Soybean phospholipidCAS# 8002-43-5 |
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 8002-43-5 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 5287971 | Appearance | Powder |
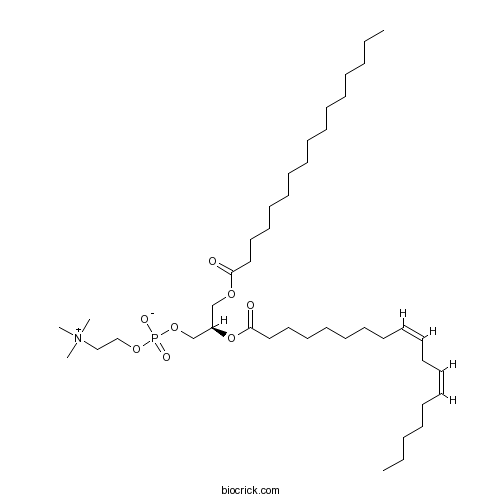
| Formula | C42H80NO8P | M.Wt | 758.1 |
| Type of Compound | Miscellaneous | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | DMSO : 5 mg/mL (6.60 mM; Need ultrasonic) H2O : 3.33 mg/mL (4.39 mM; Need ultrasonic) | ||
| Chemical Name | [(2R)-3-hexadecanoyloxy-2-[(9Z,12Z)-octadeca-9,12-dienoyl]oxypropyl] 2-(trimethylazaniumyl)ethyl phosphate | ||
| SMILES | CCCCCCCCCCCCCCCC(=O)OCC(COP(=O)([O-])OCC[N+](C)(C)C)OC(=O)CCCCCCCC=CCC=CCCCCC | ||
| Standard InChIKey | JLPULHDHAOZNQI-ZTIMHPMXSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C42H80NO8P/c1-6-8-10-12-14-16-18-20-21-23-25-27-29-31-33-35-42(45)51-40(39-50-52(46,47)49-37-36-43(3,4)5)38-48-41(44)34-32-30-28-26-24-22-19-17-15-13-11-9-7-2/h14,16,20-21,40H,6-13,15,17-19,22-39H2,1-5H3/b16-14-,21-20-/t40-/m1/s1 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Soybean phospholipid has a growth-promoting effect and it is suitable as a lipid and phospholipid source in microdiets for P. fulvidraco larvae feed.Soybean phospholipid and safflower phospholipid can suppress the elevation of plasma and liver cholesterol and that this effect may be brought about by inhibiting the absorption of cholesterol in the small intestine. |
| In vivo | Effect of soybean phospholipid supplementation in formulated microdiets and live food on foregut and liver histological changes of Pelteobagrus fulvidraco larvae[Reference: WebLink]Aquaculture, 2008, 278(1-4):119-27.
|

Soybean phospholipid Dilution Calculator

Soybean phospholipid Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 1.3191 mL | 6.5954 mL | 13.1909 mL | 26.3817 mL | 32.9772 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.2638 mL | 1.3191 mL | 2.6382 mL | 5.2763 mL | 6.5954 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.1319 mL | 0.6595 mL | 1.3191 mL | 2.6382 mL | 3.2977 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0264 mL | 0.1319 mL | 0.2638 mL | 0.5276 mL | 0.6595 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0132 mL | 0.066 mL | 0.1319 mL | 0.2638 mL | 0.3298 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
Lecithin is regarded as a safe, conventional phospholipid source. Phospholipids are reported to alter the fatty acid composition and microstructure of the membranes in animal cells.
In Vitro:After culturing in MRS broth with 0.2 to 1.0% soy Lecithin, the survival rate of harvested cells increases significantly (P<0.05) in the 0.3% bile challenge compare with the no added soy Lecithin group. The cells incubated with 0.6% soy Lecithin are able to grow in an MRS broth with a higher bile salt content. The cell surface hydrophobicity is enhanced and the membrane integrity in the bile challenge increases after culturing with soy Lecithin. A shift in the fatty acid composition is also observed, illustrating the cell membrane changes in the soy Lecithin culture[1].
References:
[1]. Hu B, et al. Enhancement of bile resistance in Lactobacillus plantarum strains by soy lecithin. Lett Appl Microbiol. 2015 Jul;61(1):13-9.
- Dihydrocholesterol
Catalog No.:BCN2749
CAS No.:80-97-7
- Sulfisoxazole Acetyl
Catalog No.:BCC5630
CAS No.:80-74-0
- Tiglicacid
Catalog No.:BCN2976
CAS No.:80-59-1
- Alpha-pinene
Catalog No.:BCN3855
CAS No.:80-56-8
- Homatropine Methylbromide
Catalog No.:BCC4571
CAS No.:80-49-9
- Sulfamethoxypyridazine
Catalog No.:BCC4728
CAS No.:80-35-3
- Dapsone
Catalog No.:BCC5220
CAS No.:80-08-0
- Blumeatin B
Catalog No.:BCN4335
CAS No.:79995-67-8
- Fmoc-D-Ala-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3036
CAS No.:79990-15-1
- Quinovic acid 3-O-beta-D-glucoside
Catalog No.:BCN4334
CAS No.:79955-41-2
- Boc-His(Bom)-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3400
CAS No.:79950-65-5
- Idazoxan hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC6798
CAS No.:79944-56-2
- Agatharesinol acetonide
Catalog No.:BCN4574
CAS No.:800389-33-7
- Boc-D-Phe(3-Cl)-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3169
CAS No.:80102-25-6
- H-D-Phe(2-Cl)-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3166
CAS No.:80126-50-7
- H-Phe(3-Cl)-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3168
CAS No.:80126-51-8
- H-D-Phe(3-Cl)-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3167
CAS No.:80126-52-9
- YC 170
Catalog No.:BCC1212
CAS No.:59946-73-5
- GSK256066
Catalog No.:BCC2285
CAS No.:801312-28-7
- L-Alanosine
Catalog No.:BCN7253
CAS No.:5854-93-3
- Tussilagine
Catalog No.:BCN1984
CAS No.:80151-77-5
- Methyl demethoxycarbonylchanofruticosinate
Catalog No.:BCN1348
CAS No.:80151-89-9
- Helicid
Catalog No.:BCN1056
CAS No.:80154-34-3
- Sorbic acid, 1-p-tolylhydrazide
Catalog No.:BCN2219
CAS No.:802048-02-8
Codelivery of Adriamycin and P-gp Inhibitor Quercetin Using PEGylated Liposomes to Overcome Cancer Drug Resistance.[Pubmed:30610857]
J Pharm Sci. 2019 Jan 2. pii: S0022-3549(18)30815-3.
Transmembrane protein P-gp's overexpression at the drug-resistant cell membrane is the most important characteristic of multidrug resistance (MDR). Quercetin (QUE) can effectively suppress the function of P-gp to reverse MDR. This study uses QUE as the P-gp inhibitor andfilm-ultrasound technique with ammonium sulfate transmembrane gradient method to prepare long-circulating liposomes simultaneously encapsulating QUE and Adriamycin (doxorubicin) (AMD/DOX). The optimal conditions for the preparation of AMD_QUE_long-circulating liposomes (SLs) are as follows: hydrogenated Soybean phospholipids (HSPC):cholesterol:DSPE-PEG 2000 = 73.07:24.36:2.57 mol/mol, QUE:HSPC = 1:20 mol/mol, AMD:HSPC = 1:7.9 w/w (NH4)2SO4 0.15 mol/L, drug loaded (AMD) at 55 degrees C for 25 min). The average encapsulation efficiency of AMD and QUE was 97.49% and 95.50%, respectively. The average particle size is 85 nm (n = 3), and the average zeta potential is -14.9 mV. First, the pharmacokinetic study proved that codelivery liposomes enveloping QUE and AMD (AMD_QUE_SL) can obviously increase the blood concentration of AMD (Cmax: 140.50 +/- 32.37 mug/mL) and extend the half-life period of AMD in plasma (t1/2:14.02 +/- 1.54 h). Second, AMD_QUE_SL can obviously enhance the cell toxicity to AMD-resistant cell strains (HL-6/ADR and MCF-7/ADR), and the reverse effects on the resistance of HL-6/ADR and MCF-7/ADR is increased to 4.81-fold and 3.21-fold, respectively. Third, according to the in vivo pharmacodynamic study, the relative tumor volume and relative tumor growth of the AMD_QUE_SL group were the lowest. The inhibition rate of tumor growth of this group was the highest. It can be concluded that AMD_QUE_SL can effectively reverse MDR, lower cardiac toxicity of AMD in clinical treatment, and improve the clinical treatment effect of AMD.
Lecithin soybean phospholipid nano-transfersomes as potential carriers for transdermal delivery of the human growth hormone.[Pubmed:30506803]
J Cell Biochem. 2019 Jun;120(6):9023-9033.
Pharmaceutical molecules such as peptides and proteins are usually injected into the body. Numerous efforts have been made to find new noninvasive ways to administer these peptides. In this study, highly flexible vesicles (transfersomes [TFs]) were designed as a new modern transdermal drug delivery system for systemic drug administration through the skin, which had also been evaluated in vitro. In this study, two growth hormone-loaded TF formulations were prepared, using soybean lecithin and two different surfactants; F1 _sodium deoxycholate and F 2 _sodium lauryl sulfate. Thereafter, the amount of skin penetration by the two formulas was assessed using the Franz diffusion cell system. TF formulations were evaluated for size, zeta potential and in vitro skin penetration across the rat skin. Results indicated that vesicle formulations were stable for 4 weeks and their mean sizes were 241.33 +/- 17 and 171 +/- 12.12 nm in the F 1 and F 2 formulation, respectively. After application to rat skin, transport of the human growth hormone (hGH) released from the TF formulations was found to be higher than that of the hGH alone. Maximum amounts of transdermal hormone delivery were estimated to be 489.54 +/- 8.301 and 248.46 +/- 4.019 ng.cm-2 , for F 1 and F 2 , respectively. The results demonstrate the capability of the TF-containing growth hormone in transdermal delivery and superiority of the F 1 to F 2 TFs.


