalis roots to Alpha-pinene enhanced solute leakage, and increased levels of malondialdehyde, proline and hydrogen peroxide, indicating lipid peroxidation and induction of oxidative stress. Activities of the antioxidant enzymes SOD, CAT, GPX, APX and GR were significantly elevated, thereby indicating the enhanced generation of reactive oxygen species (ROS) upon Alpha-pinene exposure. Increased levels of scavenging enzymes indicates their induction as a secondary defence mechanism in response to Alpha-pinene. CONCLUSIONS: It is concluded that Alpha-pinene inhibits early root growth and causes oxidative damage in root tissue through enhanced generation of ROS, as indicated by increased lipid peroxidation, disruption of membrane integrity and elevated antioxidant enzyme levels.


